Moss Landing battery fire renewable energy industry: This incident has sent shockwaves through the renewable energy sector, raising critical questions about battery safety and the future of clean energy storage. The fire, with its immediate and long-term implications, has sparked a crucial conversation about the potential risks and rewards of deploying large-scale battery systems for renewable energy projects.
The investigation into the causes and potential solutions is crucial to understanding the robustness of current battery technology in the renewable energy landscape.
The fire at the Moss Landing facility serves as a critical case study, prompting a deeper look into the complexities of battery technology in renewable energy systems. Factors like manufacturing processes, regulatory frameworks, and public perception will all be scrutinized as we examine the incident’s impact on the industry.
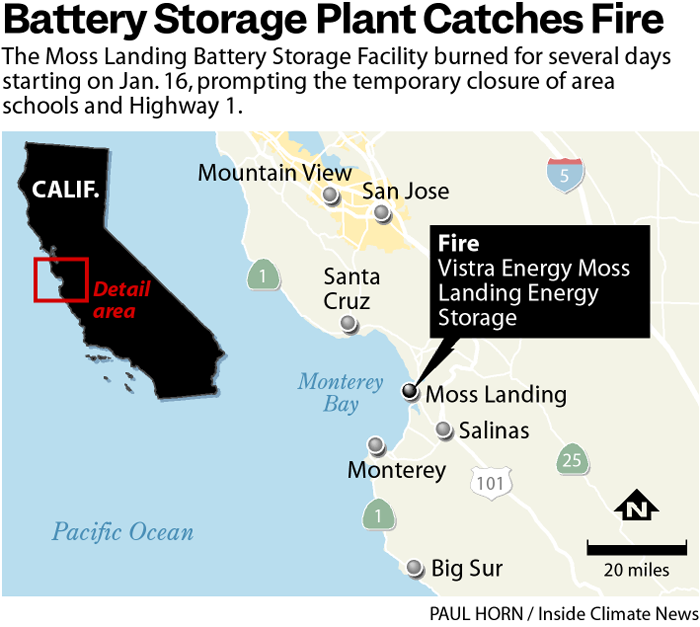
Introduction to the Moss Landing Battery Fire
The Moss Landing battery fire, a significant incident in the renewable energy sector, highlighted the critical need for robust safety protocols and advanced fire prevention measures in large-scale energy storage facilities. The fire, while localized, sent ripples through the industry, prompting scrutiny of battery technology and its deployment within the rapidly expanding renewable energy infrastructure. This event served as a stark reminder that even cutting-edge technologies can pose inherent risks, requiring careful consideration and proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Key Factors Contributing to the Fire
Several factors, while not fully understood in their entirety, likely contributed to the fire at Moss Landing. These factors included issues with the battery management system, potentially leading to overheating and thermal runaway within the battery packs. Manufacturing defects or inconsistencies in the battery cells themselves could also have played a role. Poorly designed or implemented fire suppression systems, while not necessarily the direct cause, might have hindered efforts to contain the fire.
Finally, the sheer scale of the battery storage facility could have complicated response and containment efforts, making it a crucial factor in the incident’s severity.
Immediate Impacts on the Renewable Energy Industry
The Moss Landing fire generated significant immediate concerns about the safety and reliability of large-scale battery storage systems. Investor confidence was likely impacted, and the insurance industry’s assessment of risks associated with these technologies was re-evaluated. Construction and deployment of new projects experienced temporary delays and scrutiny, as regulatory bodies and companies alike reassessed safety protocols and operational standards.
Furthermore, the incident sparked public discussion about the risks associated with lithium-ion batteries, prompting a closer look at the technology’s inherent safety mechanisms and their application in renewable energy projects.
Long-Term Impacts on the Renewable Energy Industry
The Moss Landing fire, while unfortunate, has had a long-term effect on the evolution of renewable energy infrastructure. There’s a heightened emphasis on battery safety standards and testing protocols. Improved battery management systems and advanced fire suppression technologies are now priorities for researchers and manufacturers. A shift toward more stringent regulatory frameworks to mitigate risks and promote the safe development of battery storage technologies is also evident.
These developments have prompted greater collaboration between industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, operators, and regulatory bodies. The Moss Landing incident has been instrumental in advancing battery safety best practices, laying the groundwork for more robust and reliable energy storage solutions.
