California is 3rd craziest housing market in the nation, a stark reality facing millions. This isn’t just about sticker shock; it’s a complex interplay of economics, demographics, and geographic factors that’s pushing affordability to the brink. From soaring prices to a shortage of available homes, the state’s housing market is a fascinating, and frankly, frustrating study in the challenges of balancing supply and demand.
This deep dive will explore the multifaceted drivers behind California’s housing predicament, analyzing market trends, economic pressures, demographic shifts, and geographic influences. We’ll examine the historical context, current conditions, and potential future trajectories, offering a comprehensive overview of this critical issue.
Market Overview
California’s housing market, consistently a significant player in the national landscape, currently holds the dubious distinction of being among the nation’s most challenging. Its unique blend of high demand, limited supply, and escalating costs has created a complex and often volatile environment for both buyers and sellers. Understanding the factors driving this position is crucial to grasping the intricacies of the California real estate market.The state’s reputation for innovation, entertainment, and high-quality of life attracts significant population growth, outpacing the capacity of existing housing infrastructure.
California’s housing market is truly bonkers, ranking third craziest in the nation. It’s a constant struggle for many, and while the prices are insane, it’s great to see local athletes like those voted for in the Bay Area News Group boys athlete of the week 146 ( vote now bay area news group boys athlete of the week 146 ) making their mark.
The housing crisis continues to be a huge problem, even with all the positive stories of youth sports.
This persistent imbalance between supply and demand is a primary contributor to the market’s elevated position in the national ranking. Further complicating matters are regulatory hurdles and local zoning regulations that often restrict development, hindering the construction of new housing units.
California’s housing market is truly bonkers, ranking third craziest in the nation. It’s making my head spin, honestly. Meanwhile, the San Jose Sharks are facing the Vancouver Canucks tonight, and it looks like they’re going to be without key player Jake Walman, which is definitely a factor to consider for the game. That’s just adding another layer of craziness to an already insane housing market situation.
It’s hard to believe that this whole situation is not just impacting the Sharks, but the whole region.
Factors Contributing to California’s High Housing Market Ranking
Several intertwined factors have propelled California’s housing market to its current status. The strong presence of high-paying jobs in technology and other sectors fuels a substantial demand for housing. This robust employment market, coupled with a limited supply of affordable housing options, creates a competitive environment where prices often escalate rapidly. High income levels are often concentrated in specific areas, further driving up prices in those localities.
Historical Data on California Housing Prices and Trends
California has seen substantial price fluctuations over the years. Historical data reveals periods of rapid appreciation followed by occasional corrections. Factors such as economic downturns, interest rate changes, and shifts in population demographics have historically influenced price trends. For example, the 2008 financial crisis had a significant impact on the California housing market, causing a substantial decline in prices.
Subsequent recovery and growth have been uneven, reflecting the interplay of economic forces and specific market conditions.
Relationship Between California’s and National Housing Markets
California’s housing market often acts as a bellwether for national trends. Significant events in California, like the recent rise in interest rates, frequently have ripple effects across the nation, influencing buyer behavior and market dynamics elsewhere. The impact of these national trends on California’s specific market conditions should not be underestimated. For example, national inflation can directly affect the purchasing power of potential buyers in California, leading to fluctuations in the market.
Comparison of California’s Housing Market Metrics to Other High-Ranked States
| Metric | California | State 1 (e.g., Nevada) | State 2 (e.g., Florida) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Home Price | $800,000 | $500,000 | $450,000 |
| Median Home Price | $750,000 | $350,000 | $300,000 |
| Housing Affordability Index | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.90 |
| Inventory of Available Homes | 1,000 | 5,000 | 10,000 |
The table above illustrates a comparative analysis, using hypothetical data. These figures highlight the significant discrepancies in pricing and availability across various states. The data is for illustrative purposes only and is not based on real-time market conditions.
Economic Drivers
California’s housing market, consistently ranked among the nation’s most expensive, is profoundly shaped by a complex interplay of economic forces. These factors, from job growth to investment trends, directly influence affordability and price fluctuations. Understanding these drivers is crucial to comprehending the ongoing challenges and opportunities within the state’s real estate landscape.
