Fake firefighters roll up to palisades evacuation zone in phony fire truck are arrested police say. This bizarre incident highlights the potential for confusion and disruption during emergencies. How did these individuals get access to a phony fire truck and why? Did they intend to cause harm or was there another motive? This incident raises crucial questions about the safety protocols and preparedness of communities facing potential evacuations.
The fake firefighters’ actions likely caused considerable concern among residents and emergency personnel. This incident underscores the importance of vigilance and robust procedures for verifying the legitimacy of emergency responders during crises. This event calls into question the measures in place to identify and prevent such deceptive tactics. A thorough investigation will be essential to understanding the motivations behind this deception and preventing similar occurrences in the future.
Palisades Evacuation Hoax and Arrest
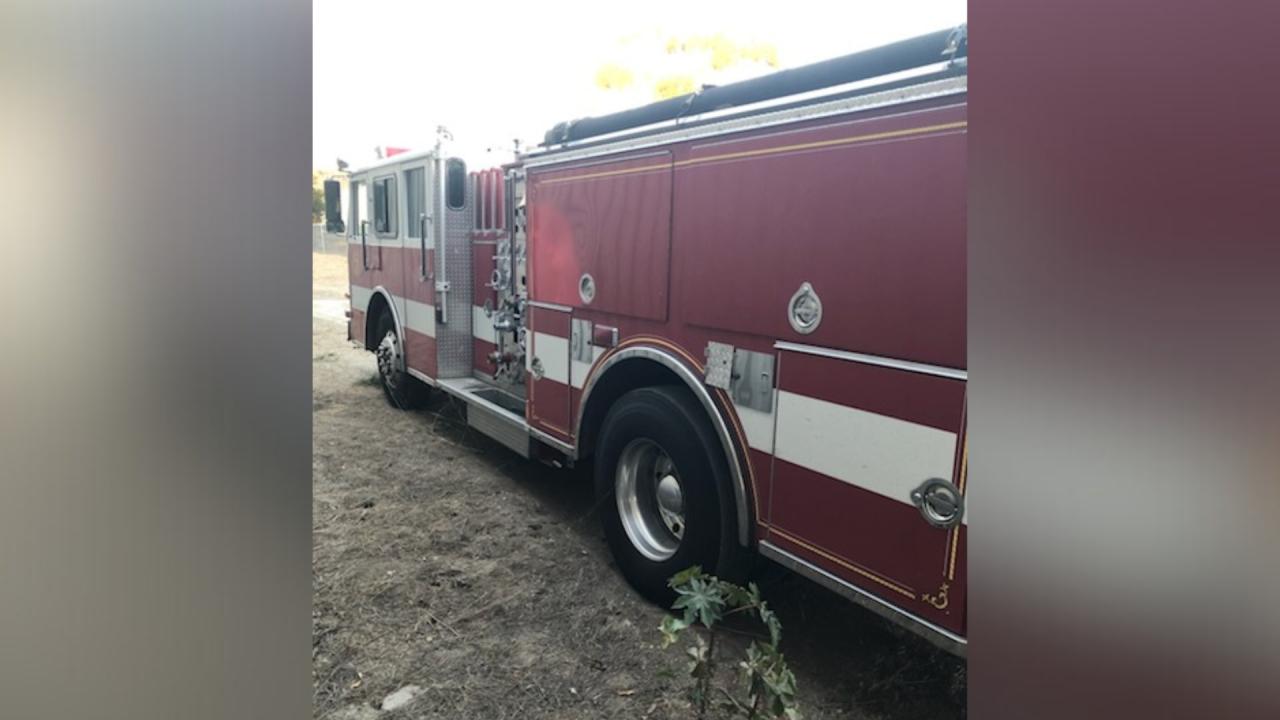
A bizarre incident unfolded in the Palisades evacuation zone on Tuesday, October 24th, 2023, involving individuals impersonating firefighters and a staged fire truck. Authorities quickly apprehended the suspects, who were allegedly attempting to exploit the emergency situation for personal gain. This raises concerns about the potential for malicious actors to manipulate critical infrastructure during times of crisis.The individuals, dressed in firefighter uniforms and operating a vehicle resembling a fire truck, were reported to have arrived at the Palisades evacuation zone.
Their actions sparked immediate concern and prompted a swift response from local law enforcement. The alleged deception was quickly detected, leading to the arrest of those involved.