Broader Context of Battery Fires in the Renewable Energy Sector
While the Moss Landing fire was a notable incident, it’s crucial to understand that battery fires are not exclusive to the renewable energy sector. Such events are also observed in electric vehicles (EVs) and other applications utilizing lithium-ion batteries. The context for battery fires extends beyond the specific incident, highlighting the need for a holistic approach to safety management in battery technology.
The fire’s significance lies in its occurrence within a sector rapidly expanding its use of battery storage, thus emphasizing the need for proactive measures to prevent and mitigate such incidents. A thorough understanding of the potential hazards and proactive measures to address them are crucial in preventing similar occurrences in the future.
Impact on Renewable Energy Technologies
The Moss Landing battery fire, while a localized incident, has reverberated through the renewable energy sector, raising crucial questions about the safety and future of battery storage solutions. This incident has sparked a renewed focus on safety protocols, material science advancements, and the overall public perception of battery technology. The implications extend beyond the immediate consequences, potentially influencing investment decisions and the pace of innovation in the field.The fire served as a stark reminder that even cutting-edge battery technologies can face unforeseen challenges.
Addressing public concern and maintaining public trust in these technologies is paramount for their continued adoption and development. The renewable energy industry needs to proactively address potential risks associated with battery storage systems, thereby bolstering public confidence and driving responsible innovation.
Effect on Public Perception of Battery Storage Solutions
The Moss Landing fire, unfortunately, likely contributed to a negative perception of battery storage solutions. The incident, given its prominence in media coverage, may lead to increased skepticism and concern regarding the safety of large-scale battery storage systems. This is especially true when combined with other, albeit less publicized, incidents. The public now faces a complex information landscape regarding battery safety, and this may lead to a cautious approach toward adopting battery-powered solutions.
Comparison with Other Battery Fire Incidents
Numerous battery fire incidents have occurred in various contexts, including electric vehicles, stationary energy storage, and portable devices. Each incident is unique, involving different battery chemistries, manufacturing processes, and operating conditions. Comparing these incidents can help identify common factors, such as thermal runaway mechanisms or design flaws, that may contribute to the risk of fires. For example, comparing the Moss Landing incident to lithium-ion battery fires in electric vehicles reveals potential differences in safety protocols and regulatory oversight.
Potential Safety Concerns Associated with Battery Technology
Several safety concerns are associated with battery technology, particularly lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in renewable energy projects. These concerns include thermal runaway, where a single cell failure can trigger a chain reaction, leading to a fire. Other issues include the risk of electrolyte leakage, the potential for explosions, and the variability in battery quality across different manufacturers. A deeper understanding of these risks and proactive measures are critical for mitigating these hazards.
Potential Consequences for the Future Development of Battery Storage
The Moss Landing fire could potentially slow the development of battery storage technology. The incident may cause investors to pause or reduce investment in large-scale battery storage projects. This could lead to a delay in deploying renewable energy resources that rely on battery storage for energy management and grid stability. To counteract this, rigorous safety standards, advanced materials research, and transparent communication about safety protocols are critical for maintaining public trust and driving innovation.
Table of Battery Technologies and Safety Records
| Battery Technology | Safety Record | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | Mixed. Numerous incidents reported, but also widely used and improved safety features implemented. | Electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, portable electronics |
| Sodium-ion | Emerging technology with fewer reported incidents than lithium-ion. | Potential for large-scale energy storage applications |
| Flow batteries | Generally considered safe, with less propensity for thermal runaway. | Large-scale energy storage, grid stabilization |
Safety and Regulatory Implications
The Moss Landing battery fire highlighted critical vulnerabilities in the safety protocols surrounding renewable energy storage. This incident underscored the urgent need for enhanced safety standards and regulatory frameworks to prevent similar catastrophes. The fire served as a stark reminder that the rapid growth of battery-based renewable energy storage necessitates a proactive and comprehensive approach to risk mitigation.
The Moss Landing battery fire highlights the complex challenges within the renewable energy industry, especially when dealing with large-scale storage. While the focus is on safety and environmental impact, consider the broader implications, like the recent Supreme Court ruling on Planned Parenthood and Medicaid funding, supreme court planned parenthood medicaid. These rulings can drastically alter the landscape of healthcare access, impacting community well-being, just as the battery fire has affected the future of renewable energy projects.
