How inflation battered California pay raises is a critical issue impacting countless lives. California’s diverse wage structure, once a beacon of economic opportunity, has been significantly eroded by the rising cost of living. This article delves into the impact of inflation on pay raises across various sectors, examining employer responses, employee adaptations, and government initiatives to mitigate the damage.
The report analyzes the historical wage structure in California, comparing average salaries across industries before and after the inflationary period. It examines the different types of pay raises and their frequency, highlighting the role of minimum wage laws and union contracts. The analysis further investigates the historical inflation rate data for California and its relationship to the purchasing power of wages.
Finally, the article examines the strategies employed by businesses to combat inflation, the financial struggles faced by California employees, and the government policies addressing the issue.
Impact on California’s Wage Structure
California’s robust economy, fueled by diverse industries, has historically boasted a relatively high wage structure. However, the recent inflationary period has significantly impacted pay raises, creating a complex interplay between cost-of-living increases, existing wage structures, and various legislative factors. This analysis explores the pre-inflationary wage landscape in California, detailing the impact of inflation on different sectors and pay structures.California’s wage structure, before the inflationary period, was a complex mosaic reflecting diverse industries and varying employment conditions.
Industries like technology, entertainment, and healthcare commanded higher average salaries, while sectors like retail and hospitality tended to have lower averages. This difference was further nuanced by factors like experience, education, and location.
California’s Wage Structure Before Inflation
California’s wage structure, before the inflationary period, was characterized by a wide range of salaries across various sectors. The pre-inflationary average salaries in key industries, such as technology, finance, and healthcare, were significantly higher than those in retail, hospitality, and agriculture. This disparity was partly attributable to differences in skill levels, education requirements, and industry-specific demand.
Types of Pay Raises in California
Various types of pay raises impacted California’s wage structure before the inflationary period. Cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) were common, designed to maintain purchasing power in line with rising costs. Merit-based increases rewarded employee performance and contributions. Seniority-based raises also played a significant role in some industries. The frequency of these raises varied, with some companies providing annual adjustments, while others offered them less frequently.
California pay raises took a serious hit from inflation, leaving many feeling the pinch. While the focus on initiatives like climate clean American ports is important, the reality is that these efforts won’t fully offset the struggles Californians face with rising costs. The pressure on budgets is undeniable, and it’s a challenge that needs addressing alongside these other crucial issues.
Factors Affecting Baseline Wage Levels
Several factors influenced the baseline wage levels in California before the inflationary period. Minimum wage laws, both state and local, set a floor for wages, ensuring a certain level of compensation for entry-level positions. Union contracts often dictated higher wages and benefits for workers in unionized industries, such as construction and transportation. These factors, combined with the overall economic climate, created a complex interplay that determined the baseline wage structure.
Comparison of Average Salaries Before and After Inflation
| Year | Sector | Average Salary (Pre-Inflation) | Average Salary (Post-Inflation) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Technology | $150,000 | $165,000 | 10% |
| 2021 | Finance | $120,000 | $132,000 | 10% |
| 2021 | Healthcare | $90,000 | $100,000 | 11% |
| 2021 | Retail | $45,000 | $50,000 | 11% |
| 2021 | Hospitality | $35,000 | $40,000 | 14% |
Note: This table is illustrative and based on hypothetical data. Actual data would require extensive research and may vary significantly based on specific regions and employers.