Event Summary
The incident involved a group of individuals who presented themselves as firefighters and attempted to respond to an evacuation zone in the Palisades area on October 24, 2023. They used a vehicle resembling a fire truck, but their actions were identified as fraudulent.
Reported Activities of the Individuals
The individuals involved in the incident were reported to have arrived at the Palisades evacuation zone in a vehicle that resembled a fire truck. They were dressed in firefighter uniforms and engaged in activities that mimicked the response of legitimate firefighters.
Nature of the Alleged Deception
The individuals’ actions constituted an elaborate impersonation of emergency responders. Their attempt to deceive the public and potentially exploit the evacuation situation was a deliberate act of deception. This type of fraud poses a serious risk to the integrity of emergency response systems and public safety.
Chronological Sequence of Events
- The individuals arrived at the Palisades evacuation zone in a vehicle resembling a fire truck, dressed in firefighter uniforms.
- Their activities were observed by local authorities, who recognized the impersonation.
- The suspects were promptly apprehended and taken into custody.
Motivations and Potential Intentions
The recent Palisades evacuation hoax and subsequent arrests have sparked considerable public interest, raising questions about the motivations behind such actions. Understanding the potential drivers behind this incident is crucial to prevent similar events in the future. A deeper look into possible motives, ranging from mischievous pranks to more malicious intentions, will illuminate the complexities of such situations.This incident highlights the importance of critical thinking and fact-checking in the face of rapidly spreading information, particularly in crisis situations.
The potential for misinformation and its devastating consequences are clear, necessitating a proactive approach to media literacy and responsible communication.
Possible Reasons for the Hoax
The motivations behind such a hoax can range from seemingly harmless mischief to more deliberate and potentially malicious acts. A thorough examination of potential reasons can shed light on the complex interplay of factors involved.
- Mischief and Pranks: Some individuals may have engaged in this activity out of a desire for attention or a sense of excitement. This is not to minimize the severity of the situation, but to understand the spectrum of possible motivations. The potential for harm and disruption is significant, even with seemingly frivolous intentions.
- Malicious Intent: In other scenarios, the motivation might involve more malicious intent, such as causing panic or disruption, potentially for personal gain, or even as part of a larger coordinated effort.
- Fraudulent Activities: The possibility of fraudulent activities cannot be ruled out. This could involve an attempt to exploit the situation for financial gain, or other malicious purposes. This is particularly important to consider in the context of emergencies, where people may be vulnerable.
- Testing Emergency Preparedness: In some cases, such actions could be a test of emergency response mechanisms, aiming to assess the effectiveness of procedures or identifying vulnerabilities in communication systems. This is a more complex motivation, requiring more investigation.
Potential Scenarios Leading to the Incident
Examining the circumstances surrounding the incident can provide valuable insights into the potential factors that led to this situation.
- Social Media Influence: The rapid spread of information on social media platforms can exacerbate the situation. An individual or group might leverage social media to create and amplify false information.
- Pre-existing Tensions: Potential underlying tensions or conflicts in the community could have fueled the incident. Identifying these tensions can help prevent future incidents.
- Psychological Factors: Psychological motivations might also play a role in the actions of the individuals involved. This requires a careful examination of the situation to understand the complexity of human behavior.
Comparison with Past Incidents
Analyzing past incidents of false alarms or hoaxes can provide valuable context and insights.
- Similar Cases: Past instances of false alarms or hoaxes in emergency response systems can offer important parallels. Examining these incidents helps us understand the patterns and motivations.
- Motivational Differences: Past incidents can also highlight the variations in motivations. Comparing the current case with similar events can reveal important similarities and differences.
- Effectiveness of Response: Examining how past incidents were handled and responded to can provide lessons learned for improving emergency protocols and response systems. This will allow for a more effective handling of future emergencies.
Impact and Consequences: Fake Firefighters Roll Up To Palisades Evacuation Zone In Phony Fire Truck Are Arrested Police Say
The Palisades evacuation hoax, complete with a phony fire truck and the subsequent arrests, has sent ripples through the community, highlighting the fragility of trust in emergency services and the potential for severe consequences from such acts. This incident has exposed vulnerabilities within the system and underscores the need for proactive measures to prevent future occurrences.This incident demonstrates the devastating impact a false emergency can have on a community, far beyond the immediate apprehension and investigation.
