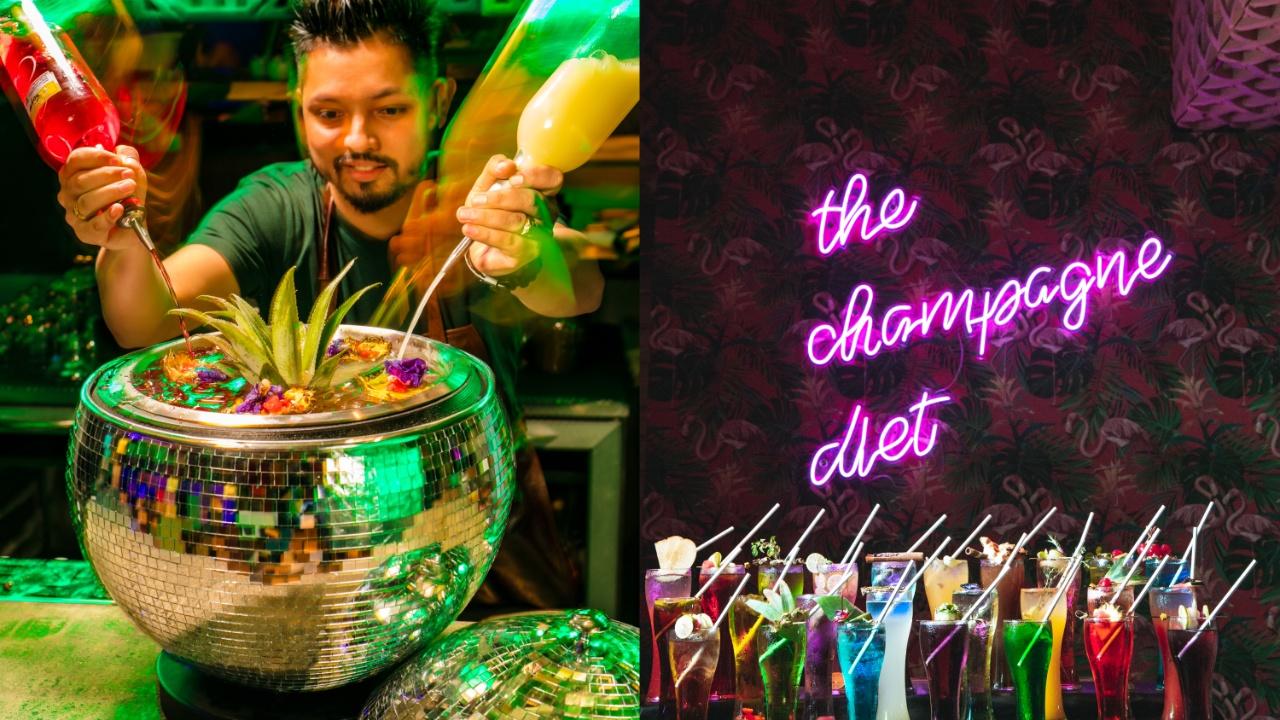Loretta a chic cocktail bar with a grateful dead connection is coming to downtown menlo park – Loretta, a chic cocktail bar with a Grateful Dead connection, is coming to downtown Menlo Park! Get ready for a unique experience blending sophisticated cocktails with the iconic legacy of the Grateful Dead. This isn’t just another bar; it’s a destination, promising a vibrant atmosphere and a taste of history. Expect a curated cocktail menu inspired by the band, a design reflecting their music and imagery, and a location primed to draw a devoted clientele.
Mark your calendars for the opening and get ready for the buzz to start!
Located in the heart of downtown Menlo Park, Loretta will be a welcome addition to the vibrant local scene. The surrounding area boasts a mix of trendy restaurants and shops, creating a lively and walkable environment perfect for pre- or post-dinner drinks. The bar is set to open its doors soon, creating excitement among locals and music enthusiasts alike.
Loretta: A Menlo Park Cocktail Haven with a Grateful Dead Vibe
Loretta, a new cocktail bar poised to open in downtown Menlo Park, promises a unique experience blending expertly crafted drinks with a nod to the iconic Grateful Dead. The bar is designed to transport patrons to a vibrant atmosphere reminiscent of the band’s legendary concerts, complete with music, decor, and a menu that reflects the spirit of the Dead.The location in downtown Menlo Park is ideal, nestled within a bustling area with numerous restaurants, shops, and other entertainment options.
