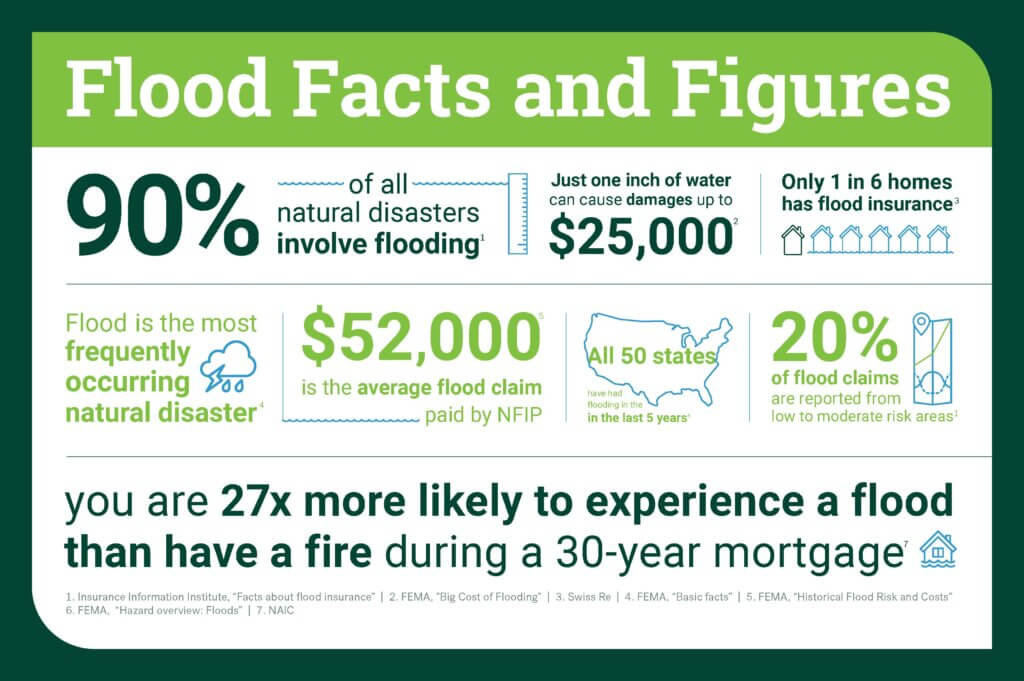
Do californians need flood insurance few homeowners it – Do Californians need flood insurance? Few homeowners consider it, but understanding California’s flood risks is crucial. This guide delves into the requirements, homeowner experiences, flood risks, insurance options, and the financial implications, ultimately empowering you to make informed decisions about protecting your property.
California’s diverse geography and history of flooding highlight the need for proactive measures. From coastal areas to valley floors, the risk varies significantly. This comprehensive overview will help you understand your specific vulnerability and whether flood insurance is a necessary part of your financial strategy.
California Flood Insurance Requirements

California’s unique geography, prone to both coastal flooding and inland valley inundation, necessitates careful consideration of flood insurance for homeowners. Understanding the requirements helps residents proactively protect their properties and financial interests. The state’s varied landscapes and flood risks result in different levels of mandated insurance coverage.California’s flood insurance regulations are designed to mitigate the financial impact of flooding.
These regulations vary depending on the property’s location and type, reflecting the diverse and complex flood risks across the state.
California Flood Insurance Mandates
California’s flood insurance mandates are governed by the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP). The NFIP provides federally backed flood insurance coverage to properties in designated flood zones. Homeowners and property owners within these designated zones are often required to obtain flood insurance.
Types of Properties Requiring Flood Insurance
Numerous property types in California can be subject to flood insurance requirements. The mandates extend to a broad range of properties, not just residential ones. These include single-family homes, mobile homes, multi-family dwellings, and commercial buildings. The specific requirements are dependent on the property’s location within a flood zone.
Criteria for Determining Flood Insurance Needs
The criteria used to determine if a property needs flood insurance in California are based on the property’s location and the flood risk associated with that area. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) designates flood zones, which are categorized based on the risk of flooding. Properties located within these zones might be required to have flood insurance.