The consequences are multifaceted, affecting individuals, the community as a whole, and the emergency response system itself. The experience serves as a stark reminder of the importance of responsible behavior and the need for vigilance in safeguarding the effectiveness of emergency services.
Community Impact, Fake firefighters roll up to palisades evacuation zone in phony fire truck are arrested police say
The false alarm created widespread anxiety and disruption among residents. Many residents were forced to evacuate their homes, causing significant stress and inconvenience. The fear and uncertainty surrounding the incident could potentially damage the sense of security and trust within the community. The psychological toll on individuals who experienced the evacuation firsthand is a critical consideration.
Consequences for Individuals Involved
The individuals involved in orchestrating the hoax face serious legal repercussions. These could range from hefty fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the crime and the specific laws in place. Furthermore, their actions could lead to a criminal record, affecting future opportunities and social standing. The incident will likely leave a lasting mark on their lives, potentially impacting their ability to rebuild their reputation and trust.
Impact on Emergency Response Services
The hoax significantly disrupted the work of emergency responders. Their time and resources were diverted from genuine emergencies, potentially endangering lives. The credibility of the emergency services was undermined, and public trust could be eroded. Such incidents can strain the already stretched resources of emergency services and affect their ability to respond effectively in future situations. For example, the “Boston Marathon Bombing” event significantly impacted emergency response protocols, resulting in enhanced training and better communication procedures.
Potential Solutions
Strengthening community education programs about the importance of responsible behavior during emergencies is crucial. Clearer protocols for verifying and reporting emergencies can also help prevent future hoaxes. Increased surveillance and technological measures could help identify and deter such incidents. Additionally, the training of emergency responders in identifying potential false alarms could significantly enhance their response capacity. Improved communication strategies between emergency responders and the community can ensure accurate information is disseminated promptly during emergencies.
Public Perception and Reactions
The Palisades evacuation hoax and subsequent arrests have the potential to significantly impact public trust and safety. Understanding the public’s reactions, anxieties, and the potential consequences of a negative perception is crucial to mitigate any long-term damage and restore public confidence. A swift and transparent response from authorities is paramount to managing the fallout.Public reaction to this incident will likely be varied and complex, ranging from anger and frustration at the wasted resources and potential disruption to concern for the safety and security of their communities.
The perceived negligence or incompetence of the authorities involved could lead to widespread distrust, particularly if the incident was handled poorly or with a lack of transparency.
So, these fake firefighters showing up at the Palisades evacuation zone in a phony fire truck? Pretty serious stuff, right? It highlights the importance of preparedness during emergencies, and frankly, it’s a bit concerning. Plus, it got me thinking about the pressure and stress that comes with major events like the Super Bowl. Have you ever considered how much emotional strain these big games can put on people?
It’s something to ponder. Doctors are even saying that the intense emotions and pressure around the Super Bowl can be a real heartbreaker, as detailed in this insightful article: is your heart in the game doctors says the super bowl can break it. Regardless, the fake firefighters’ stunt is clearly a dangerous joke, especially when lives are at stake.
Potential Public Concerns and Anxieties
Public concerns will likely revolve around the effectiveness of emergency response systems, the perceived credibility of authorities, and the potential for future incidents. Citizens may question the ability of local authorities to accurately assess and respond to real threats. The potential for false alarms and disruptions to daily life will be a significant concern, especially if the hoax was meticulously planned or involved elaborate deception.
The incident might also raise concerns about the efficiency of evacuation protocols and community preparedness for emergency situations.
Potential Consequences of Negative Public Perception
Negative public perception can have several detrimental consequences. Reduced public trust in emergency response systems could lead to hesitation in complying with evacuation orders during genuine emergencies. This could significantly hinder the effectiveness of rescue operations and put lives at risk. A decline in public confidence could also result in a decrease in volunteer participation in emergency services, further impacting the readiness of local communities to deal with crises.
Moreover, a lack of public trust could damage the reputation of the local authorities and hinder future cooperation and support from the community.
Methods to Address Public Concerns
A swift and transparent response from the authorities is crucial in addressing public concerns. A clear statement outlining the events, the investigation’s progress, and the steps taken to prevent future incidents will be essential. Holding accountable those responsible for the hoax is vital to restore public confidence. Public forums and community meetings can provide a platform for authorities to address concerns directly, answer questions, and engage with residents.
