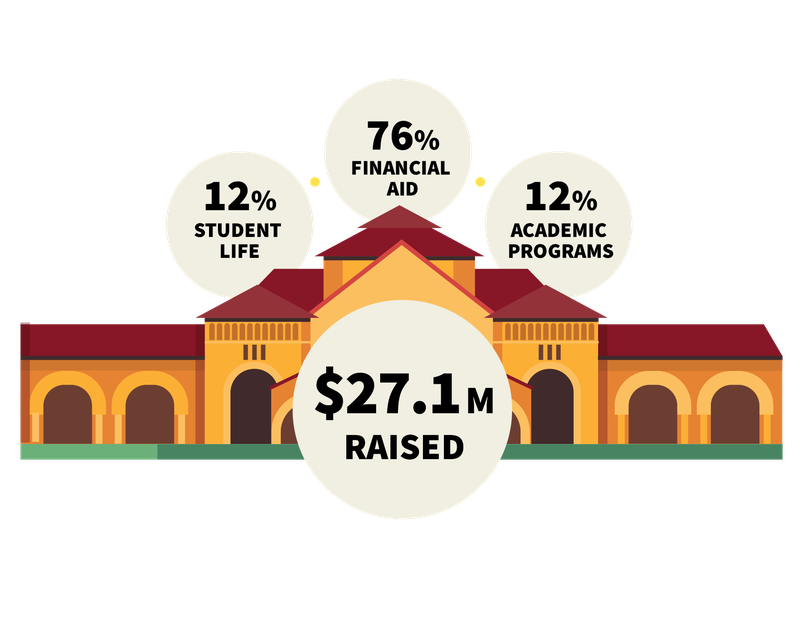
Stanford University funding uncertainties are a critical issue facing the prestigious institution. This exploration delves into the various funding sources, recent trends, financial projections, and potential impacts on different departments. Understanding the complex interplay of factors influencing Stanford’s financial future is essential for appreciating the challenges and opportunities ahead.
This analysis examines Stanford’s funding sources, ranging from government grants and endowments to donations and tuition. Recent trends, including growth or decline in funding from each source, are scrutinized. Potential factors influencing these trends, such as economic conditions and competitive pressures, are also considered. The analysis forecasts Stanford’s financial projections over the next three to five years, incorporating optimistic, pessimistic, and realistic scenarios for funding levels.
This includes potential impacts on specific departments, like engineering and medicine, and strategies for mitigating risks.
Funding Sources and Dependencies
Stanford University, a global leader in education and research, relies on a complex web of funding sources to maintain its operations and ambitious initiatives. Understanding these sources and their relative importance is crucial for appreciating the university’s financial health and anticipating potential challenges. The stability of these funding streams directly impacts Stanford’s ability to invest in groundbreaking research, attract top talent, and provide an exceptional educational experience.
Funding Source Breakdown
Stanford’s financial well-being hinges on diverse funding streams. These sources include substantial endowments, significant tuition revenue, substantial government grants, philanthropic donations, and auxiliary revenue generated from various university services. The relative importance of each source shifts over time, but a healthy balance across these pillars is vital.
Endowment Funds
Endowment funds are a cornerstone of Stanford’s financial strength. These funds, invested in a diversified portfolio, generate substantial income that supports various university activities. Historically, endowments have been a reliable source of revenue, providing a buffer against fluctuations in other funding sources. For example, the substantial returns from Stanford’s endowment in recent years have enabled significant investments in facilities and research initiatives.
Stanford University’s funding woes are definitely a concern, especially considering the recent economic climate. Meanwhile, the huge column of black smoke seen at the Martinez refinery, as reported in this article , highlights the unpredictable nature of events that can impact various sectors, including the ones that provide crucial resources for universities like Stanford. These uncertainties just add another layer of complexity to the already challenging funding situation for institutions like Stanford.
Tuition Revenue
Tuition fees from students are a substantial source of funding. Tuition income directly supports operating costs, faculty salaries, and student services. Changes in tuition rates and student enrollment directly impact the university’s financial position. For instance, declining enrollment or tuition increases can impact revenue projections and budget allocations.
Government Grants
Government grants play a vital role in supporting research initiatives. These grants often fund specific projects, encouraging cutting-edge discoveries. Fluctuations in government funding, particularly in competitive research areas, can affect Stanford’s ability to secure research projects.
Philanthropic Donations
Philanthropic donations from individuals and corporations are crucial for supporting specific projects, programs, and initiatives. Donations can significantly influence the focus and direction of Stanford’s research and educational endeavors. Examples of major donations impacting specific departments and research areas are common, highlighting the influence of this source.