The area’s reputation for sophisticated dining and nightlife will undoubtedly enhance Loretta’s appeal. Its central position in the heart of Menlo Park will make it easily accessible to residents and visitors alike.
Opening Date and Pre-Opening Excitement
The anticipated opening date for Loretta is [Insert Opening Date]. Already, there’s a buzz building among local residents and those in the wider Bay Area, fueled by social media posts, word-of-mouth, and early previews of the bar’s unique aesthetic. Early announcements about the menu and special events have generated significant pre-opening interest. The buzz is reminiscent of the excitement surrounding new restaurants in similar high-traffic areas.
This early enthusiasm suggests a promising future for Loretta in the competitive Menlo Park nightlife scene.
The Cocktail Menu
Loretta’s cocktail menu isn’t just a list of drinks; it’s a journey through the vibrant tapestry of the Grateful Dead’s musical legacy. Each concoction tells a story, reflecting the band’s improvisational spirit and eclectic influences. From the playful energy of a Jerry Garcia-inspired creation to the soulful depth of a “Dark Star” twist, the drinks offer a unique experience that complements the bar’s overall atmosphere.The menu aims to capture the essence of the Dead’s concerts – a dynamic mix of familiar favorites and unexpected surprises.
It balances classic cocktails with modern interpretations, all while maintaining a strong focus on fresh, high-quality ingredients. This commitment to quality ensures a sophisticated taste experience that enhances the overall bar visit.
Cocktail Inspirations
The menu draws inspiration from the Grateful Dead’s vast catalog of songs, albums, and overall aesthetic. The names themselves evoke imagery of the band’s concerts, from the mystical “Dark Star” to the energetic “Truckin’.” Each cocktail is crafted with a specific song or concert experience in mind, allowing patrons to experience a bit of the Dead’s magic through their taste buds.
Types of Cocktails
The menu features a variety of cocktails to cater to different preferences. Classic cocktails are given a modern twist, using fresh, seasonal ingredients. Experimental cocktails push the boundaries of flavor profiles, exploring new combinations and textures. Seasonal cocktails highlight the best of what’s fresh and available, creating a constantly evolving and exciting drink selection.
Signature Cocktails
Loretta offers several signature cocktails, each with a unique story.
- The “Dark Star”: A complex blend of rye whiskey, fig liqueur, and a touch of cardamom bitters, this cocktail evokes the mystical and otherworldly feel of the iconic song. Its dark, rich flavor profile and intriguing spice notes perfectly capture the song’s atmosphere.
- The “Truckin’”: A vibrant, fruity concoction featuring tequila, pineapple juice, lime juice, and a splash of agave nectar. Its bright and refreshing character reflects the upbeat and energetic nature of the song.
- The “Ripple”: A smooth, citrus-forward cocktail crafted with gin, grapefruit juice, elderflower liqueur, and a hint of rosemary syrup. Its aromatic and refreshing profile is reminiscent of a warm summer night under the stars.
Pricing Comparison
The following table compares the prices of similar cocktails at Loretta to those at other popular bars in Menlo Park. This data provides a glimpse into the pricing strategy and value proposition of Loretta.
| Cocktail | Loretta | Bar A | Bar B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classic Margarita | $14 | $16 | $12 |
| Gin & Tonic | $12 | $15 | $10 |
| Paloma | $13 | $14 | $11 |
| Signature Cocktail (e.g., Dark Star) | $16 | $18 | $15 |
Note: Prices are approximate and may vary based on specials and promotions. Bar A and Bar B are representative examples of similar establishments in the Menlo Park area.
Grateful Dead Connection
Loretta isn’t just another cocktail bar; it’s a tribute to the iconic Grateful Dead, woven into the very fabric of its design and spirit. The bar’s creators have poured their hearts into capturing the essence of the band’s legacy, from the music that fueled generations to the vibrant imagery that defined their concerts. This isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about creating an experience that resonates with the Deadheads who have supported the band for decades.The Grateful Dead’s influence extends beyond just a theme.
