Best beat making software sets the stage for a journey into the world of electronic music production. This guide delves into the features, workflows, and nuances of popular beat-making programs, providing a comprehensive overview for aspiring producers and seasoned musicians alike. We’ll explore everything from user interfaces and sound design to sample libraries and production techniques, ultimately helping you choose the perfect tool for your creative endeavors.
Choosing the right beat making software can significantly impact your workflow and creative output. This guide will compare key features, user interfaces, and sound design capabilities to help you navigate the vast selection available. We’ll cover everything from budget-friendly options to powerful professional suites, providing valuable insights to assist you in making the best choice for your needs and budget.
Introduction to Beat Making Software
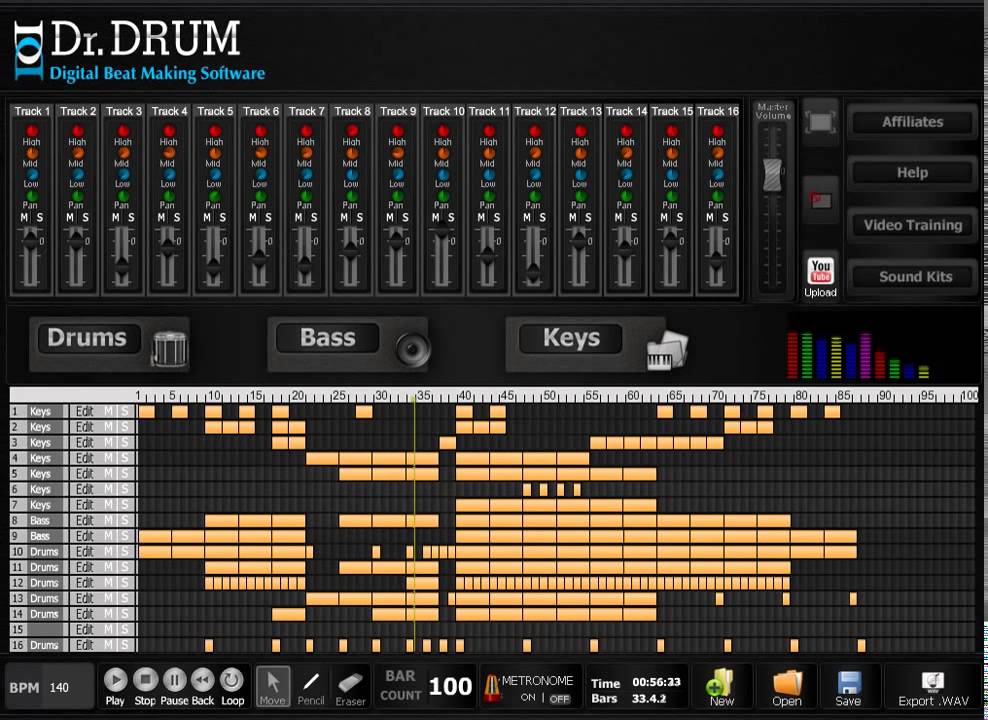
Beat making software has revolutionized the music production landscape, empowering musicians and producers of all levels to craft compelling soundscapes. From simple drum patterns to intricate melodic arrangements, these programs offer a comprehensive toolkit for sonic exploration. This diverse range of software caters to a spectrum of needs, from hobbyists seeking a fun creative outlet to professionals needing powerful tools for complex projects.Different software packages cater to various levels of experience and desired outputs.
Understanding the key features and functionalities can significantly impact the creative process and the quality of the final product. A crucial aspect of choosing the right software is aligning its capabilities with individual needs and aspirations.
Types of Beat Making Software
Beat making software encompasses a variety of applications, each with unique strengths. Some are focused on specific aspects of music production, like drum programming, while others offer a comprehensive suite of tools for composing entire tracks. This diversity allows users to select the software that best aligns with their individual needs and workflow. Popular categories include:
- Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs): DAWs are comprehensive platforms that house numerous instruments, effects, and tools for creating and editing music. They provide a centralized hub for audio manipulation and offer unparalleled flexibility in song arrangement and production. Examples include Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and FL Studio. DAWs are frequently the go-to choice for professional musicians and producers due to their versatility and expansive feature sets.