Flood Insurance Requirements by Region
California’s diverse geography leads to varied flood insurance needs across different regions. Coastal areas, like Southern California, often face higher flood risks due to tsunamis and storm surges. Inland valley areas, such as the Central Valley, experience flood risks due to heavy rainfall and river overflows. The specific flood zones and insurance requirements vary between these regions.
Table of Factors Influencing Flood Insurance Needs
| Property Type | Location | Flood Zone | Insurance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-family home | Coastal area | High-risk zone | Required |
| Mobile home | Valley floor | Moderate-risk zone | Possibly required |
| Commercial building | Floodplain | High-risk zone | Required |
This table illustrates the general guidelines. However, the exact insurance requirement depends on the specific location and the designated flood zone. Local regulations and individual circumstances may also play a role in determining insurance necessity.
Homeowner Experiences and Perceptions
Navigating the complexities of flood insurance in California can be daunting for homeowners. This section delves into the common experiences, concerns, and perspectives surrounding this crucial aspect of property protection. Understanding these factors is essential for policymakers and insurance providers to tailor policies and resources to better serve the needs of California residents.Homeowners in California often face a range of emotions and perspectives on flood insurance, ranging from apprehension about the cost to uncertainty about the necessity.
While the question of whether Californians need flood insurance plagues many homeowners, it’s a topic that’s certainly relevant right now. With the recent news of as Alex Smith golfs Pebble Beach, Patrick Mahomes pursues a Super Bowl 3-peat , it’s easy to forget the everyday struggles facing residents, especially those in flood-prone areas. Ultimately, the need for flood insurance depends on individual circumstances and local risk assessments.
It’s a crucial conversation to have, especially with California’s unpredictable weather patterns.
This spectrum of opinions shapes the decisions homeowners make regarding coverage, highlighting the need for clear communication and readily accessible information.
Common Homeowner Experiences
Homeowners in flood-prone areas frequently report encountering significant challenges with flood insurance. These challenges often stem from a combination of high premiums, perceived unnecessary costs, and difficulties navigating the complexities of the insurance process.
- High Premiums: Homeowners frequently cite high premiums as a significant deterrent. For instance, a homeowner in a flood-prone area of the Central Valley might experience premium rates exceeding their budget, even for modest coverage. The perception of high costs often outweighs the potential financial protection flood insurance offers.
- Unnecessary Insurance: Some homeowners perceive flood insurance as unnecessary, especially those in areas with a low perceived risk of flooding. This misconception often stems from a lack of understanding of historical flood patterns and the potential for unexpected events. Without readily available data showcasing flood risk in their specific areas, homeowners may undervalue the protection offered.
- Complex Regulations: The intricacies of flood insurance regulations can be daunting for homeowners. Navigating the paperwork, understanding coverage limits, and applying for discounts can be a time-consuming process. This complexity contributes to a sense of frustration and confusion.
Perceived Financial Burden
The financial burden of flood insurance is a major concern for many California homeowners. The perceived cost often outweighs the potential benefits, leading to a reluctance to purchase coverage. Understanding this perception is crucial for promoting responsible financial planning and mitigating the potential for significant property damage.
- Costly Premiums: The high premiums associated with flood insurance frequently represent a significant financial burden, especially for homeowners with limited budgets. This often leads to a reluctance to purchase coverage, potentially jeopardizing the financial security of their homes. The perception of cost often overshadows the potential for significant savings should a flood event occur.
- Discount Options: While discounts exist, their awareness and accessibility remain a challenge for many homeowners. Limited knowledge regarding available discounts often contributes to a perceived lack of affordable options. Educating homeowners on the potential for discounts could help alleviate the financial strain.