Auxiliary Revenue
Auxiliary revenue, generated from university services like athletic programs and research facilities, provides a critical buffer for operational costs. Fluctuations in auxiliary revenue often mirror economic trends and demand for university services.
Funding Source Analysis
| Source Type | Amount (Estimated) | Anticipated Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Endowment Funds | $XX Billion | Potential growth or contraction depending on market conditions |
| Tuition Revenue | $YY Million | Dependent on enrollment trends and tuition policies |
| Government Grants | $ZZ Million | Fluctuating based on funding priorities and competition |
| Philanthropic Donations | $WW Million | Dependent on donor generosity and fundraising efforts |
| Auxiliary Revenue | $VV Million | Likely to vary based on service demand and economic factors |
Recent Funding Trends: Stanford University Funding Uncertainties
Stanford University’s financial health is intricately tied to the availability and nature of its funding sources. Understanding recent trends in funding is crucial for assessing the university’s capacity to maintain its academic excellence and cutting-edge research initiatives. These trends are not isolated events but are influenced by broader economic forces and shifting priorities.Recent funding patterns reveal a complex interplay of growth and stagnation across various funding streams.
The specifics of these trends are explored below, highlighting the sources of funding and their potential impact on Stanford’s future.
Funding Sources and Growth/Decline
Understanding the specifics of funding trends necessitates a review of individual funding sources. Stanford receives funding from numerous sources, including endowments, government grants, private donations, and revenue from various activities. Analyzing the growth or decline of funding from each of these categories offers a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Endowment Growth: Stanford’s endowment, a significant funding source, has seen fluctuations over the past five years. These fluctuations are often linked to market performance. While some years have seen substantial growth, others have experienced contractions. This volatility underscores the importance of diversification and prudent investment strategies to mitigate potential risks.
- Government Grants: Government funding for research at Stanford has exhibited a varied trajectory. Specific grants may have increased or decreased depending on the areas of research and the policies of funding agencies. The stability of government funding is vital for maintaining crucial research initiatives.
- Private Donations: Private donations have also shown variability. Factors such as economic conditions and philanthropic priorities influence this source of funding. Philanthropic giving can fluctuate depending on economic cycles and individual donor preferences.
- Tuition and Fees: Tuition and fees represent a substantial revenue stream. Increases in these fees can support certain aspects of the university’s operations, but they also raise concerns about affordability for students.
Potential Influencing Factors
Several factors have impacted funding trends over the past five years. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting future trends and adjusting strategies.
- Economic Conditions: Economic downturns or recessions can significantly impact investment returns and philanthropic giving. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis led to a temporary dip in endowment values and private donations, demonstrating the sensitivity of funding to economic cycles.
- Policy Changes: Federal and state policies concerning research funding and higher education can influence the availability of grants and funding opportunities. Policy shifts can significantly impact Stanford’s research programs and overall operations.
- Competitive Pressures: The rise of other research institutions and the growing demand for funding in specific fields can increase competition for grants and resources. This increased competition might affect Stanford’s ability to secure funding for specific research initiatives.
Impact on Academic Programs and Research
The changing funding landscape can directly impact Stanford’s ability to sustain its academic programs and research initiatives. Reduced funding can lead to program cuts, staffing limitations, and diminished opportunities for innovative research.
- Program Reductions: A decline in funding may force the university to scale back or eliminate certain academic programs. This could result in fewer course offerings or a decreased focus on particular disciplines.
- Research Constraints: Limited funding can hinder research projects, potentially impacting the university’s ability to conduct groundbreaking research. This could mean a reduced number of research assistants, fewer opportunities for collaborative projects, and delayed publication of research findings.
- Faculty Recruitment and Retention: Funding is directly linked to the ability to recruit and retain top faculty. A funding crisis could impact the university’s ability to attract and retain leading researchers, potentially impacting the quality of the educational experience.
Financial Projections and Uncertainties
Stanford University’s future financial health hinges on its ability to secure and manage funding effectively. Projections for the next three to five years are crucial for strategic planning, faculty recruitment, and maintaining the university’s academic excellence. Understanding potential scenarios for different funding levels is essential for navigating the uncertainties of the academic funding landscape.
Stanford’s Financial Projections (2024-2028)
Stanford’s financial projections for the next three to five years will be affected by several factors, including enrollment trends, research grant success rates, endowment performance, and philanthropic giving. The university’s ability to balance competing priorities, like maintaining its academic rigor and adapting to changing economic conditions, will play a critical role in the accuracy of its projections.