- Specialized Beat Making Software: Some programs specialize in crafting beats, offering pre-programmed sounds and intuitive interfaces. These applications are often designed to simplify the beat creation process and are frequently utilized by producers looking to generate a large quantity of material in a short amount of time. They are more focused on drum programming and beat construction.
Key Features Distinguishing Beat Making Software
Several key features differentiate various beat making software applications. These include the breadth and depth of instruments, the quality of audio processing tools, the ease of use, and the versatility of its integration with other programs.
- Instrument Libraries: The quality and variety of instruments available within the software significantly influence its capabilities. A comprehensive library allows for a wider range of sonic explorations and greater creative freedom. Some programs boast vast collections of virtual instruments, while others focus on a more specific genre or style.
- Audio Processing Tools: Advanced audio processing tools, such as EQ, compression, and reverb, are crucial for shaping the sound and polishing the final product. The sophistication of these tools directly impacts the overall quality and professional feel of the music.
- User Interface and Workflow: An intuitive user interface and smooth workflow greatly enhance the creative process. Software with a well-designed interface allows for effortless navigation and efficient task completion. This aspect plays a crucial role in the user experience and the rate of progress.
Common Functionalities Across Beat Making Software
Despite the differences, common functionalities exist across various beat making software. These shared features contribute to the versatility and utility of these tools.
- Audio Editing: All beat making software typically provides functionalities for editing audio, including trimming, slicing, and manipulating audio waveforms. This ability allows for precise control over the audio material, ensuring a high level of detail and precision in the final product.
- Drum Programming: Many programs offer sophisticated tools for programming and sequencing drum patterns. This feature is essential for creating diverse and engaging beats.
- Mixing and Mastering Tools: The process of blending different tracks and ensuring the final product has a professional sound requires tools for mixing and mastering. All beat making software programs provide these fundamental functionalities, ensuring a polished and balanced final product.
Comparison of Key Features in Popular Beat Making Software
The following table provides a comparative overview of key features in some popular beat making software.