Homeowner Perspectives on Flood Insurance Options
This table illustrates various homeowner perspectives regarding flood insurance, highlighting their concerns and potential solutions.
| Perspective | Concern | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Costly | High premiums | Explore available discounts, evaluate coverage options, and potentially explore alternative insurance programs. |
| Unnecessary | Low risk | Provide data on historical flood patterns, local flood risk assessments, and case studies illustrating the potential impact of floods. |
| Confusing | Complex regulations | Offer simplified guidelines, readily available resources, and accessible customer service channels. |
Factors Influencing Homeowner Decisions
Several factors influence homeowners’ decisions to obtain or decline flood insurance. These factors encompass financial considerations, perceived risk levels, and the accessibility of information.
- Financial Constraints: The affordability of flood insurance is a primary factor. Homeowners with limited budgets may prioritize other financial obligations, leading them to decline coverage.
- Perceived Risk: The perceived risk of flooding in a particular area significantly impacts a homeowner’s decision. Those in low-risk areas may underestimate the potential for flood damage, leading to a lack of insurance.
- Accessibility of Information: The availability and clarity of information regarding flood insurance significantly influence homeowners’ decisions. Homeowners facing complex or confusing information may be less likely to purchase coverage.
Flood Risk in California: Do Californians Need Flood Insurance Few Homeowners It
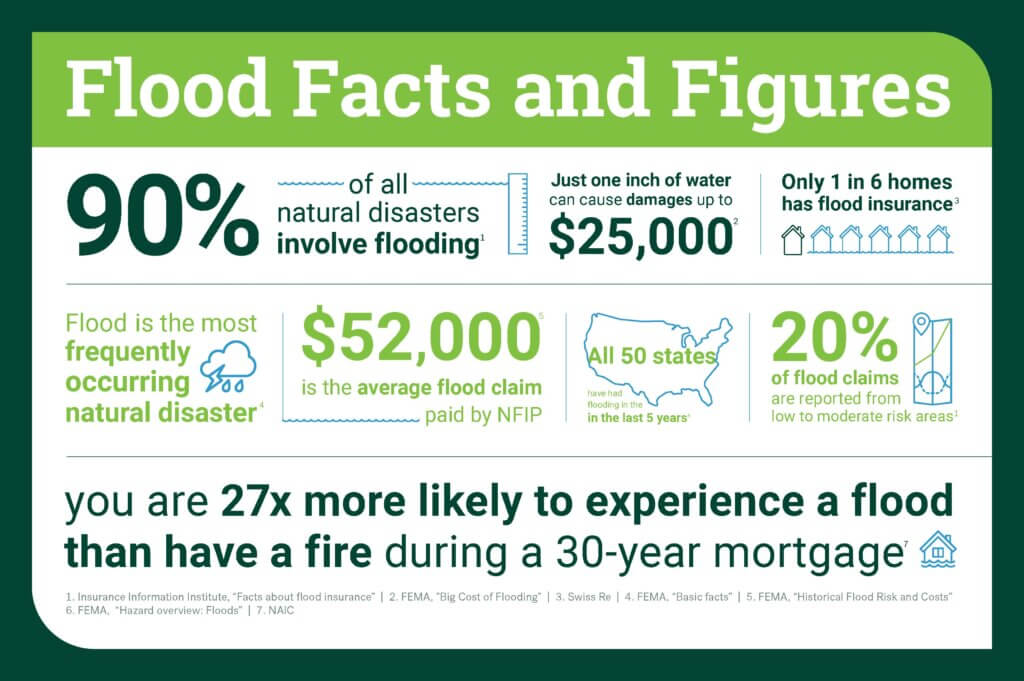
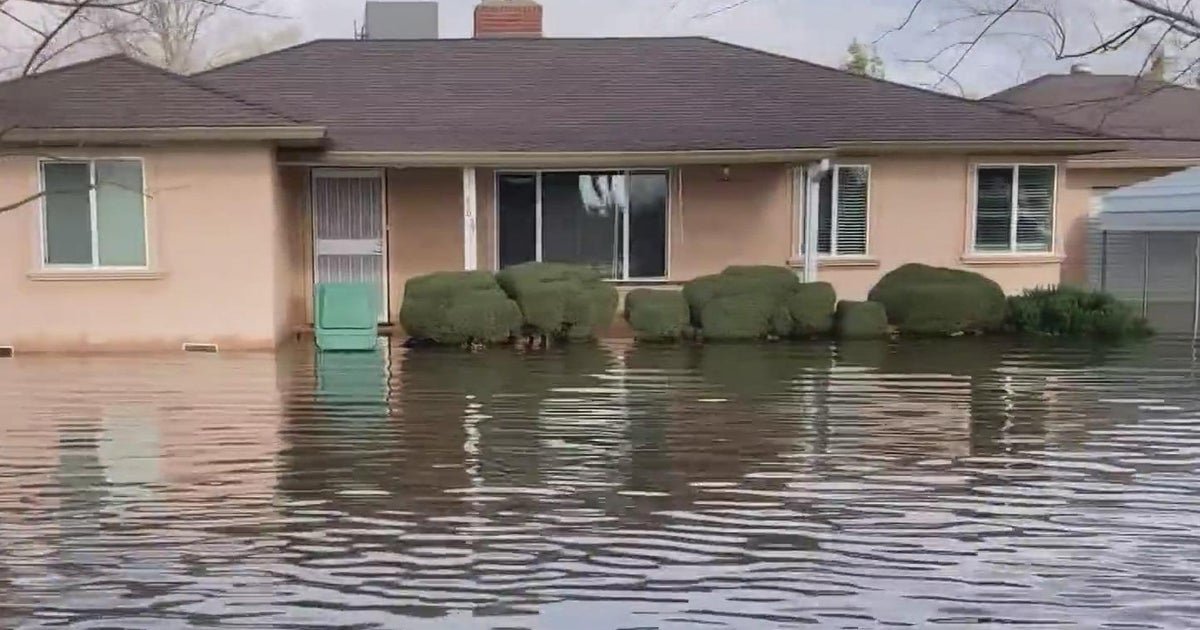
California’s stunning landscapes and vibrant cities are unfortunately vulnerable to the devastating effects of flooding. Understanding the specific flood risks across the state is crucial for proactive preparedness and effective mitigation strategies. This exploration dives into the geographical areas most prone to flooding, historical patterns, contributing factors, and the variations in risk across different regions.California’s diverse topography, from the Sierra Nevada mountains to the coastal plains, creates a complex interplay of factors that influence flood risk.