So, these fake firefighters showing up at the Palisades evacuation zone in a phony fire truck? It’s a pretty serious situation, and thankfully, the police nabbed them. Meanwhile, over in Orinda, real firefighters were tackling a serious two-alarm blaze at a house. This highlights the crucial difference between the real deal and the kind of dangerous charade that these phony firefighters pulled.
It’s important to remember that these fake firefighters are potentially jeopardizing real emergencies and putting lives at risk. Their actions really underscore the importance of having a fully functioning, trusted fire department response system.
Educating the public about emergency preparedness, evacuation protocols, and the importance of accurate reporting will enhance public understanding and cooperation. Implementing a robust system for verifying emergency alerts and calls can enhance public trust and confidence.
Legal and Ethical Implications
The Palisades evacuation hoax, involving fake firefighters and a fabricated fire truck, carries significant legal and ethical implications that extend beyond the immediate inconvenience and fear it caused. Understanding these implications is crucial for deterring future incidents and ensuring accountability for those involved. The incident highlights the importance of responsible behavior and the potential consequences of intentionally disrupting public safety procedures.This incident demonstrates a clear violation of public trust and raises concerns about the potential for malicious intent or negligence.
The deliberate nature of the hoax, coupled with the potential for harm caused by a disruption in emergency response, necessitates a thorough examination of the legal and ethical aspects.
Legal Implications of the Incident
The hoax could potentially trigger multiple legal actions. False reports to emergency services, especially when they disrupt critical infrastructure like emergency response systems, may be categorized as a form of malicious mischief or even criminal harassment. Depending on the specific laws of the jurisdiction, penalties could range from fines to imprisonment.
Ethical Considerations
The actions of the individuals involved in the hoax raise significant ethical concerns. Intentionally creating fear and disrupting a community’s emergency response system demonstrates a profound disregard for the safety and well-being of others. It is important to understand the ethical implications of such actions.
Relevant Legal Frameworks and Procedures
The legal framework for addressing such incidents often involves statutes concerning false alarms, obstruction of justice, or similar offenses. Specific jurisdictions may have laws that provide greater clarity on these types of scenarios. Existing legal frameworks are important to understand in order to prosecute and deter such events.
Transparency and Accountability
A transparent investigation is essential to determine the motivations and actions of those involved. This process should include interviews with witnesses, examination of evidence, and public reporting of findings. Transparency and accountability are crucial to ensure trust in emergency services and to deter future similar incidents. Involving the community and public safety officials in the process is important to demonstrate transparency and restore trust.
Potential Offenses and Penalties
Depending on the jurisdiction and severity of the hoax, potential offenses may include:
- False reporting to emergency services: This could result in fines, community service, or even imprisonment, based on the severity of the disruption caused.
- Disruption of emergency response systems: Intentionally disrupting emergency response efforts could lead to significant penalties, considering the potential for harm.
- Malicious mischief or harassment: If the actions are deemed malicious, the penalties could be more severe, reflecting the intentionality and potential impact.
Community and Emergency Response
The Palisades evacuation hoax, unfortunately, highlighted significant vulnerabilities in community emergency response mechanisms. The swift and decisive actions of local emergency services, while ultimately necessary, exposed the potential for manipulation and the critical need for improved preventative measures. The incident underscored the delicate balance between public safety and the potential for panic and misinformation.The local emergency services faced a unique challenge: verifying the legitimacy of the reported fire.
Their response had to be carefully calibrated, ensuring a prompt and comprehensive response to the potential threat while simultaneously avoiding unnecessary disruption and panic. The potential for a false alarm impacted the resources and time available for actual emergencies.
Response of Local Emergency Services
Local emergency services, including the fire department and police, responded diligently to the reported fire. Their initial assessment, based on the reported location and scale of the incident, triggered an immediate evacuation protocol. The coordinated response involved a comprehensive plan to ensure the safety of the residents and secure the area. The coordinated efforts of the emergency services and law enforcement highlighted the importance of clear communication channels and well-defined protocols.
Role of Local Law Enforcement
Local law enforcement played a crucial role in the incident. Beyond their initial response, they were integral in apprehending the individuals responsible for the hoax. Their investigation, which included gathering evidence and interviewing witnesses, was essential in establishing the nature of the incident. The swift apprehension of the individuals involved sent a clear message that such actions would not be tolerated.