Finding the perfect beat making software can be a real challenge, but the right tools can elevate your music production. A great way to maximize your workflow is to ensure a smooth, uninterrupted session. An ad blocker like ad blocker for windows mac ios android will keep those pesky distractions at bay, freeing up your focus to craft those killer beats.
Ultimately, having the right tools in place, from a top-notch ad blocker to the best beat making software, is crucial for success in music production.
| Software Name | Key Feature 1 (e.g., Instrument Library) | Key Feature 2 (e.g., Audio Processing) | Key Feature 3 (e.g., User Interface) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ableton Live | Extensive instrument library and synthesis capabilities | Advanced audio processing and effects | Intuitive and flexible workflow |
| FL Studio | User-friendly interface and intuitive layout | Powerful audio processing tools and effects | Focus on beat making with diverse instruments |
| Logic Pro | High-quality instrument samples and effects | Comprehensive mixing and mastering tools | Mac-centric interface and workflow |
User Interface and Workflow: Best Beat Making Software
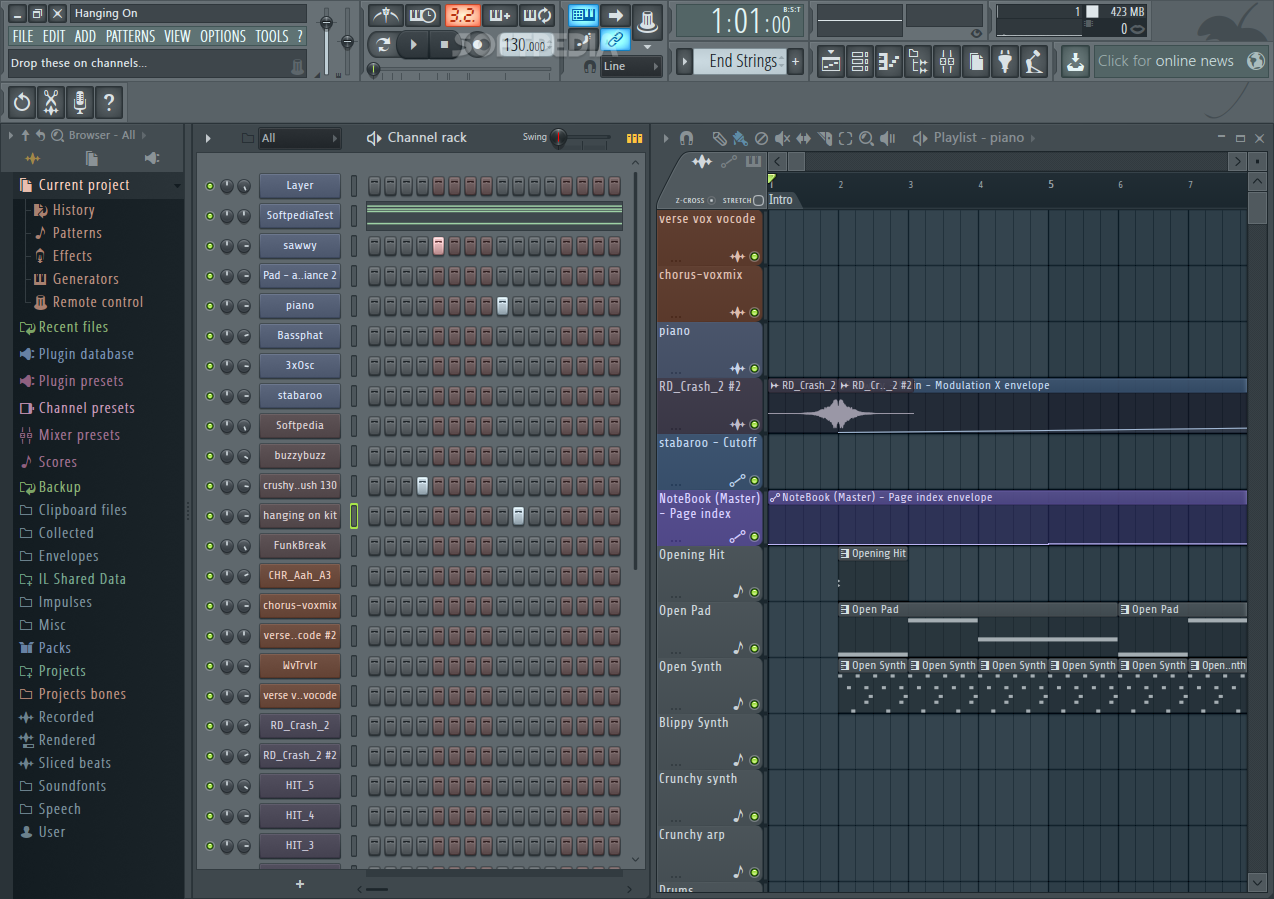
Beat making software often comes with a user interface designed to intuitively guide users through the creative process. This interface typically involves a combination of visual elements, controls, and menus to manage various aspects of the music production. Understanding the workflow within these interfaces is crucial for efficient beat creation. Different software packages, however, employ slightly different approaches to achieving the same outcome.
Typical User Interface Design
The typical beat making software interface is structured around a central audio workspace. This workspace often displays a timeline where audio clips, samples, and instruments are arranged sequentially. Visual representations of these elements, such as waveforms, are frequently used to provide a clear understanding of the audio data. Controls for adjusting volume, panning, and other parameters are often grouped logically, enabling easy manipulation of audio tracks.
Furthermore, a separate area for effects and instruments is usually included. This section is crucial for adding sonic depth and character to the beat.
Workflow for Creating Beats
The workflow for creating beats in different software packages varies slightly. Some packages prioritize a linear approach, where beats are constructed by layering sounds and applying effects step-by-step. Others offer more flexible, modular approaches that allow for parallel editing and experimentation. The choice of workflow often depends on the user’s personal preferences and the specific project. Experienced producers frequently adapt their workflow based on the demands of a particular project.