Regulatory Changes and Revisions
The Moss Landing fire is likely to trigger significant regulatory changes and revisions in battery safety standards. Expect stricter regulations regarding battery manufacturing processes, including material sourcing, quality control, and testing procedures. More stringent fire prevention measures for battery storage facilities will also likely be implemented. These changes are expected to encompass a wider range of stakeholders, from battery manufacturers to energy storage facility operators and regulatory bodies.
The recent Moss Landing battery fire highlights the complexities of the burgeoning renewable energy industry. Safety concerns are paramount, and meticulous attention to detail in battery design and infrastructure is crucial. Fortunately, there are also exciting advancements in battery technology. To effectively visualize these, you might want to learn how to add fonts to Photoshop for clearer, more impactful presentations of data related to this sector.
Mastering tools like add fonts to photoshop can greatly enhance your communication on these vital issues, from showcasing the benefits of renewable energy to addressing potential risks. The Moss Landing incident, therefore, serves as a reminder of the ongoing need for careful evaluation and proactive safety measures in this fast-developing industry.
Safety Protocols and Standards Before and After the Incident
| Aspect | Before Moss Landing Incident | After Moss Landing Incident |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Testing | Varied and often insufficient testing protocols, particularly for large-scale battery systems. | Stricter and more comprehensive battery testing standards, including accelerated aging and thermal runaway simulations. Increased emphasis on real-world performance validation. |
| Storage Facility Design | Design often focused on functionality, with less emphasis on fire safety features. | Enhanced fire-resistant building materials, robust fire suppression systems, and increased spacing between battery units to limit the spread of fire. |
| Emergency Response Protocols | Varying levels of preparedness, with gaps in communication and coordination. | Mandatory emergency response plans and training for facility staff, with clear communication protocols for different levels of emergency. Emphasis on quick response and evacuation procedures. |
| Industry Standards | Lack of unified industry standards, leading to inconsistencies in safety practices. | Increased focus on developing and enforcing standardized safety protocols across the renewable energy storage industry. Potential for a nationally recognized safety certification for battery storage facilities. |
Influence of the Moss Landing Fire on Industry Standards
The Moss Landing fire has already sparked a profound influence on industry standards for battery safety. It has accelerated the development and implementation of more rigorous safety protocols. The incident has forced manufacturers to re-evaluate their designs and manufacturing processes, leading to the adoption of more robust materials and construction techniques. This incident will likely spur the creation of new safety guidelines for battery storage, with a strong emphasis on fire resistance, thermal management, and emergency response planning.
Steps Taken to Prevent Future Incidents