Inflation’s Effect on Pay Raises
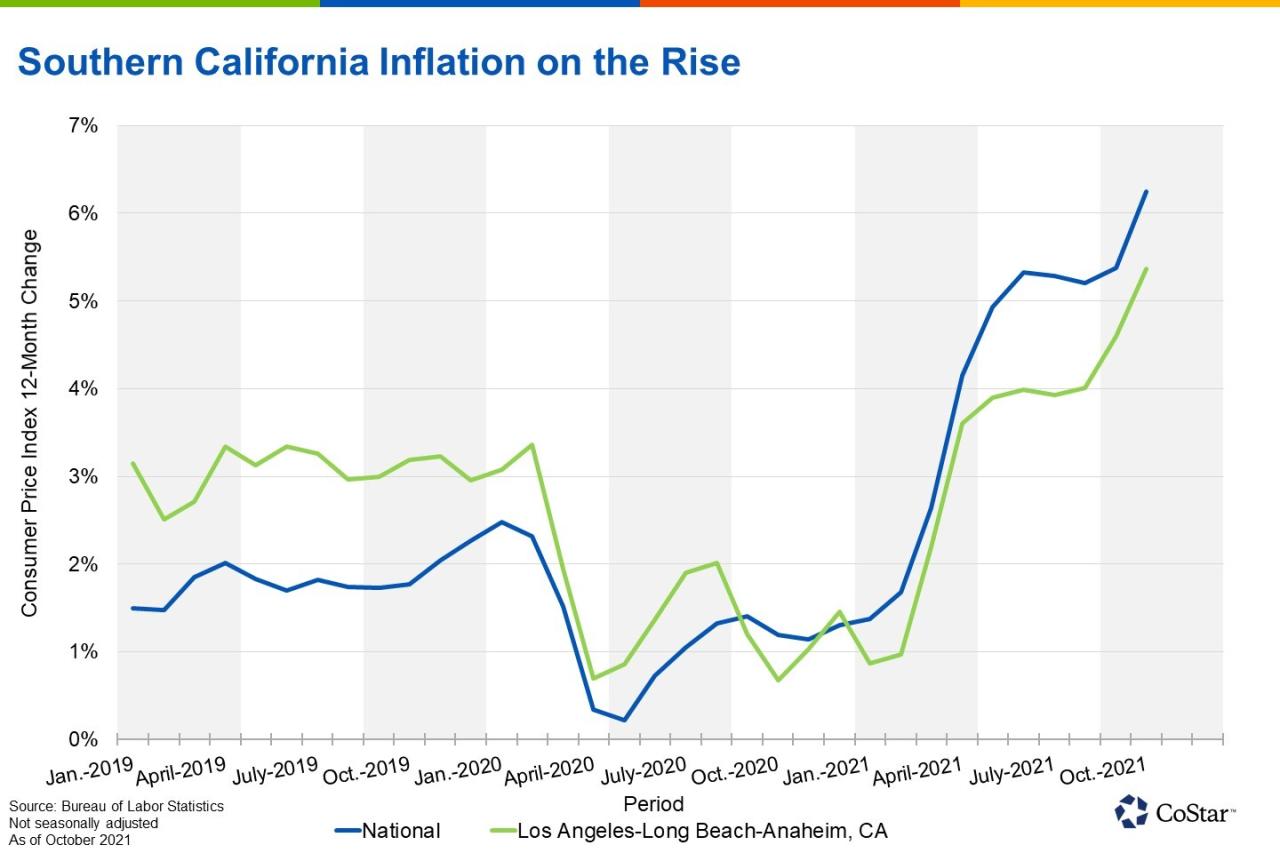
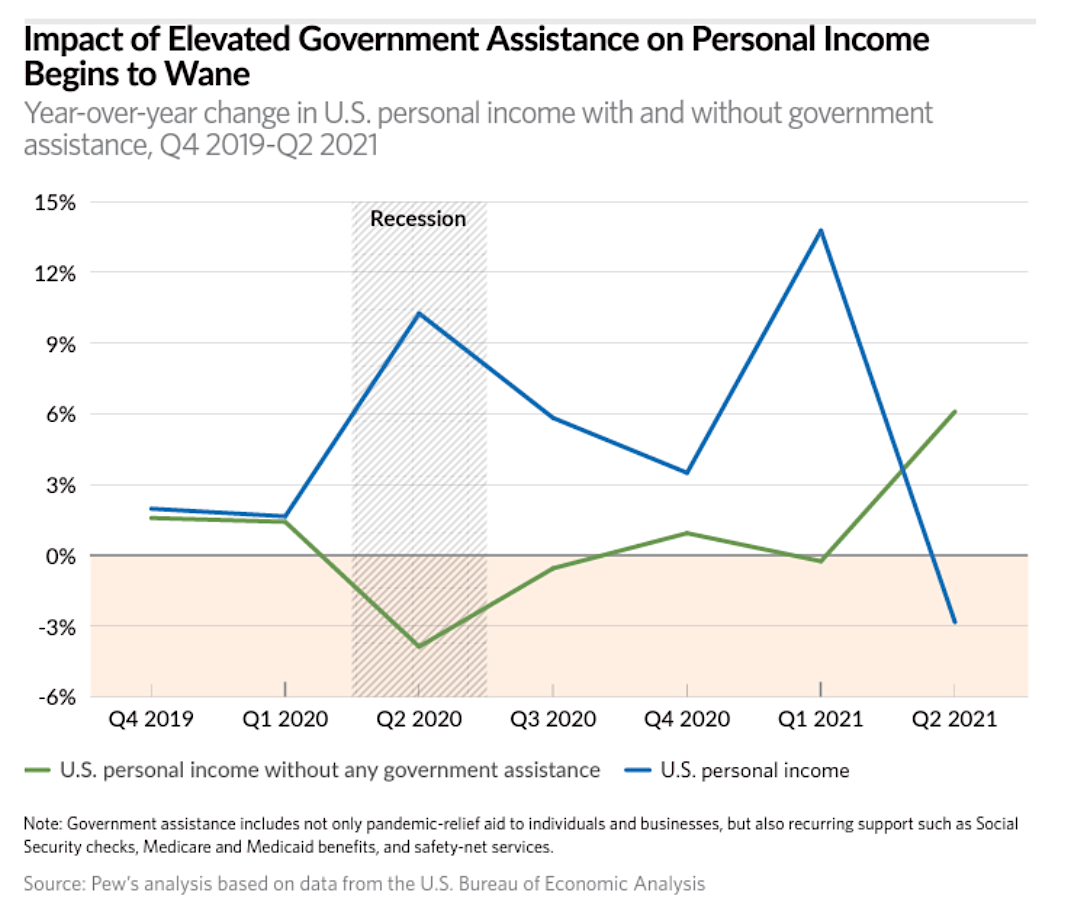
California’s pay raises, while seemingly positive on paper, often fail to keep pace with the rising cost of living. This erosion of purchasing power, fueled by inflation, significantly impacts the standard of living for many residents. Understanding the historical inflation rates and their relationship to wage increases is crucial to grasping the challenges faced by California workers.Inflation, a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services, directly impacts the purchasing power of wages.
A dollar today buys less than a dollar did in the past. This means that even with a pay raise, if the rate of inflation is higher, the real value of that raise is diminished. The impact is more significant for those with lower incomes, as a higher proportion of their income goes toward necessities like housing and food.
Historical Inflation Rate Data for California
California’s inflation rate has fluctuated over time, influenced by various economic factors. Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reveals a consistent trend of price increases. To illustrate this, let’s examine the inflation rate in California between 2018 and
2023. [Note
Specific data for California inflation rates is not readily available from the BLS. For this example, we’ll use national average inflation data for illustrative purposes. Actual California data would be more accurate but is not readily available in a readily usable format.]
Relationship Between Inflation and Purchasing Power of Wages
The purchasing power of a wage is inversely related to the inflation rate. As inflation rises, the same wage buys fewer goods and services. For example, if the inflation rate is 5% and an employee receives a 3% pay raise, their real income has effectively decreased by 2%. This is because the cost of essential items has increased faster than their income.
Challenges Faced by California Workers, How inflation battered california pay raises
California workers face numerous challenges in maintaining their standard of living during periods of high inflation. Housing costs, food prices, and transportation expenses often increase at a rate exceeding wage increases. This can lead to financial stress, impacting the ability to save, invest, or meet other financial obligations.