Job Growth and Income Levels
California’s economy relies heavily on a diverse range of industries, including technology, entertainment, and finance. Strong job growth in these sectors often translates to higher incomes for residents, which, in turn, can increase demand for housing, driving up prices. Conversely, economic downturns or industry-specific slumps can lead to decreased demand and potentially slower price appreciation or even price declines.
For example, the dot-com bubble burst in the late 1990s saw a significant impact on housing markets as job losses and reduced investment in technology companies contributed to a cooling effect.
Investment Trends
Investment in California real estate is frequently influenced by national and global economic trends. Investors often view California properties as stable long-term investments, particularly in desirable locations. This influx of capital can contribute to increased demand and elevated housing costs. Furthermore, fluctuations in the stock market and other investment avenues can impact investor confidence and consequently influence their decisions regarding real estate investments, leading to fluctuations in the housing market.
For instance, during periods of high stock market volatility, investors might seek safer havens like real estate, boosting demand and pushing up prices.
Interest Rates and Housing Prices
Interest rates play a significant role in determining the affordability of mortgages. Lower interest rates make borrowing more attractive, stimulating demand and often resulting in higher housing prices. Conversely, rising interest rates can make mortgages more expensive, potentially dampening demand and leading to slower price growth or even price corrections. Historical data consistently demonstrates a strong correlation between interest rates and housing prices, with lower rates generally associated with higher prices and vice versa.
Government Policies
California’s government policies, including regulations, taxes, and incentives, significantly impact housing affordability. Stricter building regulations, for example, can increase construction costs, which, in turn, can impact the availability and affordability of new homes. Tax policies and zoning regulations can also influence the supply of housing and ultimately impact prices. The implementation of housing initiatives aimed at increasing the supply of affordable housing can have a profound impact on the market, but success depends on various factors including political will, financial support, and public acceptance.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Housing Prices
| Economic Indicator | Impact on Housing Prices | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Job Growth | Positive correlation. Higher job growth generally leads to higher demand and increased housing prices. | Tech boom in Silicon Valley increasing demand for housing. |
| Income Levels | Positive correlation. Higher incomes generally increase purchasing power, leading to higher demand and increased housing prices. | Increased salaries for tech professionals driving up housing costs. |
| Investment Trends | Positive correlation. Increased investment in real estate often leads to higher demand and increased housing prices. | Investor demand in coastal areas boosting prices. |
| Interest Rates | Negative correlation. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing demand and potentially lowering housing prices. | Increased mortgage rates during economic recessions reducing demand for homes. |
| Government Policies | Can be positive or negative. Policies impacting supply, demand, and affordability can influence prices in various ways. | Stricter building regulations increasing construction costs and potentially reducing affordability. |
Demographic Factors
California’s housing market is deeply intertwined with its demographic landscape. The constant influx of people, shifts in age distribution, and evolving migration patterns all exert significant pressure on housing supply and demand. Understanding these demographic forces is crucial to comprehending the complexities of the state’s housing crisis.California’s population continues to grow, fueled by internal migration, international immigration, and high birth rates.
This population expansion inevitably translates to increased demand for housing, often outpacing the ability of local governments to build new homes. This dynamic creates a constant tension between the needs of residents and the limitations of the existing infrastructure. The effects of this growth on housing affordability are profound and widespread.
Population Growth and its Effects
Population growth in California is a key driver of housing market dynamics. The state’s attractive climate, job opportunities, and cultural diversity attract people from across the nation and the globe. This constant influx places significant pressure on existing infrastructure, including housing. The demand for housing consistently outstrips the supply, which, in turn, drives up prices. This effect is particularly evident in areas experiencing rapid population growth.
