California will soon require insurers to increase home coverage in wildfire prone areas – California will soon require insurers to increase home coverage in wildfire-prone areas, a move that’s expected to significantly impact homeowners, insurance companies, and the housing market. This policy aims to better protect residents and infrastructure in the face of increasingly frequent and intense wildfires, but it will inevitably lead to higher premiums and potential affordability challenges for those living in high-risk zones.
This article delves into the background of California wildfires, analyzing the existing insurance landscape, and exploring the implications of this new policy on various stakeholders. We’ll look at the potential effects on premiums, the housing market, and the insurance industry itself. Furthermore, we’ll examine the rationale behind the increased coverage requirements, comparing them to policies in other disaster-prone areas.
Background on California Wildfires: California Will Soon Require Insurers To Increase Home Coverage In Wildfire Prone Areas
California’s landscape has long been intertwined with the dramatic spectacle and devastating consequences of wildfires. The state’s unique geography, coupled with increasingly volatile climate conditions, has contributed to a pattern of ever-increasing fire risk. Understanding this history is crucial for comprehending the urgency of the situation and the need for proactive measures.The frequency and intensity of wildfires in California have escalated significantly over the past few decades.
This rise is directly linked to factors such as prolonged drought, higher temperatures, and altered weather patterns, all of which are influenced by climate change. The devastating impacts of these fires extend far beyond the immediate loss of life and property; they have profound economic, social, and environmental consequences.
California’s new rules requiring higher home insurance in fire-prone areas are a hot topic, but it makes you wonder about the bigger picture. Are these costs going to disproportionately impact lower-income homeowners? It’s a complex issue, and some argue that the financial burden ultimately falls on the most vulnerable. This raises questions about the fairness of these policies and if the costs should be spread more equitably, considering how tax cuts, like those from the Trump administration, may have shifted wealth in ways that could be problematic.
For example, take a look at this interesting piece exploring whether Republicans are ultimately asking the poor to foot the bill for past tax cuts: opinion republicans want the poor to pay for trumps tax cuts. Ultimately, the burden of these increased insurance costs needs to be carefully considered to ensure a fair and equitable outcome for everyone, particularly those in high-risk areas.
Historical Overview of California Wildfires
California’s fire history is marked by cycles of intense and destructive blazes. While wildfires have always been a part of the state’s ecosystem, the recent surge in frequency and intensity is unprecedented. Data indicates a clear upward trend in the number of large wildfires, spanning multiple counties, over the past several decades. This increased frequency and intensity has had profound and lasting impacts on communities and the environment.
California’s new rules requiring insurers to boost home coverage in fire-prone zones is a big deal, right? It’s all about safety, of course, but it’s also going to impact homeowners’ pockets. Speaking of big deals, did you hear about the Riordan Roosevelt boys state basketball championship saturday? Riordan Roosevelt boys state basketball championship saturday is a huge event, and while exciting, it doesn’t change the fact that these increased insurance premiums are going to be a factor for many Californians.
Ultimately, it’s all about protecting property and people in the face of natural disasters.
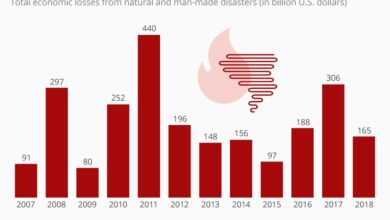
Economic Costs of Wildfire Damage
The economic toll of California wildfires is substantial and multifaceted. The damage extends beyond the direct costs of property destruction and rebuilding. Businesses are disrupted, infrastructure is damaged, and the healthcare system is strained to manage the effects of the smoke and injuries. The long-term economic consequences of wildfires can include decreased tourism, reduced property values, and a hindered labor force.
Reliable sources show that the costs of wildfire suppression and recovery are increasing year on year, reflecting the escalating nature of the problem.
Role of Climate Change in Increasing Wildfire Risk
Climate change plays a critical role in the increasing wildfire risk across California. Prolonged periods of drought, combined with rising temperatures, create the perfect conditions for fires to ignite and spread rapidly. Warmer temperatures increase the rate of evaporation, drying out vegetation and making it more susceptible to ignition. These altered weather patterns contribute to the intensity and duration of wildfires, resulting in more extensive damage.