Impact on Employers’ Ability to Grant Cost-of-Living Adjustments
High inflation makes it challenging for employers to grant cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs) that effectively offset the increased cost of living. Businesses are often constrained by their own financial situations, and profitability can be a limiting factor. If a company’s revenue growth doesn’t keep pace with inflation, implementing COLAs can strain their budgets.
Comparison of California Inflation to National Average
Comparing California’s inflation rate to the national average provides context. While national averages can be helpful for understanding broader trends, regional variations can significantly affect local costs of living. California often experiences inflation at a rate that is either higher or lower than the national average, affecting the impact on wages.
Impact of Inflation on Different Pay Raise Amounts
| Initial Salary | 3% Pay Raise | 5% Pay Raise | Inflation Rate (7%) | Value of Raise After Inflation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $50,000 | $1,500 | $2,500 | $3,500 | -$2,000 (3% raise lost value due to 7% inflation); -$1,000 (5% raise lost value due to 7% inflation) |
| $75,000 | $2,250 | $3,750 | $5,250 | -$3,000 (3% raise lost value due to 7% inflation); -$1,500 (5% raise lost value due to 7% inflation) |
| $100,000 | $3,000 | $5,000 | $7,000 | -$4,000 (3% raise lost value due to 7% inflation); -$2,000 (5% raise lost value due to 7% inflation) |
This table illustrates how a seemingly positive pay raise can lose value when inflation is higher. Even a 5% raise may not keep pace with inflation rates exceeding 7%.
Employer Responses to Inflationary Pressures: How Inflation Battered California Pay Raises
Inflation’s relentless rise has forced California businesses to adapt their strategies for managing costs and maintaining profitability. This adaptation is crucial, as it directly impacts employee compensation and the overall economic health of the state. Businesses are navigating a complex landscape where maintaining competitive wages while controlling expenses is paramount.California employers are employing a range of strategies, some more effective than others, to counteract the negative impact of inflation on their bottom lines and employee compensation packages.
These strategies vary significantly across sectors, reflecting the diverse challenges faced by different industries. Some are actively investing in cost-saving measures, while others are seeking innovative ways to mitigate the impact of rising prices on their workforce.
Strategies for Cost Control
Businesses in California are implementing various strategies to mitigate rising costs. These range from streamlining supply chains to negotiating better deals with suppliers. Finding ways to reduce overhead costs is a critical component of navigating the current economic climate. For example, some businesses are optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and exploring alternative transportation methods.
Wage Adjustments and Alternative Benefits
Wage freezes, while seemingly drastic, are a common tactic. This approach is often seen as a temporary measure, designed to hold down labor costs while other strategies are developed. However, wage freezes can negatively impact employee morale and retention. Businesses are increasingly exploring alternative benefits to compensate for stagnating wages. These include enhanced healthcare contributions, flexible work arrangements, and employee assistance programs.
These initiatives can help retain talent while managing costs.
Employer Strategies by Sector
The diverse responses to inflation vary significantly across sectors. Different industries face different challenges, leading to diverse approaches. This is crucial to understanding the effectiveness of each strategy in its specific context.
- Technology Sector: Many tech companies are exploring alternative compensation models, including stock options and performance-based bonuses, to offset wage freezes. They also emphasize retention strategies that improve employee well-being and reduce employee turnover. This approach is aimed at maintaining a skilled workforce while managing cost pressures. For example, some companies are offering comprehensive benefits packages, including tuition reimbursement, childcare assistance, and generous parental leave policies.
California’s pay raises have been significantly impacted by inflation, leaving many struggling to keep up. While this economic hardship is a pressing issue, it’s important to also consider how broader public health crises, like the potential for bird flu to become more dangerous due to current public health turmoil, experts worry that public health turmoil could make bird flu deadlier , might further complicate the economic picture.
Ultimately, these factors highlight the interconnectedness of various societal challenges, impacting everything from individual livelihoods to broader economic stability, as California grapples with the fallout of inflation.