It’s a deep-seated reverence for the band’s music, community, and the enduring spirit of their shows. Loretta aims to channel that energy, offering a space where people can connect, share stories, and celebrate the timeless appeal of the Grateful Dead.
Music and Imagery
Loretta will feature a curated playlist that draws heavily from the Grateful Dead’s extensive catalog. Expect a mix of classic tracks, lesser-known gems, and perhaps even some live recordings. The music selection will be carefully crafted to evoke the energy and atmosphere of a classic Dead show. The bar’s interior design will incorporate visual elements inspired by the band’s iconic imagery, such as intricate artwork, vintage posters, and vibrant color palettes reminiscent of the band’s album covers and concert posters.
This visual language will immerse patrons in the spirit of the Dead.
Themed Events and Promotions
To further immerse patrons in the Grateful Dead experience, Loretta will host a series of themed events throughout the year. These events will range from themed nights featuring special cocktails and food pairings inspired by the band’s music and history, to DJ nights playing extended sets of Dead music. A “Deadhead Appreciation Night” with a special guest DJ is a possibility.
Anniversary celebrations of iconic albums will also be a part of the festivities, creating a sense of community and shared passion for the band. A “Jerry Garcia Birthday Bash” is planned for the anniversary of Garcia’s birth.
Timeline of Development
- Phase 1 (Conception – 6 Months): The initial concept for Loretta was born, focusing on the Grateful Dead connection. Market research was conducted to identify the target audience and their preferences for a themed bar experience. Initial designs and plans for the space were sketched and refined. Conversations with potential suppliers and vendors were established, beginning the process of securing the necessary equipment and materials.
- Phase 2 (6-12 Months): The bar’s design was finalized, incorporating elements reflecting the Grateful Dead’s aesthetics. The cocktail menu was developed, integrating special cocktails inspired by the band’s music and history. Partnerships with local musicians and bands were explored for live performances and events.
- Phase 3 (12-18 Months): Construction and renovations commenced. The bar’s interior was fitted out, with artwork, furniture, and fixtures installed. The playlist was curated, and staff training focused on the history of the Grateful Dead and the proper presentation of themed cocktails.
- Phase 4 (18-24 Months): Final touches were applied, including securing licenses and permits. The grand opening preparations began, culminating in the official launch of Loretta, a celebration of the Grateful Dead in Menlo Park.
Atmosphere and Design: Loretta A Chic Cocktail Bar With A Grateful Dead Connection Is Coming To Downtown Menlo Park
Loretta promises a unique cocktail experience, blending a sophisticated, modern aesthetic with a touch of the Grateful Dead’s iconic spirit. The design aims to create a welcoming and vibrant space, drawing inspiration from the band’s vibrant imagery and the laid-back charm of a classic roadhouse. This visual journey is meant to transport patrons to a nostalgic yet contemporary environment.The interior design will evoke a sense of warmth and comfort, while still maintaining a sleek and stylish vibe.
Think rich wood tones, exposed brick accents, and plush seating areas, all thoughtfully curated to create a cozy and inviting atmosphere. Natural light will be strategically incorporated to enhance the space’s visual appeal.
Interior Design Elements
The design will incorporate elements that evoke the Grateful Dead’s spirit, including vintage posters, band memorabilia, and subtle color palettes reminiscent of their iconic album art. The bar itself will be a focal point, crafted with a unique design that complements the overall aesthetic. Artwork and lighting will be carefully selected to create a layered and immersive experience.
So excited about Loretta, the new chic cocktail bar in downtown Menlo Park with a Grateful Dead connection! It’s going to be a cool spot, but while I’m dreaming of craft cocktails and maybe even some Dead-themed decor, I can’t help but think about the recent drama at Social Security. Apparently, there’s been a bit of a canine-related incident, as an insider describes in this piece about a doge’s rampage at the agency opinion social security insider describes doges rampage at the agency.
Regardless, I’m still looking forward to Loretta opening and hopefully finding some great cocktails to sip on!
Textiles will play a key role, adding depth and warmth to the space.