Potential Funding Scenarios
Different scenarios for funding levels will have varying effects on Stanford’s operations and strategic direction. Forecasting these scenarios provides a framework for understanding the potential implications of different funding levels.
| Scenario | Funding Level | Effect on University |
|---|---|---|
| Optimistic | Above-average growth in all funding sources | Continued expansion of research initiatives, enhanced faculty recruitment, and potential for new facilities development. |
| Pessimistic | Significant decline in funding from major sources | Reduced investment in research, potential limitations on faculty recruitment, and possible budget cuts in core operations. |
| Realistic | Moderate growth in funding, with some fluctuations | Sustained academic excellence, gradual expansion of key programs, and cautious investment in infrastructure. |
Detailed Funding Projections Table
This table provides a more granular view of potential funding projections across different funding sources for the next three to five years. It includes projected amounts and associated potential risks for each source.
| Year | Source | Projected Amount (USD) | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | Endowment Income | $1,250,000,000 | Market fluctuations, inflation, and potential need for increased investment in certain areas. |
| 2024 | Tuition Revenue | $2,500,000,000 | Competition from other universities, enrollment trends, and potential need for adjustments in tuition rates. |
| 2024 | Research Grants | $1,500,000,000 | Competition for grants, funding priorities of granting agencies, and potential for funding cuts. |
| 2025 | Philanthropic Contributions | $500,000,000 | Economic downturns, changes in donor priorities, and potential need for more robust fundraising strategies. |
| 2026 | Government Funding | $750,000,000 | Government budget constraints, policy changes, and competition from other institutions. |
| 2027 | Other Revenue | $250,000,000 | Fluctuations in licensing income, development activities, and external collaborations. |
| 2028 | All Sources | $6,750,000,000 | Overall market conditions, potential for increased competition for funding, and need for diversification of funding sources. |
Impact on Specific Areas
Stanford’s financial health is intricately tied to its ability to secure and manage funding across various departments. Uncertainty surrounding funding sources creates ripple effects, impacting research, faculty recruitment, and ultimately, the educational experience. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for strategic planning and resource allocation.
Potential Impact on Engineering
Engineering departments, often reliant on grants for cutting-edge research, are particularly vulnerable to funding fluctuations. Reduced grant funding could lead to delays or cancellations of crucial projects, hindering innovation and potentially affecting national competitiveness. The impact is further compounded if industry partnerships, another significant funding source for applied research, falter. Consequently, faculty recruitment in specialized areas may suffer, potentially impacting Stanford’s ability to attract top talent.
The loss of key researchers can have a detrimental effect on student opportunities for advanced study and research.
Potential Impact on Medicine
Medicine, with its substantial research and clinical needs, faces unique challenges. Funding uncertainties could affect clinical trials, leading to delays in the development of new treatments and therapies. This could have serious implications for patient care and public health. Decreased funding might also hinder the recruitment of top medical faculty, impacting training opportunities for future generations of physicians and researchers.
A decrease in grant funding can also have a cascading effect on allied programs, such as nursing and public health, which often rely on grant funding for their research initiatives.
Stanford’s funding worries are definitely a bummer, but hey, at least the Bay Area is shining bright with festive spirit! Check out these fantastic photos capturing the vibrant Hanukkah celebrations here. While the holiday cheer is infectious, the financial challenges facing Stanford still need a strong solution, and it’s going to take more than just a menorah to resolve them.
The university’s future is still uncertain, so let’s hope for positive developments soon.
Potential Impact on Humanities
The humanities, often reliant on smaller, less predictable funding sources, are especially vulnerable to funding cuts. Reduced funding could lead to decreased faculty support, potentially impacting research and teaching quality. The humanities play a vital role in critical thinking and societal understanding, and the loss of faculty and support programs could have long-term consequences for intellectual discourse and academic rigor.
Public funding, which is sometimes used for arts initiatives and programs within the humanities, is also prone to fluctuation, which can severely affect the department’s capacity to maintain its programs.
Impact on Research Initiatives
Reduced funding directly impacts research initiatives across all departments. Delayed or cancelled projects, and the inability to attract and retain top researchers, could halt progress in critical areas. The loss of funding can also affect the availability of equipment, technology, and other resources essential for research. This is especially detrimental to exploratory and high-risk projects, which are often the most groundbreaking.