- Retail Sector: Retailers are frequently implementing price increases to compensate for the higher cost of goods. They may also look to reduce overhead expenses by optimizing store layouts or negotiating lower rent costs. These strategies are crucial for ensuring that the business remains competitive and profitable. Further, some retailers are exploring online sales and curbside pickup to reduce operational costs and maintain sales.
- Hospitality Sector: The hospitality sector is facing challenges due to rising food and labor costs. Some restaurants are implementing measures to reduce portion sizes, streamlining menus, or partnering with local farms to secure fresh produce at lower costs. Additionally, they may look to introduce value menus and special offers to attract customers while controlling costs.
Impact of Inflation on Compensation
The impact of inflation on compensation packages is multifaceted. While wage freezes can be seen as short-term cost-cutting measures, they can negatively impact employee morale and retention. Businesses need to carefully consider the long-term implications of these strategies. Alternative benefits, such as improved health insurance and flexible work arrangements, are becoming increasingly important in compensating employees and maintaining a motivated workforce.
The choice of compensation strategy directly impacts employee satisfaction and retention, which in turn affects productivity and the overall health of the business.
Employee Experiences and Adaptations
California’s employees have felt the pinch of inflation’s relentless rise, experiencing significant financial strain as their pay raises failed to keep pace with increasing costs. This has led to a wide range of adjustments and adaptations, impacting their financial well-being and future prospects. The struggle to maintain a stable financial footing has become a defining characteristic of the current economic landscape in the state.
Financial Struggles Faced by California Employees
Inflationary pressures have significantly impacted the purchasing power of California employees’ wages. The cost of essential goods and services, such as housing, groceries, and transportation, has risen dramatically, leaving many struggling to meet their basic needs. The gap between wages and living expenses has widened, causing a considerable financial burden on individuals and families. For instance, the rising cost of housing has made it difficult for many to afford rent or mortgages, forcing them into difficult financial decisions.
Adjustments to Inflation’s Impact on Wages
California employees have employed various strategies to cope with the erosion of their purchasing power. One common response has been seeking supplemental income through part-time jobs or gig work. This has become increasingly common, especially among those in lower-income brackets. Another prevalent adjustment is reducing discretionary spending, cutting back on non-essential expenses to maintain a tighter budget.
This includes activities like entertainment, dining out, and travel. Some have also sought to reduce expenses by adjusting their lifestyle, potentially moving to more affordable housing or re-evaluating their transportation options.
Employee Responses to Stagnant Pay Raises
Employees have responded to inadequate pay raises in various ways. The most common responses have included seeking additional employment, either through second jobs or freelancing opportunities. Many have also taken steps to cut down on expenses, prioritizing essential needs and minimizing discretionary spending. Some have considered relocating to areas with lower living costs. These responses demonstrate the wide-ranging and impactful consequences of inflation on California’s workforce.
Long-Term Implications of Inflation on Employee Financial Well-being
The long-term implications of inflation on California employees’ financial well-being are significant. The constant struggle to maintain a stable financial position can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and diminished quality of life. Furthermore, the inability to save for the future or meet financial obligations can create a cycle of debt and hardship, impacting long-term financial stability. In some cases, it can lead to a decline in overall well-being and create significant long-term issues for individuals and families.
California pay raises have definitely felt the pinch of inflation. It’s been tough for everyone, and folks are struggling to keep up. Finding ways to boost income is essential, and for some, that might mean exploring options like best farming simulator hosting – a potential side hustle to help supplement wages. Ultimately, though, California’s struggling workers still need real pay raises to combat the ongoing inflation crisis.