Handling Instruments and Effects
Different software handles instruments and effects in various ways. Some packages offer virtual instruments with sophisticated synthesis capabilities, allowing users to design sounds from scratch. Other packages provide pre-loaded samples or instruments that can be modified or layered. Effects are usually applied through dedicated panels or effects racks that allow users to control various parameters like gain, EQ, reverb, delay, and distortion.
Finding the perfect beat making software can be tricky, but I’ve been digging into some options lately. It’s a bit of a cold one out there, though – the north bay interior mountains are under a frost advisory Wednesday, as reported here. Hopefully, the chill won’t dampen my enthusiasm for experimenting with these new beat making tools! Still, I’m determined to find the best software to get my creative juices flowing.
The complexity and number of available instruments and effects vary between software packages.
Navigation Tools and Features, Best beat making software
The ability to navigate effectively within beat making software is crucial for efficiency. Different software packages employ various tools and features for this purpose. These tools are essential for quickly locating specific sections of a project, adjusting parameters, and organizing the audio elements. A well-designed navigation system significantly enhances the creative process.
| Software | Navigation Tool 1 | Navigation Tool 2 | Navigation Tool 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FL Studio | Timeline navigation | Channel rack navigation | Mixer section |
| Ableton Live | Session view | Arrangement view | Device rack |
| Logic Pro X | Project browser | Timeline controls | Mixer section |
Sound Design and Effects
Sound design and effects are crucial elements in beat making, allowing producers to shape the sonic landscape of their tracks. Mastering these tools empowers musicians to sculpt sounds from scratch, transform existing sounds, and create unique textures that enhance the overall mood and feel of the music. The range of available tools and effects varies considerably across different beat-making software, impacting the creative possibilities for each user.Understanding the capabilities of sound design tools within different software is essential for selecting the right platform for specific creative needs.
Different tools excel in distinct sonic realms, from synthesizing unique soundscapes to meticulously altering existing audio. This section delves into the sound design and effect tools available in various beat-making software, highlighting their specific functionalities and how they can be used in practical applications.
Sound Design Capabilities
Beat-making software typically includes various instruments and sound design tools, often categorized as synthesizers, samplers, and effects processors. Synthesizers allow the creation of new sounds by manipulating parameters like pitch, timbre, and waveform. Samplers enable the manipulation and layering of existing audio samples, opening up avenues for creating intricate sonic textures. The range of instruments and tools varies across different software, catering to diverse production styles.
Effects Available
The variety of effects available in beat-making software significantly influences the sonic palette. Common effects include EQ, reverb, delay, compression, distortion, and modulation effects. Each software often provides a comprehensive suite of effects, with variations in their specific parameters and user interfaces. Understanding these effects and their functionalities is vital for creating unique soundscapes.
Audio Manipulation Tools
Beat-making software offers diverse tools for manipulating audio, allowing for precise control over sounds. These tools range from simple volume adjustments to complex waveform editing. Detailed control over parameters enables fine-tuning of sound characteristics, leading to more nuanced and artistic results. These tools are critical for shaping and refining the sound elements in a production.
Detailed Description of Effects
- EQ (Equalization): EQ allows adjusting the amplitude of different frequency bands within an audio signal. This is a crucial tool for shaping the timbre and presence of sounds. Parameters like cutoff frequency, gain, and Q factor determine the specific adjustments. For example, boosting the high frequencies of a snare drum can make it sound brighter, while cutting the low frequencies of a bass can make it sound cleaner.
EQ is essential for balancing the overall sound of a mix.
- Reverb: Reverb creates a sense of space and ambience by simulating the reflections of sound in an environment. Parameters like decay time, room size, and diffusion determine the specific reverb characteristics. A long reverb tail creates a spacious feel, while a short reverb adds a subtle sense of ambience.
- Delay: Delay creates a sense of echo by repeating a sound at a specified time interval. Parameters like delay time, feedback, and modulation determine the characteristics of the delay effect. Delay is frequently used to add depth and complexity to sounds, such as adding a sense of spaciousness to a drum beat or creating a rhythmic effect on a vocal line.
- Compression: Compression controls the dynamic range of an audio signal. This helps to even out the volume fluctuations, resulting in a more consistent sound level. Parameters like threshold, ratio, attack, and release determine the degree and characteristics of compression. Compression is used to improve the loudness of a mix while maintaining a dynamic feel.