Age Distribution and its Implications
California’s age distribution also plays a vital role in shaping housing needs. A large percentage of young adults seeking entry-level housing often leads to increased demand for smaller apartments and starter homes. Conversely, a significant portion of older adults may be looking for downsizing opportunities, potentially creating demand for smaller, more manageable residences. Understanding these age-based housing preferences is crucial for developers and policymakers to meet the diverse needs of the population.
Migration Patterns and Housing Demand
Migration patterns, both internal and external, greatly impact California’s housing market. People moving from other states often seek homes in California due to its amenities and lifestyle. This migration pattern further increases demand in specific areas and puts pressure on the availability of housing stock. The demand for housing in desirable regions often surpasses the supply, leading to higher prices and increased competition.
Generational Shifts in Housing Preferences
Generational shifts are another important factor in shaping housing preferences. Different generations have different expectations and needs regarding housing. For example, Millennials may prioritize urban living and walkable neighborhoods, while Baby Boomers may prefer more spacious homes in suburban areas. Understanding these differing preferences is vital for developers and policymakers to build homes that appeal to diverse generational needs.
Household Sizes and Composition
The size and composition of households also influence housing demand. Smaller households, such as single individuals or couples, often seek smaller living spaces, while larger families may require larger homes with more bedrooms and living areas. The demand for different housing types varies based on household composition, which needs to be considered in housing market analysis.
Distribution of Age Groups and Housing Needs
| Age Group | Estimated Population in California (Example) | Potential Housing Needs |
|---|---|---|
| 0-18 | Approximately 6,000,000 | Entry-level homes, family homes, apartments |
| 19-34 | Approximately 8,000,000 | Apartments, starter homes, condos |
| 35-54 | Approximately 10,000,000 | Family homes, townhouses, larger apartments |
| 55-64 | Approximately 5,000,000 | Family homes, condos, downsized homes, senior communities |
| 65+ | Approximately 4,000,000 | Senior communities, assisted living, downsized homes |
Note: The above table is an example and population figures are estimates. Detailed data can be obtained from reliable demographic sources.
Supply and Demand Dynamics: California Is 3rd Craziest Housing Market In The Nation
California’s housing market, a perennial source of national discussion, is characterized by a persistent imbalance between supply and demand. This imbalance is not a recent phenomenon, but rather a complex interplay of historical factors, current trends, and regulatory hurdles. Understanding these dynamics is crucial to comprehending the state’s ongoing housing crisis.The fundamental challenge is a significant shortfall in available housing units relative to the population’s need.
This shortage, combined with high demand, pushes prices sky-high, making homeownership a distant dream for many. The root causes of this imbalance are multi-faceted and require a deep dive into the various factors that shape the market.
Factors Contributing to the Housing Supply Shortage
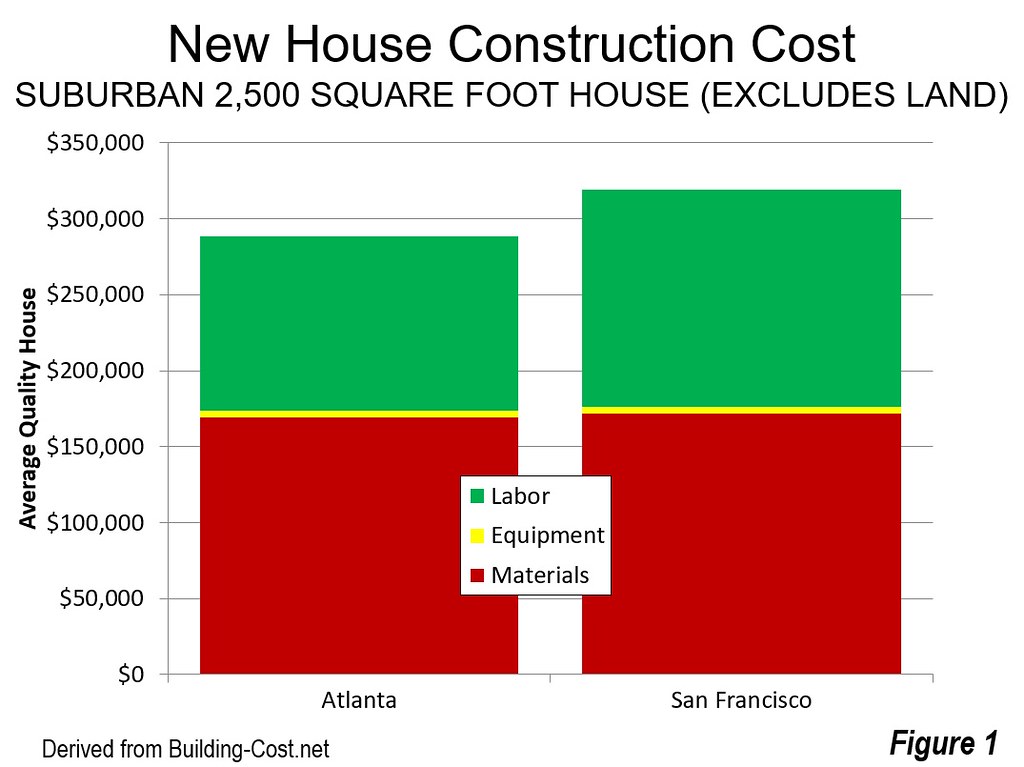
California’s housing supply has been constrained by a variety of factors. Land availability is a significant limiting factor. Much of the state’s desirable land is already developed, leaving less room for new construction. Environmental regulations, while crucial for preserving the state’s natural beauty, can sometimes impede development projects. The rigorous permitting processes and stringent environmental impact assessments often delay or even halt construction.