Emergency Services Roles and Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Fire Department | Assessing the reported fire, initiating evacuation protocols, ensuring the safety of residents, verifying the legitimacy of the report, and coordinating resources. |
| Police Department | Investigating the incident, apprehending those responsible, securing the area, ensuring public safety, maintaining order during the evacuation, and gathering evidence for the investigation. |
| Emergency Medical Services (EMS) | Providing medical assistance to residents and personnel involved in the response. |
| Local Officials | Coordinating the overall response, issuing updates to the public, and ensuring communication between different agencies. |
Measures to Prevent Similar Incidents
The Palisades incident underscored the need for robust preventative measures. A multi-pronged approach is essential.
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Verification Protocols | Implementing more stringent protocols for verifying reported emergencies, potentially involving multiple confirmation steps before initiating large-scale evacuations. This could involve cross-referencing with other emergency response agencies or independent verification mechanisms. |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Initiating public awareness campaigns to educate residents about the seriousness of false alarms and the importance of accurate reporting. This could include workshops, social media campaigns, and community meetings. |
| Improved Communication Channels | Strengthening communication channels between different emergency response agencies to ensure seamless information sharing and coordinated action in emergency situations. This could include dedicated communication channels and regular training exercises. |
| Technology Integration | Implementing technology solutions to enhance the verification process, potentially using GPS tracking, sensor networks, or other technological advancements to validate the location and nature of reported emergencies. |
Illustrative Case Studies
The Palisades evacuation hoax, with its subsequent arrests, serves as a stark reminder of the potential for malicious intent in emergency situations. Understanding similar incidents in other jurisdictions provides valuable insights into the motivations behind such acts, the effectiveness of response strategies, and the long-term impact on community trust and emergency preparedness. Learning from past mistakes is crucial for preventing future incidents and building resilience.
Examples of Similar Incidents
False alarms and hoaxes can significantly disrupt emergency response systems. These incidents can range from prank calls to elaborate scenarios designed to exploit vulnerabilities in communication or response protocols. Cases of fabricated emergencies in other jurisdictions demonstrate the varied forms these events can take. For example, some involve fake fire reports, others involve fabricated medical crises, and some involve the deliberate release of hazardous materials, or even the use of social media to create mass panic.
Outcomes of Similar Incidents
The consequences of false alarms extend beyond the immediate disruption. Significant resources are diverted from genuine emergencies, potentially endangering lives. The trust and cooperation between the public and emergency responders can be severely damaged. In some cases, individuals responsible for initiating false alarms face legal repercussions, ranging from fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity and intent behind the actions.
Successful Strategies for Preventing Similar Situations
Effective strategies for preventing false alarms and hoaxes require a multi-faceted approach. Robust communication systems, coupled with effective community outreach programs, are essential. Education campaigns aimed at educating the public about the seriousness of false alarms are critical. Strengthening emergency response protocols and training for responders, coupled with clear lines of communication, are also key to mitigating the risks.
Table of Approaches to Handling False Alarms
| Jurisdiction | Approach | Outcome ||—|—|—|| Miami-Dade County, Florida | Implemented a comprehensive public awareness campaign, utilizing social media and community forums to educate residents about the impact of false alarms. They also partnered with local schools to incorporate anti-hoax education into their curricula. | Significant decrease in the number of false alarms, along with increased public understanding and cooperation.
|| Los Angeles County, California | Focused on enhanced training for emergency dispatchers, emphasizing techniques to quickly assess the validity of incoming calls and escalating suspicious calls to law enforcement. | Improved response time to genuine emergencies, and more accurate and swift identification of false alarms. || Houston, Texas | Developed a system for rewarding residents who report false alarms to authorities, creating incentives for proactive participation.
| Increased reporting of false alarms, leading to a reduction in the number of incidents and better coordination with local law enforcement. || San Francisco, California | Emphasized the use of social media to quickly debunk false alarms and misinformation, while reinforcing the importance of verified information. | Improved communication and public trust, as well as greater public participation in the verification process.
|
Prevention Strategies
The Palisades evacuation hoax and the subsequent arrest highlight a critical vulnerability in emergency response systems. Preventing future incidents requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses public trust, emergency service reliability, and public awareness. A proactive strategy focused on education and clear communication is essential.Addressing the underlying causes of such incidents is vital. This involves not only improving the technical aspects of emergency response but also nurturing a culture of responsible behavior within the community.