Existing Insurance Landscape for Homes in Wildfire-Prone Areas
California’s insurance market for homes in wildfire-prone areas presents a complex landscape. Insurance companies assess risk factors, including the proximity to known fire hazards, vegetation types, and fire-resistant construction materials. Premiums for homes located in high-risk zones are often significantly higher than for those in safer areas. The availability of insurance can also be limited in areas with a history of frequent and severe wildfires.
Comparison of Insurance Policies for Different Regions in California
| Region | Average Insurance Premium (USD) | Coverage Limits (USD) | Coverage Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern California (High-Risk) | $1,500 – $3,000 | $500,000 – $1,000,000 | Dwelling, Personal Property, Liability |
| Central California (Moderate-Risk) | $800 – $1,500 | $400,000 – $800,000 | Dwelling, Personal Property, Liability |
| Southern California (High-Risk) | $1,200 – $2,500 | $500,000 – $1,200,000 | Dwelling, Personal Property, Liability |
Note: These are estimated figures and can vary based on individual factors such as the home’s construction, location within a region, and specific insurance policies. Insurers typically adjust rates based on assessed risk factors, and coverage limits and types may differ.
Implications of Increased Coverage Requirements
California’s new mandate for increased wildfire insurance coverage in high-risk areas promises a significant shift in the state’s insurance landscape. This shift will undoubtedly impact homeowners, insurance providers, and the housing market itself. The increased costs and potential market adjustments will reshape the way Californians interact with their homes and the insurance industry.Increased coverage requirements are expected to have a direct and substantial effect on insurance premiums.
Homeowners in high-risk areas will likely face higher premiums due to the need for greater financial protection against wildfire damage. This increase could be substantial, potentially leading to a significant burden on those already struggling with high housing costs.
Impact on Home Insurance Premiums
The increased coverage requirements will inevitably translate to higher premiums for homeowners in wildfire-prone zones. Insurers will need to adjust their pricing models to reflect the higher potential payout amounts. This is a direct consequence of the increased liability they face, and the added cost of handling potential damage claims. Insurance companies have to balance their profitability with the need to provide adequate coverage, which means that higher premiums are a probable outcome.
Affordability of Home Insurance in High-Risk Areas
The affordability of home insurance in high-risk areas will likely decrease as a result of the new regulations. Homeowners in vulnerable communities may find it more difficult to secure coverage at a price they can afford. This could lead to a decrease in the number of insurers willing to operate in these areas, creating a further barrier for homeowners.
In some cases, it may even force some homeowners to sell their properties due to unaffordable insurance premiums.
Effect on the Housing Market
The new regulations may have a significant impact on the housing market, especially in vulnerable communities. Higher insurance premiums could discourage potential buyers from purchasing homes in these areas. This could lead to a decrease in property values and a potential decline in the housing market in high-risk zones. Real estate developers may also be deterred from building in these regions due to the high insurance costs.
Changes in Construction and Building Practices
The increased coverage requirements may spur changes in construction and building practices for homes in wildfire-prone zones. Homeowners and builders may adopt more fire-resistant materials and construction techniques. This could lead to higher initial construction costs, but in the long run, it could help to reduce the risk of wildfire damage and lower insurance premiums. Regulations and incentives may also play a role in encouraging the use of fire-resistant materials.
Potential Price Adjustments for Homeowners
| Risk Category | Estimated Premium Increase (%) |
|---|---|
| Low Risk | 5-10% |
| Moderate Risk | 10-20% |
| High Risk | 20-30% or more |
Note: These are estimates and actual premium increases may vary based on individual property characteristics and insurer policies.
California’s new rules for wildfire insurance are definitely a game-changer. Insurers will soon have to up the ante on home coverage in high-risk areas. This necessitates a robust project management office, to effectively manage the complexities of the insurance changes, and ensure the smooth implementation of the new coverage standards. The need for a well-organized project management office ( creating project management office ) is crucial for handling the significant influx of claims and policy adjustments.