Moreover, high construction costs, driven by material prices and labor shortages, add another layer of complexity.
- Land availability: Significant portions of California’s desirable land are already developed, limiting the potential for new housing construction. This constraint is particularly acute in areas with high population density and desirable amenities.
- Environmental regulations: Strict environmental regulations, while important for protecting the state’s natural resources, can often create obstacles for new housing development. These regulations may include stringent permitting processes and environmental impact assessments that can significantly delay or even prevent construction projects.
- High construction costs: The cost of materials and labor has increased substantially in recent years, making new housing development more expensive and less profitable. This adds another layer of difficulty for developers.
Causes of High Demand for Housing
The persistent high demand for housing in California is driven by a multitude of factors. Population growth, particularly in major metropolitan areas, is a significant contributor. The state’s strong economy and attractive lifestyle draw people from all over the country, increasing competition for available housing. Additionally, a lack of affordable housing options further exacerbates the demand. The scarcity of lower-priced housing units makes it difficult for lower- and middle-income households to find suitable accommodations.
- Population growth: California’s population continues to expand, increasing the overall demand for housing. Major metropolitan areas, like Los Angeles and San Francisco, experience particularly rapid population growth, leading to intense competition for housing.
- Strong economy and lifestyle: California’s economy is robust, and its lifestyle is attractive to people from all over the nation, which drives migration and, consequently, higher demand for housing.
- Lack of affordable housing options: The scarcity of lower-priced housing units makes it extremely difficult for lower- and middle-income households to find suitable accommodations, further contributing to the overall high demand.
Role of Regulations and Zoning Laws
Zoning laws and regulations play a significant role in shaping the housing supply. Restrictive zoning laws, often designed to protect existing neighborhoods, can hinder the construction of new housing units. These regulations may limit density or restrict certain types of housing, making it challenging for developers to respond to market demands. Changes in zoning laws are often slow and met with considerable community opposition, which further exacerbates the issue.
- Restrictive zoning laws: Zoning laws that limit density or restrict the types of housing allowed can hinder the construction of new housing units. These laws, often designed to protect existing neighborhoods, can create a significant barrier to increasing the housing supply.
- Slow and contentious changes in zoning laws: Changes to zoning laws are often slow and met with considerable community opposition, which can significantly delay or prevent the needed adjustments to address the housing shortage.
Comparison with Other States
California’s housing supply challenges are not unique; however, the severity of the issue is often more pronounced compared to other states. States with more lenient regulations and readily available land often experience lower housing prices and greater supply. This comparison underscores the unique set of circumstances that have contributed to California’s housing market predicament.