For instance, the inability to fund a particular research line may prevent the discovery of a new treatment or solution to a critical problem.
Impact on Faculty Recruitment
Funding uncertainties can make it challenging to recruit and retain top faculty. Competitive salaries and research support are critical to attracting and retaining leading scholars in various fields. Reduced funding could limit Stanford’s ability to offer competitive compensation packages, potentially leading to a loss of talented faculty to other institutions. This can have a significant impact on the quality of education and research, as well as the overall reputation of the university.
Impact on Student Support Services
Student support services, including financial aid and counseling, often rely on specific funding streams. Reduced funding could affect the availability of these essential services, impacting the overall student experience and success. This is particularly important for underrepresented students and those from low-income backgrounds, who may be disproportionately affected by funding cuts.
Impact on Various Departments and Funding Needs
| Department | Funding Source | Potential Impact | Funding Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engineering | Grants, Industry Partnerships | Delayed/Cancelled projects, Difficulty recruiting faculty | Increased funding for research grants, industry partnerships |
| Medicine | Grants, Clinical Trials | Delayed treatments, Reduced faculty recruitment | Stable funding for clinical trials, faculty recruitment |
| Humanities | Grants, Public Funding | Reduced faculty support, decreased research | Increased funding for smaller grants, alternative funding sources |
Strategies for Mitigating Funding Risks

Stanford University faces a complex landscape of funding uncertainties, requiring proactive and multifaceted strategies to ensure its continued success. Addressing these uncertainties necessitates a robust approach that considers diverse funding streams and adaptable financial planning. This section details potential strategies for mitigating these risks.
Diversifying Funding Sources
Stanford’s reliance on a few key funding sources makes it vulnerable to shifts in those areas. Diversifying its funding portfolio across multiple sources, including corporate sponsorships, philanthropic endowments, and government grants, is crucial. This approach reduces dependence on any single source, making the institution more resilient to potential downturns in a particular area.
- Corporate Partnerships: Stanford can actively seek partnerships with corporations whose interests align with the university’s research priorities. This could involve joint research initiatives, sponsored faculty appointments, and industry-specific fellowships. Successful examples include collaborations between universities and tech companies in areas like artificial intelligence and renewable energy.
- Philanthropic Giving: Cultivating strong relationships with high-net-worth individuals and philanthropic organizations is essential. This involves strategic outreach, demonstrating the impact of past funding, and highlighting the university’s commitment to specific areas of research. Yale University has a strong history of securing large donations for specific initiatives.
- Government Grants: Exploring and securing grants from federal and state agencies aligned with Stanford’s research strengths can provide crucial funding. This involves demonstrating the university’s ability to deliver impactful research that addresses national needs. The University of California system has a long-standing history of successfully pursuing federal research grants.
Strengthening Endowment Management
Effective endowment management is critical for long-term financial stability. This involves optimizing investment strategies to maximize returns while minimizing risk, ensuring that the endowment can support the institution’s mission and programs over the long term.
- Risk-Adjusted Investment Strategies: A well-defined investment policy that balances risk and return is essential. This strategy should consider the long-term needs of the institution, ensuring that investments remain aligned with the institution’s mission. Harvard University’s endowment has been lauded for its long-term success in managing investments.
- Impact Investing: Integrating impact investing into the endowment strategy can generate returns while contributing to social and environmental goals. This approach attracts investors aligned with the university’s mission and demonstrates a commitment to responsible stewardship.
Improving Financial Planning and Forecasting
Accurate financial projections and contingency planning are essential for managing funding uncertainties. Regularly assessing potential risks and developing contingency plans are key elements in proactively addressing potential funding gaps.
- Comprehensive Financial Modeling: Stanford should develop detailed financial models that incorporate various scenarios for funding fluctuations. These models should allow for adjustments in operating budgets and priorities as needed.
- Contingency Funding Reserves: Maintaining adequate contingency reserves will provide a financial cushion to address unexpected funding shortfalls or unforeseen expenses.
Developing Innovative Revenue Streams, Stanford university funding uncertainties
Exploring new revenue streams, such as licensing intellectual property, creating educational programs for the community, and developing new technologies, can supplement traditional funding sources. This approach can enhance the institution’s financial resilience and provide diversification in revenue streams.
- Intellectual Property Licensing: Stanford should have a robust system for identifying, protecting, and licensing intellectual property developed by its faculty and researchers. Successful licensing programs generate significant revenue and provide further financial security.
- Community Education Programs: Creating and offering educational programs for the broader community can generate revenue while expanding outreach and engagement.