Ultimately, this will impact how homeowners are protected and insurers operate in the long run. The new California insurance regulations will be challenging, but essential for mitigating future wildfire damage.
The table above provides a general illustration of potential premium adjustments for homeowners in different risk categories. The actual figures will depend on numerous factors, including the specific construction of the home, its location within the risk zone, and the insurance company’s underwriting criteria.
Potential Impacts on Insurance Companies
California’s new wildfire coverage mandates will significantly reshape the insurance landscape, especially for companies operating in high-risk areas. These changes will force insurers to reassess their risk profiles, pricing models, and potential strategies for navigating the evolving wildfire threat. The implications for profitability and market positioning are substantial.Insurers face a complex challenge in adjusting to the increased coverage requirements.
They must weigh the financial implications of higher payouts, the potential for increased claims frequency, and the possibility of market shifts. The new regulations will demand a comprehensive review of their existing policies, actuarial models, and operational procedures.
Financial Implications for Insurance Companies
The increased coverage requirements translate into a significant financial burden for insurers. Higher coverage limits mean larger payouts in the event of a wildfire, potentially leading to substantial losses for insurance companies. This, combined with the rising frequency of catastrophic events in wildfire-prone regions, necessitates a significant recalibration of their risk assessment methodologies. For instance, a home with a $500,000 coverage limit may now require $1,000,000.
This significantly alters the financial outlook for the insurers.
Potential for Premium Increases or Withdrawal from High-Risk Areas
Insurers may respond to these increased financial burdens in several ways. One predictable response is raising premiums for policies in high-risk areas. This will likely disproportionately affect homeowners in areas with a history of severe wildfires. Another response is to withdraw from high-risk areas altogether. This would leave residents in these areas with fewer insurance options, potentially creating a critical shortage of coverage in these communities.
This is often seen in insurance markets where the cost of providing coverage exceeds the revenue potential.
Potential Strategies to Mitigate Financial Risks
To mitigate the financial risks, insurance companies can adopt several strategies. They can improve their underwriting processes to more accurately assess wildfire risks. This might include incorporating factors like proximity to firebreaks, vegetation type, and the presence of defensible space. Additionally, companies can invest in advanced risk modeling tools to better predict the likelihood of wildfire damage.
Alternative Risk-Management Strategies for Insurers
Beyond traditional risk management, insurers could explore alternative strategies. These include partnering with local governments or non-profit organizations to implement preventative measures. For instance, providing incentives for property owners to adopt fire-resistant building materials or develop fire-safe landscaping. Also, developing innovative products and services designed to address the unique risks of wildfire, such as providing coverage for specific fire-resistant features.
Table Summarizing Potential Actions
| Potential Action | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Premiums | Raise the cost of insurance policies in high-risk areas. | Higher costs for homeowners, potential market instability. |
| Withdraw from High-Risk Areas | Refuse to offer coverage in areas deemed too risky. | Reduced insurance options for residents, potential insurance gaps. |
| Improve Underwriting Processes | Enhance risk assessment by considering factors like fire risk and defensible space. | More accurate risk assessment, potentially lower claims. |
| Invest in Advanced Risk Modeling | Utilize technology to predict wildfire damage and refine pricing. | Improved accuracy in risk assessment, better informed pricing. |
| Partner with Local Governments/Non-profits | Collaborate on preventative measures, such as fire-resistant building codes. | Reduced risk, potential cost-sharing, community support. |
| Develop Innovative Products | Offer specialized coverage tailored to wildfire risks, e.g., fire-resistant building materials. | Addressing specific risks, potential for new revenue streams. |
Impact on Homeowners and Communities
California’s new wildfire insurance mandates are a necessary step to protect communities and ensure responsible risk management. However, these changes will undoubtedly present significant challenges for homeowners, particularly in high-risk areas. The increased premiums and coverage requirements could have a substantial impact on affordability, potentially leading to displacement and requiring a comprehensive approach to support affected residents.Increased insurance costs will likely strain the budgets of homeowners in high-risk areas, particularly those with lower incomes.