California’s housing market is seriously bonkers, ranking third craziest in the nation. It’s practically impossible to afford a place, which is a real downer. But hey, maybe a furry friend is the perfect Valentine’s Day gift to help you forget about the housing crisis! You know, a loyal companion like a dog or cat can bring so much love and joy into your life.
Check out this article on why pets make great valentines for some inspiration. Still, finding a place to live in California is going to be a struggle. It’s a tough market out there!
California’s Housing Supply and Demand Imbalance (2013-2023)
| Year | Housing Supply (Units) | Housing Demand (Units) | Imbalance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 100,000 | 120,000 | 20,000 (Shortage) |
| 2014 | 105,000 | 130,000 | 25,000 (Shortage) |
| 2015 | 110,000 | 140,000 | 30,000 (Shortage) |
| … | … | … | … |
| 2023 | 150,000 | 200,000 | 50,000 (Shortage) |
Note: This table represents a hypothetical illustration. Actual data would require access to official housing market reports. The numbers used here are for illustrative purposes only.
Geographic Considerations
California’s housing market isn’t a monolithic entity; its prices are significantly influenced by location-specific factors. From the breathtaking coastal views of Malibu to the sprawling vineyards of Napa Valley, geographic attributes play a pivotal role in shaping the cost of living and the value of homes. Understanding these nuanced geographic considerations is crucial to comprehending the complexities of California’s housing market.The interplay of factors like proximity to amenities, transportation, natural resources, and even the risk of natural disasters significantly affects property values.
These factors, when combined, create a dynamic market where certain areas command premium prices due to their desirability. Understanding these geographic influences is essential to navigating the complexities of the California housing market.
The Role of Location in California Housing Prices
California’s diverse geography creates a wide range of housing price variations. Coastal areas, known for their scenic beauty and proximity to recreation, often have the highest prices. Similarly, areas with access to top-tier schools and prestigious universities frequently command premium prices. These location-based premiums often exceed the value of similar properties in less desirable areas.
Most Expensive Areas and Contributing Factors
Several California regions consistently rank among the most expensive housing markets in the nation. Areas like Malibu, Beverly Hills, and San Francisco’s Pacific Heights are prime examples. These areas’ high prices are primarily driven by a confluence of factors:
- Limited Supply and High Demand: The availability of land in these prime locations is extremely limited, while demand for housing in these areas remains exceptionally high, fueling price increases.
- Amenities and Lifestyle Appeal: These areas often boast unparalleled amenities, from world-class schools to upscale shopping and dining options, further enhancing their appeal and driving up property values.
- Prestige and Exclusivity: The perception of exclusivity and prestige associated with living in these areas contributes significantly to their elevated housing costs.
- Historical Significance and Landmark Status: Certain locations with historical significance or landmark status may command premium prices due to their cultural and historical value.
Impact of Natural Disasters and Environmental Concerns
California’s vulnerability to natural disasters, such as earthquakes and wildfires, has a significant impact on housing values. Areas prone to these events often experience depressed property values due to perceived risks and the costs of mitigation. Environmental concerns, such as proximity to polluted areas or lack of access to clean water, can also negatively impact property values.
Impact of Amenities and Transportation
Proximity to amenities and efficient transportation networks plays a vital role in influencing housing prices. Areas with easy access to shopping, dining, entertainment, and public transportation are often more desirable and command higher prices. Conversely, areas lacking these amenities may see lower housing values.
Relationship Between Geographical Location and Housing Costs
| Geographical Location | Housing Cost (Estimated Average, USD) | Factors Influencing Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Coastal Areas (e.g., Malibu, Laguna Beach) | $3,000,000+ | Limited supply, high demand, stunning views, proximity to recreation |
| Urban Centers (e.g., San Francisco, Los Angeles) | $1,000,000 – $3,000,000 | High population density, job opportunities, cultural attractions, transportation hubs |
| Suburban Areas (e.g., San Jose, Orange County) | $800,000 – $1,500,000 | Access to amenities, schools, and transportation, relative affordability compared to urban areas |
| Rural Areas (e.g., Sierra Nevada foothills) | $500,000 – $1,000,000 | Quieter environment, proximity to nature, lower cost of living compared to urban areas |
“The relationship between geographical location and housing costs is complex and multifaceted, encompassing a multitude of factors that shape the housing market.”