Sample Libraries and Instruments
Sample libraries and virtual instruments are the heart of any beat-making software. They provide the sonic building blocks for creating diverse and compelling beats. The quality, variety, and ease of use of these resources significantly impact the creative process and final output. Understanding the available instruments and samples within each software is crucial for selecting the right tool for your needs.
Types of Sample Libraries and Virtual Instruments
Different software packages offer varying types of sample libraries and virtual instruments. These range from traditional acoustic instruments to futuristic synthesizers and everything in between. Some software focuses on a specific genre or sound, while others provide a broader spectrum of possibilities. The key is to determine which instruments and sounds align with your desired sonic palette.
Quality and Variety of Samples
The quality and variety of samples directly affect the richness and depth of your beats. High-quality samples often feature professional recordings, high fidelity, and a wide dynamic range, enabling a more polished final product. Variety in the sample libraries is essential for exploration and creating unique soundscapes. A wide selection of instruments and soundscapes enables the creation of a broader range of musical styles.
Ease of Use and Workflow for Importing and Using Samples
The workflow for importing and using samples should be intuitive and efficient. Easy-to-navigate interfaces, well-organized folders, and logical sample management systems are crucial for a seamless creative process. Quick access to parameters, intuitive controls, and seamless integration with the overall software environment are key elements in optimizing workflow.
Comparison of Sample Libraries Across Different Software
| Software | Instrument Type 1 | Instrument Type 2 | Instrument Type 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software A | Acoustic Guitars (various styles) | Modern Synth Leads (futuristic sounds) | Drum Samples (808-inspired kits) |
| Software B | Vintage Electric Pianos | Bass Lines (deep and punchy) | Ambient Pads (atmospheric textures) |
| Software C | Hip-Hop Drum Kits (pre-built loops) | Sampled Vocals (diverse vocal styles) | Analog Synthesizers (classic sounds) |
The table above provides a basic comparison of sample libraries. It highlights the potential instrument types and sonic palettes each software offers. Note that this is a simplified overview, and each software typically contains many more instruments and samples than are shown here.
Production Techniques and Tips
Mastering beat making goes beyond simply using software; it’s about understanding the
Finding the perfect beat making software can be a real game-changer for any aspiring producer. So many options out there, but some stand out more than others. With all the political drama going on, like the recent news about hundreds of federal offices potentially closing this summer at the Doge’s behest, hundreds of federal offices could begin closing this summer at doges behest ap reveals , it’s good to have something creative to focus on, like crafting the next hit track.
Ultimately, the best beat making software is the one that inspires you to keep making music.
- techniques* and
- workflows* that bring your creative vision to life. This section delves into various production methods, genre-specific workflows, and crucial tips to enhance your sonic palette. From crafting unique sounds to leveraging software features, these insights will elevate your beat making.
Beat Making Techniques
Different beat-making techniques can drastically alter the character of your music. These techniques, often combined, are the building blocks of a compelling beat. Using a combination of additive synthesis, subtractive synthesis, and sampling, a beat maker can shape a vast sonic landscape. Drum programming, melodic composition, and harmonic structuring are all integral to the creation of a unique and captivating beat.
- Additive Synthesis: This approach involves building a sound by layering individual oscillators and waveforms. This allows for precise control over timbre and allows for complex soundscapes.
- Subtractive Synthesis: By starting with a complex sound and filtering out unwanted frequencies, subtractive synthesis creates unique textures and tones. Experimenting with filters, EQ, and other tools can shape the overall sound in significant ways.
- Sampling: This technique involves recording and manipulating audio samples to create new sounds. Sampling can be used to create percussive elements, melodic motifs, and even entire textures.
- Drum Programming: Drum programming involves meticulously creating and arranging drum patterns. This process involves using software’s drum sequencer to craft the rhythm and groove of the beat.
- Melodic Composition: This involves creating and arranging melodies that complement the rhythm and harmony of the beat. The melodic elements can be generated through synthesis or sampling and arranged in the software’s sequencer.