These added expenses could make homeownership unsustainable, potentially leading to a decrease in property values and reduced access to housing options. The burden of these increased costs could disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, exacerbating existing inequalities.
Potential Challenges for Homeowners
The rising cost of insurance is a significant concern for homeowners in wildfire-prone areas. Higher premiums can significantly impact household budgets, potentially affecting other essential expenses like food, healthcare, and education. For example, a homeowner in a high-risk area might see their monthly insurance payments increase by thousands of dollars, impacting their overall financial stability. This could lead to financial stress and potentially impact their ability to maintain their homes.
Impact on Housing Affordability
Increased coverage requirements could further diminish housing affordability in wildfire-prone areas. As insurance premiums rise, the cost of purchasing or renting a home will increase, potentially making it difficult for individuals and families to enter or remain in the housing market. This could result in a decline in property values in affected regions.
Potential for Displacement and Relocation
High insurance costs can potentially lead to displacement or relocation of residents. Some homeowners might be unable to afford the increased premiums and may be forced to sell their homes, even if they desire to remain in the community. This could lead to a significant shift in demographics and potentially destabilize local communities. In some cases, the escalating costs may force residents to relocate to less expensive areas, potentially leading to a decrease in the local population and a reduction in community services.
Role of Government Assistance Programs
Government assistance programs can play a crucial role in mitigating the impacts on homeowners. Targeted programs that offer financial aid, subsidies, or educational resources to help homeowners manage rising insurance costs could significantly reduce the burden on residents. The availability and accessibility of these programs will be crucial to minimizing the impact on homeowners and preserving communities.
Potential Financial Aid Programs
| Program Type | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Subsidies | Financial assistance to reduce insurance premiums. | Reduces the financial burden of high premiums, helping homeowners afford coverage. |
| Home Improvement Grants | Financial aid for wildfire-resistant home improvements. | Reduces the risk of wildfire damage and lowers insurance costs in the long run. |
| Emergency Housing Assistance | Temporary housing assistance for homeowners unable to afford their homes due to insurance costs. | Provides temporary shelter and support during the transition process. |
| Community Development Block Grants | Federal funds for community development initiatives. | Could be used to support wildfire mitigation efforts, including affordable housing initiatives, and infrastructure improvements. |
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
California’s proposed increase in wildfire insurance coverage requirements reflects a growing recognition of the escalating threat posed by wildfires. The state’s vulnerability to these devastating events necessitates a proactive approach to risk mitigation, and this policy change aims to incentivize better building practices and financial preparedness in wildfire-prone areas. The rationale behind this policy is multi-faceted, addressing both the safety of residents and the financial stability of the insurance industry.
Rationale Behind Increased Coverage Requirements
The escalating cost of wildfire damage in California, coupled with the increasing frequency and intensity of these events, necessitates a shift in the way homeowners and insurance companies approach risk management. The proposed policy aims to incentivize the construction of more fire-resistant homes in high-risk zones, effectively reducing the potential for catastrophic losses. This includes encouraging the adoption of improved building materials, upgraded fire safety systems, and stricter building codes in wildfire-prone areas.
A crucial aspect is also to strengthen the financial capacity of insurers to cope with the growing financial burdens associated with wildfire damage claims. This is particularly important given the immense costs associated with restoring homes and infrastructure after a wildfire.
Examples of Similar Policies in Other Areas
Several other regions facing natural disaster risks have implemented similar policies to incentivize improved building practices and strengthen insurance coverage. Florida, for instance, has regulations focused on hurricane-resistant construction and flood insurance requirements, directly addressing the unique challenges posed by their specific natural hazards. Similarly, areas prone to earthquakes, like California, have building codes designed to minimize structural damage and ensure compliance with seismic standards.
These examples demonstrate that proactive measures are being taken across various regions to mitigate the impact of natural disasters and foster more robust risk management strategies.