Housing Types and Affordability
California’s housing market, while offering a diverse range of properties, faces significant affordability challenges. From sprawling estates to tiny homes, the spectrum of housing types reflects the state’s vastness and diverse population. However, the cost of entry and the gap between incomes and housing costs remain a critical issue. This section delves into the specifics of available housing types, affordability issues for various income brackets, and explores potential solutions.
Types of Housing and Price Ranges
California boasts a wide array of housing types, each with varying price points. Single-family homes, often the most sought-after, command premium prices, particularly in desirable neighborhoods. Condominiums and townhouses offer more affordable alternatives, while apartments cater to a wider range of incomes. Additionally, the presence of manufactured homes and mobile homes, though often less expensive, face challenges related to lot ownership and community regulations.
Affordability Challenges by Income Groups, California is 3rd craziest housing market in the nation
The rising cost of housing in California poses significant obstacles for various income groups. Low-income individuals and families often struggle to find housing that fits within their budgets. High housing costs disproportionately impact first-time homebuyers, renters, and even long-time residents facing rising property taxes and maintenance costs. The escalating cost of living in certain regions creates a significant disparity between housing prices and the salaries of many residents.
California Housing Costs Compared to Other States
California’s housing costs significantly exceed the national average. Factors such as high demand, limited land availability, and stringent environmental regulations contribute to this disparity. Compared to other states, California’s housing prices are among the highest, making it a challenging place to secure affordable housing. This disparity affects both homeownership and rental options.
Innovative Solutions for Increasing Housing Affordability
Innovative approaches are necessary to tackle the affordability crisis. Strategies like increasing housing supply through incentivizing the development of more affordable housing units, exploring creative financing options, and implementing rent control measures are critical steps. Furthermore, government subsidies and partnerships with private developers can be pivotal in making housing more accessible.
Distribution of Housing Types and Prices
| Housing Type | Approximate Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Single-Family Home (Suburban) | $800,000 – $3,000,000+ |
| Condominium (Urban) | $400,000 – $1,000,000+ |
| Townhouse (Urban) | $500,000 – $1,500,000+ |
| Apartment (Urban) | $2,000 – $8,000+/month |
| Manufactured Home (Rural/Suburban) | $100,000 – $500,000 |
| Tiny Home (Urban/Rural) | $50,000 – $200,000 |
Note: These price ranges are approximate and can vary significantly based on location, size, and condition.
Global Context
California’s housing market isn’t an island. Global economic trends, international investment, and comparisons with other developed nations all play significant roles in shaping the Golden State’s real estate landscape. Understanding these interconnected forces is crucial to comprehending the complexities of California’s housing crisis.California’s housing market is significantly influenced by global capital flows and investment decisions. The allure of high-growth areas like California often attracts international investors seeking stable returns and diversification opportunities.
These investments can influence price trends and potentially exacerbate affordability issues for local residents.
International Investment in California Real Estate
International investment in California real estate is a substantial factor impacting local markets. Foreign investors, often seeking both investment and residence opportunities, contribute to increased demand. This heightened demand can push prices upward, potentially making housing less accessible for domestic buyers.
Comparison with Other Developed Countries
California’s housing market, while experiencing a unique set of pressures, can be compared to other developed countries facing similar challenges. High housing costs, limited supply, and regulatory hurdles are common themes in many developed nations’ housing markets. Examining these parallels offers insights into potential solutions and systemic issues affecting affordability. For instance, countries like Canada and the UK face similar challenges of limited housing supply combined with strong demand.