- Harmonic Structuring: The choice of chords and harmonies forms the harmonic foundation of the track. This includes selecting chord progressions, adding basslines, and using harmonic instruments like synthesizers.
Workflows for Different Genres
The approach to beat making varies greatly depending on the desired genre. Understanding the characteristics of different genres allows for a tailored workflow.
- Hip-Hop: Often involves layering samples, drum programming, and creating intricate melodic lines. Emphasis is placed on the rhythmic elements, with the incorporation of unique samples and effects to add depth.
- Electronic Dance Music (EDM): Emphasizes rhythmic complexity, using synthesizers and effects to create dynamic and energetic sounds. Often involves the creation of intricate rhythmic patterns and melodic motifs. Heavy use of modulation effects, filters, and automation is common.
- Trap: A subgenre of hip-hop, characterized by its intricate drum patterns, often featuring 808 basslines and heavy use of effects. Emphasis on precision and intricate rhythmic patterns is key.
- Pop: Involves a more balanced approach to melody, rhythm, and harmony. The focus is on creating catchy hooks and using a combination of instruments, synthesizers, and samples to achieve a polished sound. Consideration of vocal arrangements and harmonies is crucial.
Tips for Achieving Specific Sounds and Effects
Specific techniques and software features are crucial for achieving desired sounds and effects. These tools allow for a wide range of sounds and dynamic control.
- Creating Unique Drum Sounds: Use different drum samples, alter their pitch, use EQ and compression to sculpt the sound, and experiment with reverb and delay to achieve unique drum sounds.
- Generating Atmospheric Soundscapes: Layer different sound effects, use reverb and delay to create depth, and modulate synthesizers to produce ethereal sounds.
- Achieving Specific Textures: Use various filters and EQ settings to shape the timbre of sounds. Experiment with different synthesis techniques to create the desired textures.
Effective Use of Software Features
Tip 1: Use the software’s built-in sampler to record and manipulate audio samples for unique textures. Tip 2: Employ the sequencer to create and arrange intricate drum patterns, melodic lines, and chord progressions. Tip 3: Utilize the EQ and filter tools to sculpt the timbre of your sounds and remove unwanted frequencies.
Cost and Pricing Models
Beat making software comes in a variety of pricing structures, making choosing the right option a crucial decision for aspiring producers. Understanding these models is essential for aligning your budget with your needs and maximizing your investment. Different software caters to various skill levels and desired features, leading to varying price points.The cost-effectiveness of a particular software package depends not just on the initial price, but also on the long-term value offered.
A more expensive option might provide a wider range of tools and features, ultimately saving time and effort in the long run. However, a more budget-friendly option could suffice for simpler projects, offering a worthwhile return on investment.
Pricing Structures for Beat Making Software
Beat making software pricing models encompass various options, from one-time purchases to monthly subscriptions. Understanding these models is essential to make informed decisions. Some software offers a free trial period, allowing potential buyers to experience the software before committing to a purchase.
Comparison of Cost-Effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of a beat making software package depends heavily on the features it offers, the user’s experience level, and the intended use cases. A software with advanced features might be more expensive, but its comprehensive tools could lead to faster production times and higher-quality results. Conversely, simpler software packages might be sufficient for users with basic needs and a smaller budget.
It’s crucial to weigh the value proposition against the cost.
Subscription Models and One-Time Purchases
Many beat making software packages now utilize subscription models, offering a recurring fee for access to the software and its updates. One-time purchase options remain available for those seeking a permanent license without ongoing payments. The choice between subscription and one-time purchase depends on individual preferences and budget.