Several steps are being taken to prevent future battery fire incidents, including:
- Enhanced battery testing and certification procedures: Testing procedures will be more comprehensive, including thermal runaway simulations, to identify and mitigate potential fire risks in batteries before deployment.
- Improved storage facility design: Facilities will incorporate fire-resistant materials, robust fire suppression systems, and enhanced spacing to limit the spread of fire.
- Comprehensive emergency response planning: All storage facilities will be required to have well-defined emergency response plans and trained personnel to handle incidents effectively.
- Collaboration between stakeholders: Manufacturers, regulators, utilities, and researchers will collaborate to establish a unified set of safety standards.
Roles of Different Stakeholders in Battery Safety
| Stakeholder | Role in Battery Safety |
|---|---|
| Manufacturers | Responsible for designing, manufacturing, and testing batteries that meet safety standards. Implementing rigorous quality control measures. |
| Regulators | Developing and enforcing safety standards, conducting inspections, and ensuring compliance. Responding to incidents. |
| Utilities | Implementing safety protocols at their facilities, ensuring compliance with regulations, and investing in safe storage solutions. |
| Researchers | Conducting research on battery safety, identifying potential risks, and developing innovative solutions to mitigate hazards. |
| Consumers | Understanding and complying with safety guidelines. Reporting any issues related to battery safety. |
Innovation and Development: Moss Landing Battery Fire Renewable Energy Industry
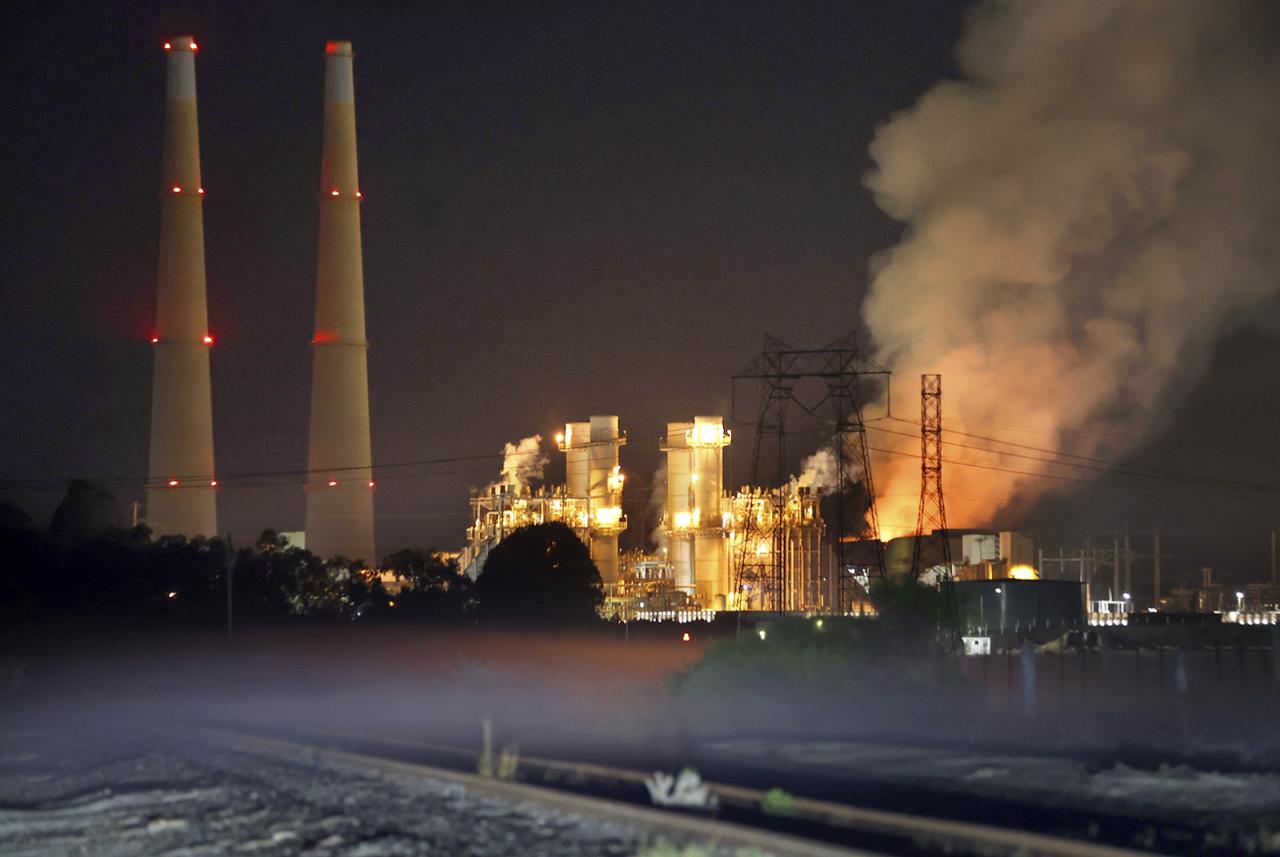

The Moss Landing battery fire highlighted critical safety concerns in the burgeoning renewable energy sector, particularly regarding battery technology. Addressing these concerns requires a multi-faceted approach, including innovative battery designs, robust safety measures, and exploration of alternative energy storage solutions. This section delves into potential innovations and advancements in the field.The incident underscored the need for a paradigm shift in battery design, moving beyond simply increasing capacity and focusing on inherent safety.
This includes exploring new materials, architectures, and thermal management systems to mitigate the risk of catastrophic failures. A proactive research and development focus is essential to ensure the safe and reliable integration of battery storage into renewable energy infrastructure.
Potential Innovations in Battery Technology
Several innovative approaches are being investigated to enhance battery safety and performance. These include the development of new battery chemistries with improved thermal stability and reduced flammability. Researchers are also exploring novel battery designs, such as those with inherent fire suppression mechanisms, and advancements in thermal management systems.
Safety Measures in Battery Design
Safety features are increasingly incorporated into battery design to prevent thermal runaway and mitigate the risk of fire. This includes incorporating advanced thermal sensors and sophisticated thermal management systems, such as liquid cooling or phase-change materials. These systems actively monitor and regulate battery temperature, quickly responding to overheating conditions.