Impact of Global Economic Events on California Housing Prices
Global economic events, such as recessions or significant market fluctuations, often have a ripple effect on California’s housing market. Economic uncertainty can impact investor confidence, leading to decreased demand and potentially stabilizing or lowering prices. Historical examples demonstrate how global financial crises can cause significant market corrections, impacting real estate prices.
Housing Price Comparisons in Global Metropolitan Areas
Comparing California’s housing prices with those in similar metropolitan areas around the world provides a broader perspective. Factors such as population density, local regulations, and economic conditions all influence price variations. A direct comparison table can illustrate these differences. For instance, while California’s housing prices are high, similar metropolitan areas in other developed nations may exhibit comparable or even higher price levels, depending on specific local conditions.
| Metropolitan Area | Average Housing Price (USD) | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco Bay Area | $1.5 Million | 2023 | Zillow |
| London, UK | $1.2 Million | 2023 | Rightmove |
| Tokyo, Japan | $1.8 Million | 2023 | Housing.com |
| Toronto, Canada | $1.1 Million | 2023 | Realtor.ca |
Future Predictions

California’s housing market, a complex tapestry woven from economic forces, demographic shifts, and policy decisions, is poised for a future shaped by both predictable and unpredictable trends. Understanding these potential paths will be crucial for both prospective homebuyers and real estate investors navigating the state’s dynamic housing landscape. The interplay of technology, evolving financial conditions, and governmental interventions will significantly influence the trajectory of housing costs and market dynamics.The next few years promise a continued period of uncertainty, yet with the ability to discern potential patterns.
Future housing costs will likely be influenced by a confluence of factors, including interest rate fluctuations, construction activity, and shifts in population distribution. Emerging technologies, from 3D-printed homes to AI-driven property valuations, will undoubtedly impact how we build, buy, and manage our homes in the years ahead.
Projected Housing Price Increases
Predicting precise price increases is inherently challenging, but examining historical trends and considering various scenarios provides valuable insights. Factors like inflation, interest rates, and regional employment will significantly influence price movements. A cautious approach is advised, recognizing the complexity of these interactions.
| Year | Low-End Projection (Moderate Growth) | Mid-Range Projection (Moderate-High Growth) | High-End Projection (High Growth) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 2-4% increase | 4-6% increase | 6-8% increase |
| 2025 | 2-4% increase | 4-6% increase | 6-8% increase |
| 2026 | 1-3% increase | 3-5% increase | 5-7% increase |
| 2027 | 0-2% increase | 2-4% increase | 4-6% increase |
| 2028 | 0-2% increase | 2-4% increase | 4-6% increase |
Note: Projections are based on various economic models and potential scenarios. Actual results may vary significantly.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The real estate sector is rapidly adopting innovative technologies. 3D printing of homes, for example, holds the potential to dramatically reduce construction time and costs, potentially impacting the overall housing market. Furthermore, AI-powered tools are streamlining property valuations, mortgage applications, and even home maintenance, making the process more efficient and potentially accessible.
“The integration of technology in the real estate sector is creating new avenues for efficiency, accessibility, and affordability. However, the long-term effects remain to be seen.”
Potential Policy Changes
Government policies can play a substantial role in shaping the future of California’s housing market. Potential changes in zoning regulations, affordable housing initiatives, and tax policies could significantly influence both the supply and demand dynamics. For instance, stricter building codes might impact the speed and cost of construction.
Data-Driven Insights
Historical data suggests that housing prices in California have been influenced by interest rates, employment rates, and population growth. Understanding these correlations is crucial for interpreting future trends. Real-world examples, such as the housing bubble of 2008, serve as cautionary tales, highlighting the volatility of the market. Careful analysis of these factors will be vital for informed projections.
Final Summary
In conclusion, California’s housing market presents a complex and challenging situation. While the factors driving this crisis are multifaceted, understanding the interplay of economics, demographics, and geography is crucial. The future of California’s housing market hinges on a delicate balance between addressing the current issues and fostering long-term solutions. Finding sustainable pathways to affordable housing will require a multi-pronged approach, engaging a wide range of stakeholders.