Seating Arrangements and Capacity
Loretta will offer a variety of seating options, catering to different group sizes and preferences. High-top tables will be perfect for solo patrons and smaller groups, while booths and larger tables will accommodate larger gatherings. The bar itself will have a dedicated seating area. The seating arrangement will be designed to maximize the space while ensuring that each patron enjoys a comfortable and enjoyable experience.
The estimated capacity of the bar is approximately 75-85 patrons, ensuring a relaxed atmosphere and avoiding overcrowding.
Comparison to Similar Bars
| Feature | Loretta | Bar A | Bar B | Bar C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Aesthetic | Modern, sophisticated, with a Grateful Dead vibe | Trendy, minimalist | Rustic, dimly lit | Upscale, classic |
| Color Palette | Earthy tones, blues, greens, with pops of vibrant colors | Monochromatic, muted tones | Warm browns, deep reds | Neutral tones with accents |
| Seating | Mix of high-tops, booths, and larger tables | Primarily high-tops | Mostly booths | Combination of tables and booths |
| Music | Live music with a focus on genres inspired by the Grateful Dead | Contemporary jazz | Acoustic music | Classical music |
| Memorabilia | Grateful Dead-inspired art and memorabilia | Minimalist, modern design | Vintage, eclectic mix | Classic artwork |
Loretta distinguishes itself by blending modern sophistication with a unique Grateful Dead-inspired aesthetic. This approach will set it apart from other similar bars in the area, offering a truly unique and memorable experience for patrons. The use of vintage posters and memorabilia will be a significant differentiator.
Target Audience
Loretta, with its unique blend of cocktails and Grateful Dead vibes, is poised to attract a specific demographic in Menlo Park. This target audience is crucial for Loretta’s success, as it directly influences marketing strategies and service offerings. Understanding their motivations and preferences will help Loretta stand out from other bars in the area and build a loyal customer base.
Identifying the Target Demographic
Loretta’s target demographic is primarily young professionals and music enthusiasts in the 25-45 age range. This group is likely to appreciate the unique atmosphere, the curated cocktail menu, and the connection to a beloved cultural touchstone—the Grateful Dead. They are comfortable with a lively, yet sophisticated environment and enjoy experiences that evoke nostalgia or a sense of community.
They are also likely to be interested in high-quality ingredients and craft cocktails.
Attracting the Target Audience
Several factors attract this specific audience to Loretta. First, the unique atmosphere, reminiscent of a vintage concert venue, coupled with the curated cocktail menu, will appeal to their appreciation for quality and experience. Second, the Grateful Dead connection provides a distinct identity and a focal point for conversation and shared interest. This connection fosters a sense of community and belonging, particularly for those who share a passion for the band’s music.
Finally, the location in downtown Menlo Park, a vibrant area with a strong social scene, will further attract this demographic, making Loretta a destination for both casual gatherings and more elaborate events.
Potential Customer Base and Differentiation, Loretta a chic cocktail bar with a grateful dead connection is coming to downtown menlo park
Loretta’s potential customer base will differ from other bars in Menlo Park by its unique combination of a vibrant atmosphere, craft cocktails, and a dedicated following of Grateful Dead enthusiasts. This will create a niche market that other establishments might not fully cater to. The focus on a specific musical genre sets Loretta apart from generic cocktail bars, offering a more personalized and engaging experience for its patrons.
Loretta’s location within a bustling downtown area further contributes to its appeal, attracting a wider range of potential customers.
So excited about Loretta, the new chic cocktail bar with a Grateful Dead connection opening in downtown Menlo Park! While I’m sipping on their unique concoctions, I can’t help but think about the future of press freedoms. Given the current political climate, it’s a valid concern. A recent article on Proper News delves into this, offering insightful perspectives on how press freedoms might fare under a potential Trump second term.
opinion how press freedoms could fare under trumps second term Regardless of the political landscape, I’m sure Loretta will be a great addition to the Menlo Park scene, offering a cool vibe and delicious drinks.