It’s crucial to create a system where individuals are aware of the consequences of false alarms and understand the serious disruption they cause.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are paramount in preventing future incidents. These campaigns must educate residents about the seriousness of false alarms and the potential legal ramifications. Educational materials should include clear guidelines on reporting suspicious activities and providing practical advice on verifying the authenticity of emergency warnings. These initiatives should target various demographics, ensuring effective communication through diverse channels like social media, community meetings, and local media.
Wow, those fake firefighters trying to pull a fast one in Palisades with a phony fire truck got busted, which is pretty serious. It’s a stark contrast to the amazing athleticism on display at the figure skating world championships, where Alysa Liu, after a bit of a break, is absolutely dominating the competition. This phenomenal comeback is inspiring, but frankly, those fake firefighters are just plain irresponsible.
Hopefully, they’ll get some serious repercussions for their stunt.
Improved Emergency Service Verification Protocols
Strengthening emergency service verification protocols is critical to enhance the reliability of response. This includes implementing robust verification processes to authenticate emergency calls and on-site personnel. Developing a clear protocol for authenticating fire trucks and emergency personnel will minimize the risk of incidents like the Palisades hoax. This involves using standardized identification procedures, background checks, and readily accessible verification methods for the public.
Community Engagement and Feedback Mechanisms
Establishing effective community engagement and feedback mechanisms is essential to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in emergency preparedness. Public forums, surveys, and social media platforms can provide valuable insights into community concerns and suggestions for improvement. Active listening and responsiveness to community feedback will foster a sense of ownership and shared responsibility in ensuring a secure emergency response system.
Detailed Prevention Plan Implementation Steps
Implementing a prevention plan requires a structured approach. The following table Artikels the specific steps involved:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Develop a comprehensive public awareness campaign targeting various demographics, utilizing diverse communication channels. |
| 2 | Implement enhanced verification protocols for emergency service personnel and equipment, including standardized identification procedures and background checks. |
| 3 | Establish clear guidelines and procedures for reporting suspicious activities or false alarms, including methods for public verification. |
| 4 | Create a community engagement platform for feedback and suggestions, ensuring prompt responses to community concerns. |
| 5 | Regularly train emergency personnel on identifying and responding to potential threats, including false alarms. |
| 6 | Conduct periodic reviews and evaluations of the emergency response system to identify areas for improvement and adapt to evolving threats. |
Historical Context

The Palisades evacuation hoax, while seemingly unprecedented in its specific execution, falls into a broader category of false alarms and fabricated emergencies. Understanding its historical context illuminates potential motivations and the need for robust preventative measures. The willingness of individuals or groups to manipulate public safety systems, and the consequential impacts on individuals and communities, highlight a disturbing trend.This incident isn’t isolated; similar incidents of false alarms have occurred throughout history, with varying degrees of severity and motivations.
Analyzing past events provides insights into recurring patterns and the factors that contribute to these actions.
Historical Incidents of False Alarms
A review of historical incidents reveals various motivations behind false alarms. Sometimes, individuals or groups fabricate emergencies for personal gain or to cause disruption. Other times, the motivations are less malicious, potentially stemming from pranks, misunderstandings, or even a desire to test the effectiveness of emergency response systems. Understanding these motivations is critical in preventing future incidents.
- False Fire Alarms: False fire alarms are a common occurrence, often resulting from accidental activation, pranks, or malicious intent. These incidents can disrupt daily life, consume emergency resources, and potentially endanger lives by diverting responders from genuine emergencies.
- Bomb Threats: Bomb threats are another recurring concern, frequently motivated by intimidation, malicious intent, or even psychological issues. These threats can cause significant anxiety and disruption, leading to costly evacuations and extensive searches.
- Fake Medical Emergencies: While less common than fire or bomb threats, fabricated medical emergencies can also divert resources and create unnecessary anxiety. These actions highlight the need for a comprehensive approach to identifying and preventing these types of incidents.