Rainfall patterns, snowmelt, and the presence of rivers and streams all contribute to the potential for flooding. Recent years have seen a significant increase in extreme weather events, further exacerbating the challenges faced by communities in flood-prone areas.
Geographical Areas Susceptible to Flooding
California’s susceptibility to flooding isn’t uniform. Coastal areas, particularly those with low-lying terrain, are at significant risk from storm surges and high tides. The Central Valley, a fertile agricultural region, is susceptible to flooding from overflowing rivers and streams. Mountainous regions face risks from flash floods, triggered by intense rainfall or rapid snowmelt. The Sacramento and San Joaquin River valleys are particularly vulnerable due to their flat terrain and the potential for large-scale flooding during heavy rainfall events.
Historical Patterns of Flooding
Historical records reveal a consistent pattern of flooding in California, with significant events occurring throughout the state’s history. Recent trends show a notable increase in the intensity and frequency of extreme rainfall events, leading to more frequent and severe flooding. The 2017-2018 winter storms caused widespread damage and disruption throughout the state, highlighting the need for enhanced preparedness and mitigation measures.
These events underscore the importance of understanding and adapting to the evolving flood risks in California.
Factors Contributing to Increased Flood Risk
Several factors contribute to the heightened flood risk in specific regions. Urbanization and development in floodplains reduce the natural capacity of the land to absorb water, increasing the risk of rapid flooding. Deforestation and land-use changes in mountainous areas can alter drainage patterns and increase the risk of flash floods. Climate change is a significant contributing factor, with altered rainfall patterns and more intense storms contributing to the growing threat of flooding.
The impacts of climate change are evident in the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, which can overwhelm existing infrastructure and increase the vulnerability of communities.