Summary of Innovative Battery Designs, Moss landing battery fire renewable energy industry
| Design Feature | Description | Safety Enhancement |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Batteries | Replace liquid electrolytes with solid-state electrolytes, enhancing safety by eliminating flammable components. | Reduced risk of thermal runaway, minimized fire hazard. |
| Improved Thermal Management Systems | Advanced cooling mechanisms, such as liquid cooling and phase-change materials, efficiently dissipate heat generated during operation. | Enhanced thermal stability, preventing overheating. |
| Self-Extinguishing Materials | Incorporating materials that inherently suppress fires. | Immediate fire suppression, limiting damage. |
| Advanced Battery Monitoring Systems | Real-time monitoring and diagnostics to identify and address potential safety issues before they escalate. | Early detection of anomalies, preventing catastrophic failures. |
Research and Development in Mitigating Risks
Extensive research and development efforts are crucial to identifying and addressing potential risks associated with battery fires. This involves rigorous testing protocols, including simulations and real-world experiments, to evaluate the performance and safety characteristics of new battery technologies. Collaboration between academic institutions, research organizations, and battery manufacturers is vital to accelerate innovation.
“The goal is not just to build safer batteries, but to integrate safety as an inherent design principle from the outset.”
Alternative Energy Storage Technologies
While battery technology continues to evolve, alternative energy storage solutions are being explored to reduce reliance on batteries, potentially mitigating risks associated with battery fires. This includes technologies like pumped hydro storage, compressed air energy storage, and flywheels. These technologies offer diverse solutions for energy storage, often with distinct advantages in terms of safety and environmental impact. For instance, pumped hydro storage is a well-established technology with a proven track record of safety.
These alternative technologies are valuable in diverse contexts, from large-scale grid applications to smaller, localized storage systems.
Public Perception and Industry Response
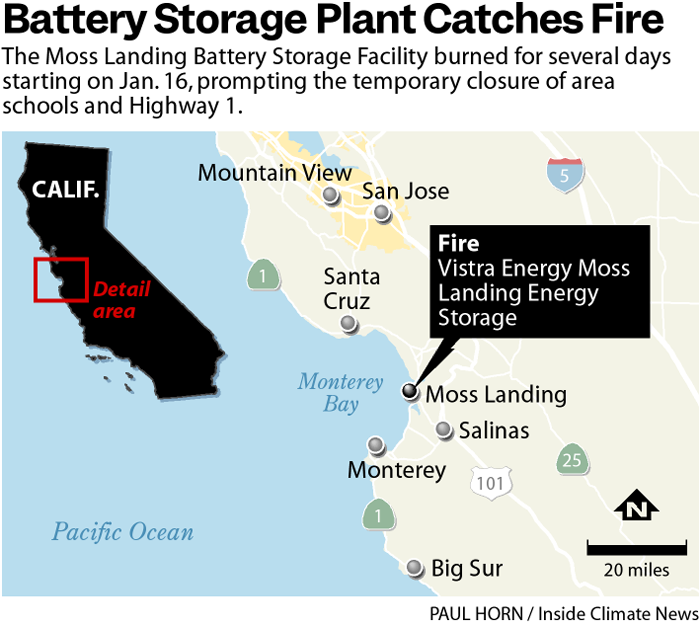
The Moss Landing battery fire ignited a complex web of public perception and industry response, casting a significant shadow over the burgeoning renewable energy sector. Investor confidence, crucial for continued growth, was undoubtedly affected by this incident. The industry needed to swiftly and effectively address public concerns to rebuild trust and maintain momentum. The challenge was not just technical but also deeply rooted in public understanding and perception of safety.
Public Response and Investor Confidence
The public response to the Moss Landing battery fire was characterized by a mixture of concern and skepticism. Initial news reports and social media discussions often focused on safety and potential environmental risks associated with large-scale energy storage solutions. This generated a degree of uncertainty, impacting investor confidence and potentially slowing down future investments in renewable energy projects.
The perception of risk became a significant factor in decision-making for potential investors.
Industry Efforts to Address Public Concerns
Renewable energy companies responded to the Moss Landing incident by implementing several measures to address public concerns. Transparency became a crucial aspect of these responses. Open communication regarding the cause of the fire, safety protocols, and long-term mitigation strategies were essential to reassure the public. Many companies actively participated in industry forums and conferences, emphasizing the importance of safety and proactive risk management in battery storage technology.
Furthermore, they emphasized the rigorous safety standards incorporated into their projects and the commitment to ongoing research and development.