Comparison with Existing California Regulations
Existing California building codes and insurance regulations address certain aspects of wildfire preparedness, but the proposed changes represent a significant expansion of these efforts. Existing codes often lack the specific fire-resistance measures required in high-risk zones. The proposed policies could potentially introduce new mandates concerning the type of materials used in construction, mandatory fire-resistant coatings for homes, or improved landscaping practices.
These enhancements are crucial to creating a more resilient infrastructure and a safer environment. A key comparison is the financial responsibility aspect, with the proposed policy directly impacting insurance premiums and payouts.
Potential Legal Challenges to the New Requirements
The proposed coverage increase might face legal challenges based on arguments concerning fairness, equal protection, and the potential burden on homeowners. Concerns could arise about the feasibility of meeting the new standards, especially for older homes in high-risk areas, potentially leading to a disproportionate impact on lower-income communities. Furthermore, there might be challenges related to the implementation and enforcement of these new requirements, particularly regarding the equitable application of the policy across different communities and property types.
These potential legal hurdles highlight the need for a careful and transparent policy implementation process.
Table Comparing Policy Requirements in California and Other States
| State | Wildfire Risk Zone | Required Coverage Increase (%) | Building Code Requirements | Insurance Premium Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | Specific zones determined by risk assessment | To be determined by policy | Likely stricter building codes and materials mandates | Potential increase for homeowners |
| Oregon | Wildfire-prone zones | Varied depending on risk level | Existing building codes under review | Premiums adjusted to risk factors |
| Washington | High-risk areas | Increase planned in high-risk areas | New requirements on fire-resistant construction | Potential increase, possibly tiered by risk |
This table provides a preliminary comparison, as the exact policy details and the required coverage increases are still under development. The table serves to illustrate the diverse approaches states are taking to address wildfire risks and their potential impacts on homeowners and insurance companies.
Future Implications and Predictions
California’s evolving wildfire insurance landscape, driven by increased coverage mandates, promises a multifaceted future. The implications extend beyond simple cost increases, impacting insurance companies, homeowners, and the real estate market itself. Adapting to these changes will require innovative solutions and a proactive approach to mitigate future risks.
Long-Term Consequences for the Insurance Industry
The insurance industry will face significant long-term adjustments. Increased coverage mandates will likely lead to higher premiums, potentially impacting profitability and market competitiveness. Insurers may need to re-evaluate risk assessment models, incorporating more sophisticated data on wildfire susceptibility and developing more nuanced pricing strategies. This will necessitate investments in new technologies and data analysis capabilities. Furthermore, the possibility of catastrophic claims could trigger a need for increased capital reserves and stricter underwriting practices.
Potential Impact on the Real Estate Market
The real estate market will undoubtedly be affected. Higher insurance premiums will directly translate to higher home purchase prices, particularly in wildfire-prone zones. This could lead to a reduction in demand for properties in these areas, influencing property values and potentially creating housing affordability challenges. Conversely, investments in wildfire-resistant building techniques could increase property values in affected areas over time.
Technological Advancements in Addressing Wildfire Risk
Technological advancements offer promising avenues to address wildfire risk. Improved fire prediction models, utilizing sophisticated weather data and historical patterns, could provide early warnings and facilitate more effective fire response strategies. Remote sensing technologies, such as drones and satellite imagery, can aid in fire detection and mapping, enabling quicker interventions. The development of self-regulating, fire-resistant building materials and smart home systems that automatically shut off gas and power lines during extreme conditions are also crucial steps.
Improving Building Codes for Wildfire Resilience
Building codes must evolve to incorporate wildfire resilience. Regulations should mandate the use of fire-resistant materials in construction, especially in roofing and exterior walls. Stricter requirements for defensible space around homes, encompassing landscaping and vegetation management, should also be enforced. Design standards should incorporate the specific wildfire risks of the region, considering factors like wind patterns and historical fire activity.