So, California flood insurance… it’s a tricky one. Many homeowners wonder if they really need it. While some areas might seem less prone to flooding, it’s worth considering the potential for devastating events. Plus, you know, sometimes you just need to consider the surprising things people do, like whether Michelle Obama likes to sleep alone or not.
Michelle Obama likes going to bed with or without husband. Ultimately, understanding your personal risk and the potential costs involved is key when deciding if flood insurance is a good idea for your home.
Comparison of Flood Risk Levels
Comparing flood risk levels across California reveals significant variations. Coastal regions, particularly those with low-lying areas and historical flooding, face high flood risk. The Central Valley, with its flat terrain and river systems, is susceptible to extensive flooding. Mountainous areas, especially those experiencing rapid snowmelt, are vulnerable to flash floods. This map representation, with shaded regions indicating varying flood risk levels, provides a visual overview of these differences.
Visual Representation of Flood-Prone Areas
Imagine a map of California, with varying shades of color representing flood risk. Deep purple/red would represent the highest risk areas, transitioning to light orange and yellow for areas with moderate to low risk. This visual representation highlights the significant variations in flood risk across the state. The color gradients illustrate the intensity of the risk, allowing for easy identification of areas requiring particular attention in terms of preparedness and mitigation efforts.
The shaded regions of the map clearly demarcate the most flood-prone areas, allowing for better understanding of the risk zones.
Insurance Options and Coverage
Navigating flood insurance can feel overwhelming, especially in a state like California, where the risk is ever-present. Understanding the various options available and the specific coverage details is crucial for homeowners to protect their properties and finances. This section delves into the different types of flood insurance, their coverage, potential limitations, and how to compare providers.California homeowners face a complex landscape of flood insurance options, ranging from standard policies to specialized coverage.
So, do Californians need flood insurance? Few homeowners seem to think so, given the recent deluge. However, the looming threat of a dockworkers’ strike, as detailed in this article about dockworkers threatening a strike over automation , highlights a different kind of potential disruption. Ultimately, the need for flood insurance in California likely hinges on individual risk assessment, not just the current headlines.
Choosing the right policy requires careful consideration of individual needs and risk factors. A thorough understanding of the different types of coverage, exclusions, and limitations is vital for making an informed decision.
Flood Insurance Policy Types
Flood insurance policies are designed to cover various potential losses arising from flooding. A crucial distinction is the difference between the standard flood insurance policy and supplemental coverage options.
- Standard Flood Insurance Policy: This policy provides coverage for direct physical damage to a structure caused by flooding. It usually covers repair or replacement costs, and it can also extend to the contents of the home.
- Supplemental Flood Insurance Options: Many homeowners opt for additional coverage beyond the standard policy, which may include coverage for business interruption or lost income, temporary housing, and valuable contents. Specific supplemental options may include provisions for certain types of valuable contents, like antique furniture or art collections.
Coverage Details
Flood insurance policies often provide coverage for a wide range of losses. These policies are designed to protect against financial ruin in the event of a flood.
- Structure Coverage: This component covers the building itself, including the foundation, walls, and roof. Replacement costs, not just repair costs, are frequently included.
- Contents Coverage: This section of the policy safeguards personal belongings within the structure, like furniture, appliances, and clothing. Policy limits and specific exclusions should be reviewed.
- Additional Coverages: Some policies might include coverage for temporary living expenses if a homeowner needs to relocate while their home is being repaired. This coverage can help manage additional costs during a crisis.
Exclusions and Limitations
It’s essential to understand what flood insurancedoesn’t* cover. Policy exclusions protect the insurance company from undue financial burdens.
- Exclusions: Flooding caused by factors
-other* than the typical water surge from a river or ocean are often excluded. This includes flooding from broken pipes or sewer backups, as well as from severe storms or extreme weather events not specifically categorized as flood events. Homeowners should consult their policies to understand these specific exclusions. - Limitations: Coverage amounts are limited, often by the policy’s deductible and the total amount payable in case of damage. There are usually limitations regarding the value of specific items or categories of belongings. It’s essential to verify the policy’s limits in relation to the assessed value of the home and its contents.