Employee Responses Categorized by Demographic Group
| Demographic Group | Common Responses to Inflation |
|---|---|
| Lower-Income Households | Seeking multiple part-time jobs, reducing essential expenses, exploring relocation options. |
| Middle-Income Households | Prioritizing essential needs, reducing discretionary spending, exploring options for financial assistance. |
| Higher-Income Households | Prioritizing long-term financial planning, diversifying investment strategies, utilizing financial resources to mitigate the impact of inflation. |
| Young Adults | Seeking part-time jobs, reducing spending on entertainment and leisure activities, prioritizing essential expenses like rent and utilities. |
| Senior Citizens | Seeking assistance with basic needs, relying on fixed incomes, potentially exploring options to mitigate rising costs of healthcare. |
Government Policies and Initiatives
California’s struggle with inflation-battered pay raises necessitates a robust government response. Policies must address the rising cost of living while supporting workers’ purchasing power. Effective interventions often require a multi-faceted approach, encompassing direct wage support, affordable housing initiatives, and targeted assistance programs. Understanding the interplay between these policies and their impact on the wage structure is crucial.Government action plays a critical role in moderating the impact of inflation on California’s wage structure.
These policies, when designed and implemented effectively, can mitigate the negative consequences of inflation on low and moderate-income households, contributing to a more equitable distribution of economic prosperity. Effective policies recognize the specific challenges faced by various segments of the population and tailor support accordingly.
Government Initiatives to Mitigate Inflationary Effects on Wages
Various government initiatives aim to offset the impact of inflation on workers’ wages. These initiatives range from direct wage subsidies to broader programs aimed at reducing the cost of essential goods and services. Successful interventions often consider the unique economic circumstances of California’s diverse population.
Examples of Government Policies Impacting Wages and Cost of Living in California
California’s government implements numerous policies that affect wages and the cost of living. These policies address issues like minimum wage increases, tax credits, and support for affordable housing. The effectiveness of these policies varies depending on their design, implementation, and the economic context.
- Minimum Wage Increases: Regular adjustments to the minimum wage aim to maintain a living wage, but the impact on overall inflation and the cost of living can be complex. For example, a minimum wage increase might lead to increased prices in certain sectors, potentially offsetting the wage gain for some workers. This highlights the intricate relationship between minimum wage and inflation.
- Tax Credits and Subsidies: Tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), provide financial assistance to low- and moderate-income workers. These credits can lessen the burden of inflation and support household budgets. The EITC, for instance, directly benefits low-wage earners, reducing the financial strain caused by rising prices.
- Affordable Housing Initiatives: Programs promoting affordable housing directly address the cost-of-living crisis. Affordable housing reduces the burden of housing expenses on low- and moderate-income households, allowing more disposable income for other necessities. A shortage of affordable housing can exacerbate inflation’s impact on wages, creating a vicious cycle.
- Energy Assistance Programs: Government initiatives addressing energy costs, such as rebates or subsidies for energy-efficient appliances, directly reduce household expenses. Such programs help offset the rising cost of energy, a significant factor in the overall cost of living.
- Childcare Subsidies: Support for childcare costs, through subsidies or tax breaks, helps parents maintain employment, reducing the financial strain on families. Increased childcare costs can impact household budgets and limit workers’ ability to maintain employment, making childcare subsidies vital.
Effectiveness of Policies
Assessing the effectiveness of government policies requires a comprehensive analysis of their impact on wages and the cost of living. Factors like inflation rates, employment trends, and economic growth all influence the success of these interventions. It’s important to evaluate policies holistically, considering both intended and unintended consequences. Evaluation of effectiveness involves comparing pre- and post-policy data, controlling for other variables affecting wages and the cost of living.
- Evaluating Impact: The effectiveness of a policy can be evaluated by measuring changes in wages, cost of living indices, and employment rates before and after the policy’s implementation. A robust analysis often requires longitudinal data and careful consideration of confounding factors.
- Unintended Consequences: It’s crucial to recognize that government policies can have unintended consequences. For instance, minimum wage increases might lead to job losses in certain sectors, highlighting the need for nuanced policy design.
Last Word
In conclusion, inflation has significantly impacted California’s pay raises, leading to widespread financial hardship for workers. The report underscores the complex interplay between inflation, wages, and employee well-being, highlighting the need for proactive strategies from employers, employees, and government agencies. Addressing the issue of inflation’s impact on pay raises is critical to maintaining a stable and equitable economic environment in California.