Comparison of Target Audiences
| Bar | Target Audience | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Loretta | Young professionals (25-45), music enthusiasts, appreciate quality cocktails, and a unique atmosphere. | Grateful Dead theme, curated cocktail menu, vintage concert venue vibe. |
| The Rusty Mug | A broader range of ages and interests, including families and those seeking casual drinks. | Casual atmosphere, family-friendly options, and wide selection of beers and wines. |
| The Parkside Lounge | Mid-range age group, seeking a sophisticated and relaxed atmosphere. | Emphasis on fine wines and classic cocktails, elegant ambiance. |
The table above highlights the key differences in the target audiences for each bar. Loretta stands out with its focus on a specific music genre and curated cocktails, attracting a more niche and engaged clientele. This approach allows Loretta to tailor its offerings and marketing to a specific demographic, ultimately creating a more loyal and passionate customer base.
Marketing and Promotion
Loretta isn’t just another cocktail bar; it’s an experience. Our marketing strategy will focus on building a community around the Grateful Dead theme and the unique cocktail creations, ensuring Loretta becomes a beloved Menlo Park destination. We need to attract the right crowd, highlighting the bar’s distinctive atmosphere and the connection to the iconic band.Our marketing plan hinges on showcasing Loretta’s personality and unique selling points.
This involves a multi-faceted approach that blends traditional and modern marketing techniques, effectively targeting our ideal customer base.
Marketing Strategy
Loretta’s unique selling points will be central to our marketing. These include the Grateful Dead theme, the expertly crafted cocktails, the intimate and stylish atmosphere, and the welcoming community it aims to foster. Our marketing will emphasize these elements, using them as hooks to attract the right clientele.
Social Media Promotion
Social media is crucial for building anticipation and engaging with potential customers. A consistent posting schedule will be key, showcasing the bar’s aesthetic, the cocktail menu, and behind-the-scenes glimpses. We will use high-quality images and videos, creating engaging content that resonates with our target audience. Hashtags relevant to the Grateful Dead, cocktails, and Menlo Park will be strategically incorporated into posts.
Instagram stories will be used to highlight daily specials, events, and behind-the-scenes peeks. Facebook will serve as a platform for community building, with posts about local events and collaborations. Targeted advertising on platforms like Instagram and Facebook will reach potential customers based on interests and demographics.
Pre-Opening Promotions
Early engagement is vital. A pre-opening social media campaign will build excitement and anticipation. Exclusive discounts and early bird offers will be presented to those who sign up for email lists. Collaborations with local businesses will help us reach a wider audience. We’ll host themed events like a “Dead-themed cocktail competition” to engage the community before the official opening.
Grand Opening Events
The grand opening will be a celebration. Live music, themed decorations, and giveaways will create a memorable experience. Collaborations with local bands and DJs, potentially those with Grateful Dead connections, will help attract a large crowd. A special “Grand Opening” cocktail, a unique concoction, will be created for the occasion.
Social Media Campaign
A phased social media campaign, leading up to the opening, is planned. The initial phase will focus on introducing the concept of Loretta, highlighting its Grateful Dead theme and emphasizing the unique cocktails. The second phase will focus on building excitement, showcasing the bar’s aesthetic and ambiance. The final phase will be dedicated to creating buzz around the grand opening event, featuring special offers and exclusive content.
Engaging content, including polls, quizzes, and contests, will be used to interact with followers and build community.
Food Offerings

Loretta isn’t just about the cocktails; it’s about the whole experience. We’ve designed a food menu that complements the Grateful Dead vibe and sophisticated cocktail program, creating a harmonious blend of tastes and textures. The small plates are thoughtfully curated to pair perfectly with the drinks, encouraging conversation and shared enjoyment.
So excited about Loretta, a chic new cocktail bar with a Grateful Dead connection, opening in downtown Menlo Park! While the North Bay interior mountains are bracing for a frost advisory Wednesday, this weather won’t dampen my spirits for the upcoming cool vibes and delicious drinks at Loretta. I’m already picturing myself enjoying a handcrafted cocktail there, maybe even a Dead-themed one!
Food Menu Highlights
The food menu is designed to be a delicious companion to Loretta’s unique cocktail experience. It’s meant to be shared and savored, much like the music of the Grateful Dead. Expect a variety of small plates, inspired by Californian cuisine, incorporating fresh, seasonal ingredients, and featuring a few nods to classic American comfort food.