- Startup Incubators: Providing support to faculty and students seeking to commercialize their research can create new ventures and provide revenue for the university.
Table of Strategies for Mitigating Funding Risks
| Strategy | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Diversifying Funding Sources | Expanding funding sources beyond traditional endowments to include corporate sponsorships, philanthropic giving, and government grants. | Increased financial resilience, reduced dependence on any single source. |
| Strengthening Endowment Management | Optimizing investment strategies to maximize returns and minimize risk, incorporating impact investing principles. | Long-term financial stability, enhanced returns on investment. |
| Improving Financial Planning and Forecasting | Developing comprehensive financial models to assess potential funding fluctuations and creating contingency plans. | Proactive management of financial risks, better resource allocation. |
| Developing Innovative Revenue Streams | Exploring new revenue streams such as licensing intellectual property, community education programs, and startup incubators. | Increased revenue diversification, enhanced financial sustainability. |
External Factors Influencing Funding
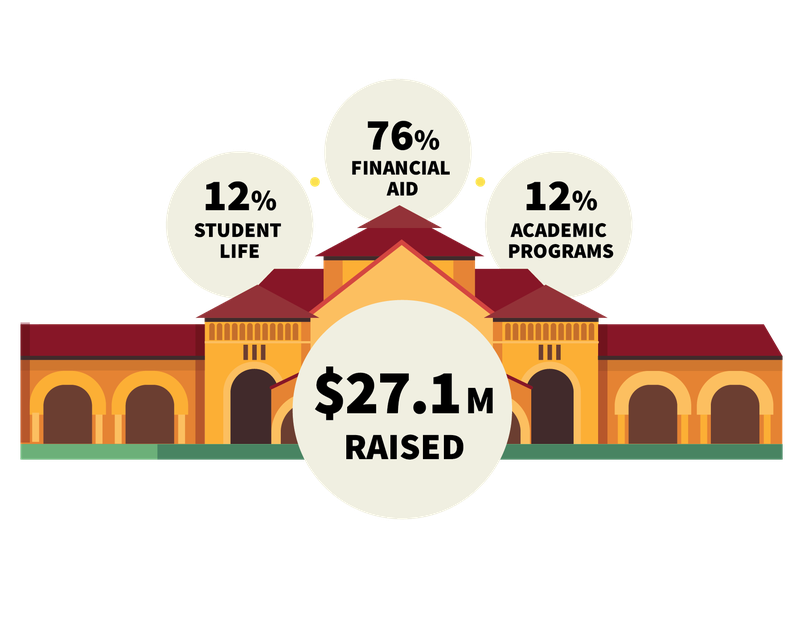
Stanford’s funding, like that of any major institution, is profoundly shaped by external forces. These factors, ranging from the national economic climate to philanthropic trends, exert significant influence on the university’s ability to secure and maintain its resources. Understanding these external pressures is crucial for proactive planning and adaptability.
National Economic Conditions
The state of the national economy plays a pivotal role in Stanford’s funding landscape. Economic downturns often lead to decreased philanthropic giving, as individuals and corporations prioritize immediate needs. Conversely, robust economic growth typically fosters increased investment in higher education, including donations and government grants. For example, the dot-com boom of the late 1990s saw a surge in tech-related donations to universities, particularly those with strong engineering programs.
Stanford’s facing some funding worries, and it’s a bit concerning. With news surfacing about potential closures of hundreds of federal offices this summer, as reported in this article , it raises questions about the broader economic climate and its impact on institutions like Stanford. The uncertainty surrounding federal funding streams could definitely complicate their future plans and research initiatives.
Recessions, on the other hand, frequently result in reduced funding from both private and public sources.
Political Climate
The political environment significantly influences funding allocations. Changes in government policies regarding research funding, educational priorities, and tax incentives can dramatically impact university budgets. For instance, shifts in research priorities can lead to funding cuts in specific areas, while new initiatives may open doors to increased grants and partnerships. Political instability or uncertainty can also create a climate of reduced investment, impacting donations from both individuals and organizations.
Philanthropic Trends
Philanthropic giving, a substantial source of funding for many universities, is subject to evolving trends. Changing societal values, emerging philanthropic priorities, and shifts in donor preferences can all influence the types of institutions and programs that receive funding. For instance, increased interest in STEM fields may lead to greater donations to programs in science and technology. Conversely, a growing emphasis on social justice issues might encourage donations to initiatives related to social equity and access.