The Moss Landing battery fire highlights the challenges within the renewable energy industry, particularly in battery storage. While accidents like this raise concerns about safety protocols, the industry is still crucial for a sustainable future. Interestingly, recent hockey news involving the San Jose Sharks and Dallas Stars, particularly regarding Klim Kostin and Mikael Granlund, san jose sharks dallas stars klim kostin mikael granlund , seems unrelated but speaks to the broader push for innovation in various sectors.
Regardless, the need for robust safety measures in battery storage remains paramount in the renewable energy space.
Comparison to Past Incidents
Analyzing the industry’s responses to similar incidents in the past reveals valuable insights. Lessons learned from past accidents involving lithium-ion batteries, though not always directly related to renewable energy, highlighted the importance of robust safety protocols and thorough risk assessments. The industry’s reaction to the Moss Landing fire showcased a commitment to learn from past mistakes and improve safety measures, which is critical for long-term success.
Role of Transparency and Communication
Transparency and effective communication are fundamental to managing public perception in crises. Openly acknowledging the challenges and outlining plans for improvement demonstrate a commitment to safety and build public trust. Clear communication channels and accessible information resources can help dissipate misinformation and foster understanding. Companies that effectively communicate their safety measures and commitment to responsible development are better positioned to regain public trust.
Industry Initiatives to Improve Public Trust
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Independent Safety Audits | Companies are conducting thorough, independent audits of their facilities and procedures to identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities. |
| Enhanced Safety Standards | Implementing and enforcing stricter safety standards and protocols in battery storage operations is a crucial step towards building trust. |
| Public Engagement Forums | Actively participating in public forums and discussions to address concerns and build trust directly with communities. |
| Investment in Research and Development | Investing in research and development focused on improving battery safety and long-term sustainability is critical to ensure the future of the industry. |
| Improved Communication Protocols | Establishing clear communication channels and procedures for reporting incidents and responding to public concerns. |
These examples demonstrate a multifaceted approach by the industry to rebuild public trust. The commitment to transparent and proactive measures is crucial for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the long-term viability of renewable energy technologies.
Future of Battery Storage in Renewable Energy
The Moss Landing battery fire serves as a stark reminder of the critical need for robust safety protocols and continuous innovation in battery technology, especially within the rapidly expanding renewable energy sector. While the incident has undoubtedly raised concerns, it hasn’t dampened the immense potential of battery storage for ensuring a reliable and sustainable energy future. The future of battery storage hinges on addressing safety issues while simultaneously pushing the boundaries of performance and cost-effectiveness.The renewable energy sector is fundamentally reliant on battery storage to smooth out the intermittency of solar and wind power.
Without effective energy storage solutions, the full potential of these clean energy sources remains unrealized. The need for dependable and efficient storage systems is driving intense research and development efforts across the globe.
Potential Future Directions of Battery Storage Technology
The pursuit of safer, more efficient, and cost-effective battery technologies is accelerating. Research into solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density, improved safety, and potentially lower costs, is a key area of focus. Lithium-sulfur batteries are another promising avenue, exhibiting higher theoretical energy storage capacity compared to lithium-ion. Further advancements in existing lithium-ion battery chemistries, including improvements in electrode materials and electrolyte formulations, are also actively pursued.
Long-Term Impact of the Moss Landing Fire
The Moss Landing incident is likely to spur increased scrutiny and stringent safety regulations for battery storage facilities. This will include more rigorous testing procedures, enhanced fire suppression systems, and potentially more stringent siting requirements for battery storage projects. The need for independent safety audits and third-party certifications could become commonplace. Such measures, while potentially slowing down the initial rollout of new projects, are crucial for building public trust and preventing future incidents.
Potential Shifts in Investment Strategies
Investment strategies for renewable energy projects are likely to incorporate risk assessments that explicitly consider battery storage safety. Investors will likely prioritize projects with robust safety measures and established regulatory compliance. This could lead to a preference for smaller, modular battery storage systems, which are often easier to manage and contain potential risks. Insurance premiums for battery storage facilities are also likely to increase, reflecting the higher perceived risk.
Summary of Potential Challenges and Opportunities
The future of battery storage presents both challenges and opportunities. Ensuring safety and reliability is paramount, while simultaneously pushing for technological advancements to enhance performance and reduce costs. The industry needs to find a balance between safety-driven caution and the need to expand renewable energy capacity. The industry can leverage the momentum from the incident to improve safety standards, leading to greater public confidence and broader investment in renewable energy.