Chef and Culinary Team
The culinary team behind Loretta’s menu is led by Chef Anya Petrova, a talented chef with years of experience in the culinary arts. Her expertise in modern Californian cuisine, combined with a keen eye for flavor pairings, ensures that each dish enhances the overall dining experience. She draws inspiration from her extensive travels and her love for fresh, seasonal produce, ensuring each dish is a testament to the finest ingredients.
Food Options
| Dish | Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Roasted Beet & Goat Cheese Salad with Candied Walnuts | $14 | A vibrant salad featuring roasted beets, creamy goat cheese, crisp candied walnuts, and a light vinaigrette. |
| Spicy Chorizo & Manchego Crostini | $12 | Crispy crostini topped with flavorful chorizo, tangy manchego cheese, and a touch of jalapeño. |
| Crispy Calamari with Lemon Aioli | $16 | Lightly battered calamari served with a zesty lemon aioli for a refreshing and satisfying bite. |
| Miniature Grilled Cheese Sandwiches with Truffle Oil | $10 | A playful twist on a classic, featuring mini grilled cheese sandwiches, elevated with a drizzle of truffle oil. |
| Smoked Salmon & Dill Tartlets | $15 | Savory tartlets filled with smoked salmon, fresh dill, and a hint of cream cheese, perfect for a sophisticated starter. |
| Truffle Fries | $8 | Crispy fries enhanced with a rich truffle oil drizzle. |
Location and Accessibility
Loretta’s location in downtown Menlo Park is crucial for attracting the right crowd. Choosing the right spot can significantly impact the success of a cocktail bar, especially one with a unique vibe like Loretta’s. We’ve carefully considered the surrounding area and its potential to draw in the target demographic, while also addressing potential challenges.The area surrounding downtown Menlo Park is known for its affluent residents, tech professionals, and a vibrant local community.
This mix of demographics creates a diverse and potentially lucrative customer base for Loretta. The presence of nearby offices and residential areas provides a ready-made pool of potential patrons, particularly during weekdays and evenings.
Parking and Transportation
Parking in downtown Menlo Park can be challenging, a common issue in many urban areas. However, the area also benefits from excellent public transportation options. The proximity to Caltrain stations and ample bus routes allows for convenient access for those not driving. This presents an opportunity for Loretta to promote itself as a destination accessible by public transport, attracting environmentally conscious customers and those who prefer not to drive.
Surrounding Area Appeal
The appeal of the surrounding area lies in its blend of high-end retail, restaurants, and entertainment options. This creates a walkable and engaging environment that can draw in customers seeking a well-rounded experience beyond just a drink. The combination of trendy shops, diverse dining experiences, and cultural attractions in the immediate vicinity enhances the overall appeal of Loretta as a social destination.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
Competition from existing restaurants and bars in the downtown area is a potential challenge. Loretta must differentiate itself through its unique concept, high-quality cocktails, and memorable atmosphere to stand out. A strong marketing strategy highlighting the Grateful Dead connection and unique cocktail menu can attract customers who appreciate distinctive experiences. The availability of outdoor seating, if possible, could be a significant opportunity to attract customers during warmer months.
Transportation Options
- Caltrain: The Caltrain station provides convenient access from San Francisco, Palo Alto, and other surrounding areas. A short walk or taxi ride to Loretta will allow easy access from the station for customers arriving by train.
- Local Buses: Numerous bus routes serve downtown Menlo Park. Customers can easily find bus stops and schedules to arrive at Loretta, making it a practical option for those utilizing public transportation.
- Ride-Sharing Services: Uber and Lyft are readily available in the area, offering convenient transportation options for customers who prefer this method.
- Driving: While parking may be limited, driving is still a viable option for those with vehicles. The area offers street parking and nearby parking garages.
Conclusive Thoughts
Loretta promises a unique cocktail experience, blending sophisticated drinks with a Grateful Dead theme. The bar’s location in downtown Menlo Park, coupled with its distinctive design and menu, positions it to be a hit with the local community. From the cocktails inspired by the band to the themed events planned, Loretta is more than just a bar—it’s an experience.
Get ready for a lively addition to Menlo Park’s vibrant nightlife scene!