Global Events and Trends
Major global events and trends can have a substantial impact on a university’s funding. Geopolitical instability, global pandemics, and technological advancements all create uncertainty and can influence funding priorities. For instance, a pandemic could lead to reduced funding for specific research areas and an increase in funding for public health initiatives. Similarly, rapid technological advancements can create opportunities for new funding sources and partnerships, while also requiring adaptation to maintain relevance.
Adaptability and Resilience
Stanford’s ability to adapt to these external factors hinges on its strategic planning, financial diversification, and proactive engagement with stakeholders. The university must be prepared to adjust its fundraising strategies, research priorities, and operational costs in response to changing circumstances. Maintaining a diverse funding portfolio, including government grants, corporate sponsorships, and individual donations, enhances resilience to fluctuations in any single source of funding.
Comparative Analysis of Funding Models
Stanford’s financial health hinges on a robust and adaptable funding strategy. Examining how other top universities secure resources can provide valuable insights for developing strategies that ensure Stanford’s continued excellence. A comparative analysis of different funding models, highlighting strengths and weaknesses, will illuminate potential avenues for adaptation and innovation.
Different Funding Models Employed by Top Universities
Top universities employ a diverse array of funding models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models is crucial for evaluating potential strategies for Stanford. These models range from traditional endowments and government grants to more innovative approaches such as philanthropic giving campaigns and industry partnerships.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Different Funding Models
- Endowment-Based Funding: Endowment funds, built on the principle of capital preservation and investment returns, are a cornerstone of many elite universities. They provide a relatively stable stream of revenue, particularly when managed effectively. However, reliance on endowment income alone can be vulnerable to market fluctuations and may not always adequately fund specific, urgent needs or strategic initiatives.
Harvard, for example, heavily relies on its endowment, which offers stability but also poses challenges in addressing immediate demands.
- Government Grants and Funding: Government funding, often earmarked for research or specific programs, can provide significant support, especially for national priorities. However, grant funding is often competitive and subject to policy changes. Funding often comes with specific stipulations and restrictions, potentially limiting flexibility and strategic direction. For instance, research grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are crucial for many institutions, but come with specific research guidelines that might not always align with a university’s broader research goals.
- Philanthropic Giving: Philanthropic donations, often driven by individual or corporate giving, can be a substantial source of funding, often tied to specific initiatives or areas of academic strength. This model fosters a strong connection between the university and the broader community. However, philanthropic support can be unpredictable and may not always reflect the university’s overall strategic priorities.
The University of California system, with its broad appeal to diverse donors, is a prime example.
- Industry Partnerships and Corporate Sponsorships: Industry partnerships and corporate sponsorships can provide funding for specific research projects or programs, especially in areas of high-tech development. These partnerships offer opportunities to address industry needs and advance research. However, such partnerships can be fraught with potential conflicts of interest, requiring careful oversight and management to ensure academic integrity. MIT, known for its collaborations with industry, has successfully used this model, but faces ethical considerations in navigating potential bias in research.
Identifying Successful Models for Stanford
Analyzing successful models employed by other top universities can yield valuable insights. Examining the relative proportions of each funding model, as well as their implementation strategies, will help Stanford develop a more resilient and adaptable funding strategy. For instance, institutions like MIT demonstrate success through industry partnerships, which can be beneficial for research and innovation, but require careful management.
Understanding the nuances of each model is critical for successful adaptation.
Comparative Table of Funding Models
| Funding Model | Strengths | Weaknesses | Potential for Stanford |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endowment-Based Funding | Stability, long-term support | Vulnerability to market fluctuations, may not address immediate needs | Maintain, but diversify |
| Government Grants and Funding | Support for national priorities, competitive funding | Competition, policy changes, restrictions | Strategically seek grants, maintain collaborations |
| Philanthropic Giving | Community engagement, targeted support | Unpredictability, may not align with all strategic priorities | Strengthen existing relationships, expand outreach |
| Industry Partnerships and Corporate Sponsorships | Research funding, address industry needs | Potential conflicts of interest, careful oversight required | Explore strategic partnerships, ensure ethical guidelines |
Last Recap
In conclusion, Stanford University’s funding uncertainties present a multifaceted challenge requiring careful consideration of various factors. The analysis reveals the complex interplay of internal and external pressures shaping the university’s financial future. Understanding these uncertainties allows for the development of proactive strategies to secure future funding and maintain Stanford’s academic excellence. By exploring diverse funding models and adapting to external factors, Stanford can navigate these challenges and continue to thrive.