Comparing Flood Insurance Providers, Do californians need flood insurance few homeowners it
Different insurance providers offer varying terms, premiums, and coverage options. Careful comparison is key to securing the most suitable policy.
- Premium Comparison: Homeowners should compare premium costs from different providers, keeping in mind the level of coverage and deductibles. Several factors influence premium costs, including the flood risk in the specific location.
- Coverage Options: Policies can differ in the specific types of coverage offered. Providers may offer supplemental coverage or specialized policies for high-risk areas. Compare the coverage specifics before selecting a policy.
- Customer Service: Review customer feedback and ratings of different providers. Having access to reliable customer support during a claim process can be essential.
Resources for Homeowners
Finding reliable information is crucial for navigating flood insurance options. Several resources can assist homeowners in this process.
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): The FEMA website offers comprehensive information on flood insurance, including eligibility requirements, coverage options, and frequently asked questions.
- National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP): The NFIP is the primary source of flood insurance in the United States. Their website provides valuable information about the program, policy details, and contact information.
- Local Insurance Agents: Consulting local insurance agents can offer personalized advice and guidance tailored to individual needs and risk factors.
Financial Implications and Cost Considerations
California’s unpredictable weather patterns, including the threat of flooding, necessitate careful financial planning for homeowners. Understanding the costs and potential consequences of not having flood insurance is crucial for protecting your investment. This section delves into the financial realities of flood insurance in the Golden State.Flood insurance premiums in California can vary significantly based on several factors, influencing the overall cost for homeowners.
Understanding these variables and the potential long-term consequences of not securing adequate coverage is essential for responsible financial management. Furthermore, it’s crucial to grasp the claim processing procedures to understand how these policies function in practice.
Average Costs of Flood Insurance
Flood insurance premiums in California are not a one-size-fits-all figure. Factors like location, property type, and the amount of coverage requested significantly impact the price. While exact figures fluctuate, general estimations provide a helpful benchmark.
Factors Influencing Flood Insurance Premiums
Several key factors contribute to the variation in flood insurance premiums. These include:
- Location: Properties situated in high-risk flood zones, near rivers, or in areas prone to storm surges will have higher premiums. The proximity to historical flood events and the likelihood of future flooding is a significant factor in determining premiums.
- Flood Zone: Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) flood maps delineate high-risk areas, influencing premiums. Properties in designated flood zones will inevitably have higher premiums.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose directly affects your premium. Higher coverage amounts generally correlate with higher premiums.
- Property Type: The type of property—single-family home, condo, or mobile home—plays a role in premium calculation. Different types of construction and potential damages from flood events can affect the premium.
Potential Long-Term Financial Implications of Not Having Flood Insurance
Failure to secure flood insurance can lead to substantial financial burdens in the event of a flood. Homeowners lacking coverage may face significant out-of-pocket expenses for repairs and rebuilding, potentially exceeding their financial capabilities. Unforeseen expenses associated with damage restoration can lead to considerable financial stress and difficulties.
Examples of Flood Insurance Claims Processing
Flood insurance claim processing typically involves several steps. Firstly, document the damage thoroughly with photographs and videos. Contact your insurance provider immediately to report the damage and begin the claim process. Provide all necessary documentation, including the insurance policy details, and the property valuation. Insurance adjusters will inspect the damage and assess the necessary repairs.
Following the assessment, the insurance company will authorize payment for covered damages, which can take time. The exact procedure can vary based on the insurance provider and the specific circumstances of the claim.
Comparison of Flood Insurance Premiums Across Property Types
| Property Type | Estimated Premium | Factors Influencing Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Single-family home | $1,000 – $5,000 | Location, flood zone, coverage amount |
| Condo | $500 – $2,000 | Location, flood zone, coverage amount |
| Mobile home | $200 – $1,500 | Location, flood zone, coverage amount |
Closure
In conclusion, while the decision to purchase flood insurance is personal, understanding California’s flood risks and the potential financial implications is essential. This guide has explored the nuances of flood insurance needs, from property types and location to coverage options and costs. Armed with this knowledge, homeowners can make well-informed choices about protecting their assets.