Pricing Models and Features
This table provides a concise overview of pricing models and key features offered by some popular beat making software.
| Software | Pricing Model | Key Features Included |
|---|---|---|
| FL Studio | One-time purchase, with optional expansions | Comprehensive audio workstation, advanced MIDI tools, powerful sound design capabilities, diverse instrument options, flexible arrangement and mixing tools. |
| Ableton Live | Subscription, with different tiers available | Intuitive workflow, extensive sound design tools, advanced MIDI sequencing, built-in effects and instruments, flexible mixing and mastering tools. |
| Logic Pro X | One-time purchase | Professional-grade audio workstation, advanced MIDI sequencing, comprehensive sound design tools, powerful mixing and mastering capabilities, integrated instrument library. |
| Cakewalk by BandLab | One-time purchase, with optional upgrades | Comprehensive DAW with a user-friendly interface, advanced MIDI sequencing, sound design tools, mixing and mastering tools, accessible to users of varying experience levels. |
| GarageBand (Mac) | Included with macOS (free) | Basic audio workstation with essential tools, beginner-friendly interface, ideal for learning, suitable for simple projects. |
Community and Support
Finding the right beat-making software is just the first step. A robust community and support network are vital for mastering the intricacies of any DAW. The quality of support significantly impacts a user’s learning curve and overall experience. Whether you’re a seasoned producer or just starting, access to tutorials, forums, and dedicated support channels can be the difference between frustration and fluency.Effective online communities foster a collaborative environment where users share knowledge, troubleshoot problems, and inspire each other.
The strength of this network can directly correlate with the software’s overall usability and potential for growth. In-depth documentation, comprehensive tutorials, and responsive support teams all contribute to a positive learning experience.
Support Resources for Beat Making Software
Support resources vary widely between different beat-making software. Some DAWs offer extensive online documentation, tutorials, and dedicated forums, while others lean more heavily on user-generated content and third-party resources. Assessing these resources is critical when choosing a software solution.
- Online Documentation: Comprehensive documentation often includes detailed explanations of features, functionalities, and troubleshooting guides. These documents serve as valuable references for users navigating the software’s interface and functionalities. Well-structured and up-to-date documentation is essential for users to effectively utilize the software.
- Tutorials and Video Guides: Step-by-step tutorials and video guides can walk users through specific tasks and processes, providing practical insights and addressing common issues. Tutorials can vary in format, from written guides to interactive video lessons, and are an effective way to understand how to use software’s specific features.
- Dedicated Support Channels: Some DAWs have dedicated support channels, such as email support or dedicated forums, where users can seek assistance from trained personnel or experienced users. Prompt and helpful support channels can resolve issues quickly and effectively.
Online Community and Forums
Online communities and forums are often vital for learning and troubleshooting. Active communities allow users to engage with other producers, share their work, and gain insights from more experienced users. The quality and engagement of a community can greatly influence a user’s overall experience with the software.
- Community Engagement: A vibrant online community fosters knowledge sharing and problem-solving. Users can ask questions, provide solutions, and contribute to a shared pool of knowledge. This interactive exchange benefits everyone, providing support and encouraging collaborative learning.
- Forum Activity: Active forums provide a platform for users to discuss specific issues, share tips, and receive guidance. The level of engagement in these forums can reflect the support available and the overall community spirit.
- User-Generated Content: Active communities often generate valuable resources, such as tutorials, plugins, and sample packs. This user-generated content extends the software’s functionality and adds value to the overall experience.
Nature of Online Community Support
The nature of online community support can range from highly active forums with rapid responses to more niche communities with a slower but still supportive pace. The responsiveness and helpfulness of the community are key factors in assessing the software’s overall support ecosystem.
- Responsiveness: A responsive community ensures quick responses to user queries and provides solutions to technical problems efficiently. Rapid support is crucial, especially when encountering urgent issues during a project.
- Helpfulness: A helpful community goes beyond simply providing solutions. Members actively share insights, offer alternative approaches, and foster a supportive environment. Constructive engagement is essential for maximizing the software’s potential.
- Community Culture: The culture of the online community significantly impacts the user experience. A positive and inclusive environment fosters a sense of belonging and encourages continued engagement. This culture encourages collaboration and knowledge-sharing.
Summary
In conclusion, the best beat making software for you hinges on your specific needs, budget, and desired workflow. This comprehensive guide has provided a framework to explore the various options available, from intuitive interfaces to powerful sound design tools. By considering your requirements and experimenting with different software, you’ll be well-equipped to find the perfect tool to fuel your musical creativity.
Remember to consider your budget, desired sound, and intended use case to make an informed decision.