Potential Future Scenarios
| Scenario | Driving Factor | Impact on Insurance | Impact on Real Estate | Impact on Communities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Premiums, Reduced Demand | High wildfire risk, inadequate mitigation | Lower profitability, potential market share loss | Decreased property values, reduced sales in affected areas | Strain on homeowners’ budgets, potential displacement of residents |
| Adaptable and Sustainable Solutions | Investment in advanced technology, proactive community engagement | Increased efficiency, diversified risk portfolios | Improved property values, increased demand in resilient areas | Enhanced community safety, reduced wildfire vulnerability |
| Catastrophic Event, Industry Crisis | Unprecedented wildfire event, lack of adequate preparedness | Significant losses, potential industry consolidation | Sharp decline in property values, potential market freeze | Severe disruption to communities, widespread displacement |
Public Perception and Community Response

The impending requirement for increased home insurance coverage in wildfire-prone areas in California is likely to generate a complex public reaction. Understanding potential concerns and crafting effective communication strategies are crucial for navigating this challenge and ensuring smooth implementation. A well-informed and engaged community is more likely to accept and comply with the new regulations.
Potential Public Reaction
Public reaction to the increased insurance requirements will likely vary, with some homeowners potentially feeling burdened by higher premiums, while others may support the measure as a necessary precaution. Concerns about affordability and fairness, especially for those with limited financial resources, are likely to arise. Misinformation and speculation could also fuel opposition. A proactive and transparent approach to communication is essential to manage these concerns.
Community Concerns and Potential Resistance
Several key concerns are likely to emerge. Financial strain is a significant concern for many homeowners, especially those in lower-income brackets. They may struggle to afford the increased premiums, potentially leading to displacement or forced sale of homes. Perceived unfairness, particularly if the increased coverage is not uniformly applied or if the costs are disproportionately high in certain areas, could also fuel resistance.
Finally, concerns about the effectiveness of the increased coverage in preventing or mitigating future wildfire damage might also arise.
Public Education Campaigns
Public education campaigns are essential to address concerns and promote understanding. These campaigns should clearly explain the rationale behind the increased coverage requirements, emphasizing the importance of risk mitigation in wildfire-prone areas. The campaigns should highlight the long-term benefits, such as reduced wildfire risks and potential government assistance programs for homeowners affected by rising premiums. Furthermore, the campaigns should dispel any misinformation or misconceptions about the new regulations.
A key component of these campaigns is using relatable examples and clear, concise language to communicate complex issues effectively.
Communication Strategies with Stakeholders, California will soon require insurers to increase home coverage in wildfire prone areas
Effective communication with stakeholders is vital to manage concerns and encourage compliance. Transparency and accessibility are key. Regular updates, accessible information via multiple channels (website, social media, community meetings), and clear explanations of the decision-making process will be crucial. Utilizing trusted community leaders and local representatives can help build trust and foster a sense of collaboration. Providing opportunities for public feedback and input, through surveys, town halls, or online forums, is crucial to address specific concerns and demonstrate a commitment to listening.
Table of Potential Communication Strategies
| Communication Strategy | Description | Target Audience | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Community Forums | Hosting town halls, workshops, and Q&A sessions in local communities to address concerns directly. | Homeowners, residents, and stakeholders in the affected areas. | Increased understanding of the regulations and fostering a dialogue. |
| Social Media Engagement | Actively engaging with residents on social media platforms, addressing queries, and providing clear and concise information. | Social media users in the affected areas. | Dissemination of accurate information and direct interaction with the public. |
| Dedicated Website | Creating a dedicated website with detailed information about the insurance requirements, FAQs, and contact information. | Homeowners, residents, and stakeholders in the affected areas. | Easy access to reliable information for the public. |
| Partnerships with Local Organizations | Collaborating with local community groups, non-profits, and businesses to spread awareness and offer support. | Community members and stakeholders. | Wider reach and increased credibility. |
End of Discussion
California’s new wildfire insurance policy, mandating increased coverage in high-risk areas, presents a complex challenge with potential benefits and drawbacks for all parties involved. The policy’s success will hinge on a balance between ensuring adequate protection for residents and mitigating the financial burden on homeowners and insurers. We will need to closely monitor the implementation and adjust as needed to minimize unintended consequences.