Potential Future Research Areas
| Research Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Advanced Battery Materials | Developing new materials for electrodes and electrolytes with enhanced safety characteristics, higher energy density, and improved thermal stability. This includes exploring alternative chemistries beyond lithium-ion. |
| Thermal Management Systems | Designing and implementing more effective thermal management systems for battery packs to prevent overheating and mitigate fire risks. Active cooling solutions and advanced thermal modeling are crucial. |
| Safety and Risk Assessment Models | Developing predictive models for assessing fire risks and potential hazards associated with battery storage systems. This includes advanced simulations of thermal runaway and fire propagation. |
| Integrated System Design | Optimizing the design of entire energy storage systems, including the integration of batteries with renewable energy sources and grid infrastructure. This involves advanced control systems to mitigate risks and enhance reliability. |
Illustrative Case Studies
The Moss Landing battery fire, while tragic, also serves as a critical juncture for the renewable energy industry. Learning from both successful and unsuccessful approaches to battery safety is paramount for future development and implementation of this crucial technology. Thorough case studies provide invaluable insights into protocols, procedures, and potential pitfalls.Understanding how different companies and organizations have approached battery safety is essential for building a robust and reliable renewable energy infrastructure.
This section delves into successful and less successful strategies, examining the Moss Landing investigation, and presenting expert opinions to offer a comprehensive view of the landscape.
Successful Battery Safety Protocol Case Study
Tesla’s battery management system (BMS) in their electric vehicles exemplifies a successful battery safety protocol. Tesla’s BMS incorporates sophisticated thermal management, rapid fault detection, and automatic shut-down mechanisms. These features mitigate thermal runaway by quickly identifying and addressing potential overheating issues. The system actively monitors individual cells within the battery pack, reacting to anomalies before they escalate into a full-scale fire.
This proactive approach, combined with robust physical containment measures, has contributed to a relatively low incidence of battery fires in Tesla vehicles compared to other electric vehicles.
Less Successful Battery Safety Approach Case Study
The case of the early iterations of certain electric vehicle battery packs highlights a less successful approach. In some instances, the initial designs lacked adequate thermal management, leading to higher risks of thermal runaway. A less sophisticated BMS, coupled with potentially inadequate containment measures, resulted in increased fire risks. The lesson learned here emphasizes the importance of thorough testing, robust thermal management systems, and continuous improvement in battery safety protocols.
Moss Landing Fire Investigation Procedures
The investigation into the Moss Landing battery fire involved a multi-faceted approach. Initial responders documented the extent of the fire and the damage to surrounding areas. Subsequent investigations focused on the specific components of the battery pack, scrutinizing the materials, construction, and potential causes of the fire. Experts analyzed the battery’s thermal performance under various conditions, attempting to pinpoint the trigger for the thermal runaway.
The investigation likely involved meticulous documentation, laboratory testing, and possibly even forensic analysis to determine the precise cause and potential systemic failures. The thoroughness of the investigation will influence future safety regulations and standards.
Expert Opinion on Battery Safety
“Proactive safety measures, rigorous testing protocols, and continuous improvement are critical in preventing battery fires. The renewable energy sector must embrace a culture of safety, recognizing that battery technology is still evolving and that continuous learning and adaptation are essential.”
Illustration of Battery Cell Internal Components
Imagine a battery cell as a small, cylindrical container. Inside, numerous alternating layers of positive and negative electrode materials are sandwiched between separators. These electrodes are often made of lithium compounds, which, when combined with electrolytes, facilitate the flow of electrons. The electrolyte, typically a liquid or gel, enables the chemical reactions that produce electricity. If these layers experience excessive heat or a short circuit, the chemical reactions can accelerate, releasing heat and potentially igniting the materials.
This rapid increase in temperature and the chain reaction can lead to thermal runaway and a fire. The illustration would visually represent these layers, highlighting the potential points of failure and emphasizing the need for robust containment and thermal management systems.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the Moss Landing battery fire has illuminated critical safety concerns within the renewable energy industry’s reliance on battery storage. The incident highlights the need for enhanced safety protocols, robust regulatory oversight, and continued innovation in battery technology. The industry’s response, both in terms of immediate actions and long-term strategies, will shape the future of renewable energy and battery storage.
While the fire represents a setback, it also presents an opportunity for improvement, ensuring the responsible and safe development of this vital clean energy sector.