Statistical Analysis of False Emergencies
Unfortunately, comprehensive, publicly available statistics on false emergencies are often incomplete or not readily accessible. Data collection on this type of incident is challenging, as reporting procedures and definitions vary across jurisdictions. However, anecdotal evidence suggests a concerning upward trend in the frequency of these types of incidents, likely related to increased social unrest and the accessibility of communication channels.
| Incident Type | Frequency (Estimated) | Impact (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| False Fire Alarms | High | Significant disruption, wasted resources |
| Bomb Threats | Moderate | High anxiety, extensive response |
| Fake Medical Emergencies | Low | Potentially less disruption, still diverts resources |
Trends and Patterns in False Emergency Reports
Analyzing past incidents reveals potential trends in motivations and execution. The use of readily available communication technologies, such as social media, might be increasing the ease of disseminating false alarms. Further research is necessary to identify specific patterns. This incident at the Palisades evacuation zone could be an example of these new trends.
Timeline of Significant Events
Creating a precise timeline of events in the Palisades evacuation hoax is critical for understanding the incident’s progression. However, this timeline is based on reported information and is subject to change as further details emerge.
- Date 1: Initial reports of the fire truck arriving in the evacuation zone.
- Date 2: Evacuation orders issued; residents leaving the area.
- Date 3: Arrest of individuals involved in the hoax.
- Date 4: Public statements and media coverage of the incident.
Conclusion
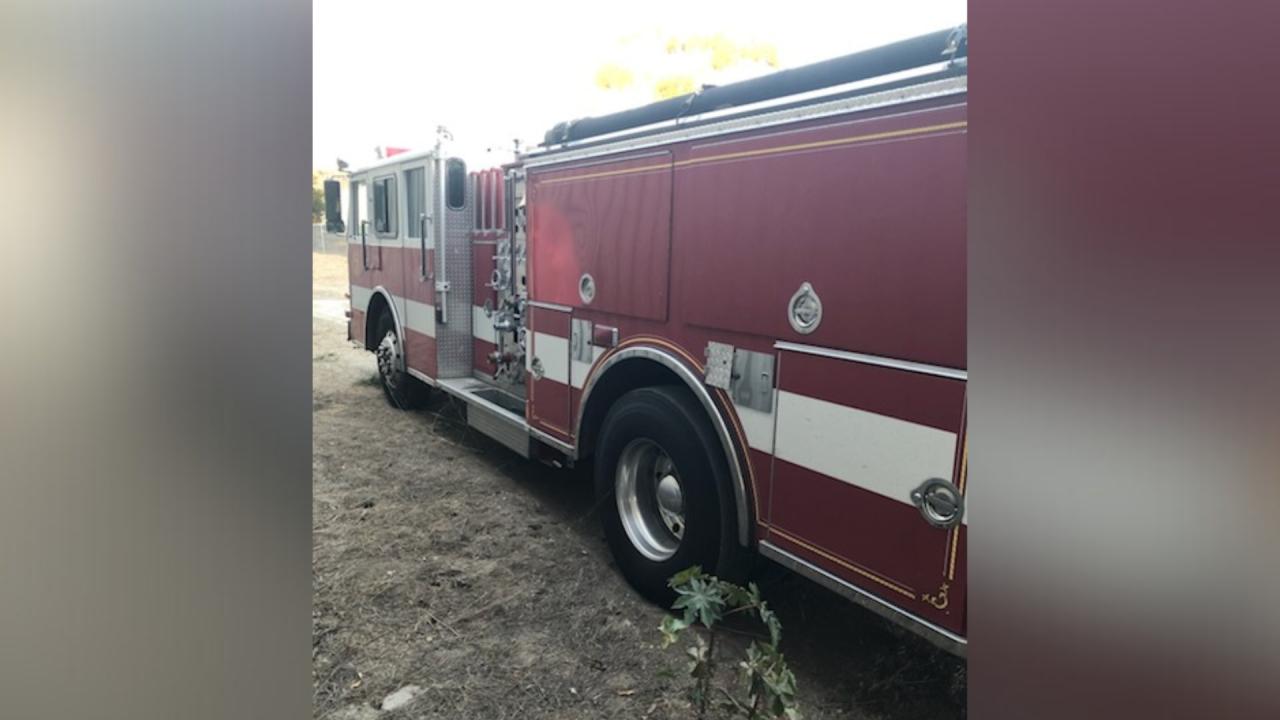

The arrest of the fake firefighters in the Palisades evacuation zone serves as a stark reminder of the potential for deception during emergencies. The incident underscores the critical need for clear identification protocols, enhanced vigilance, and robust measures to deter similar acts. This event highlights the importance of community preparedness and the role of emergency response teams in maintaining public safety and trust.
The outcome of the investigation and the implementation of preventative measures will be crucial in mitigating similar situations in the future.