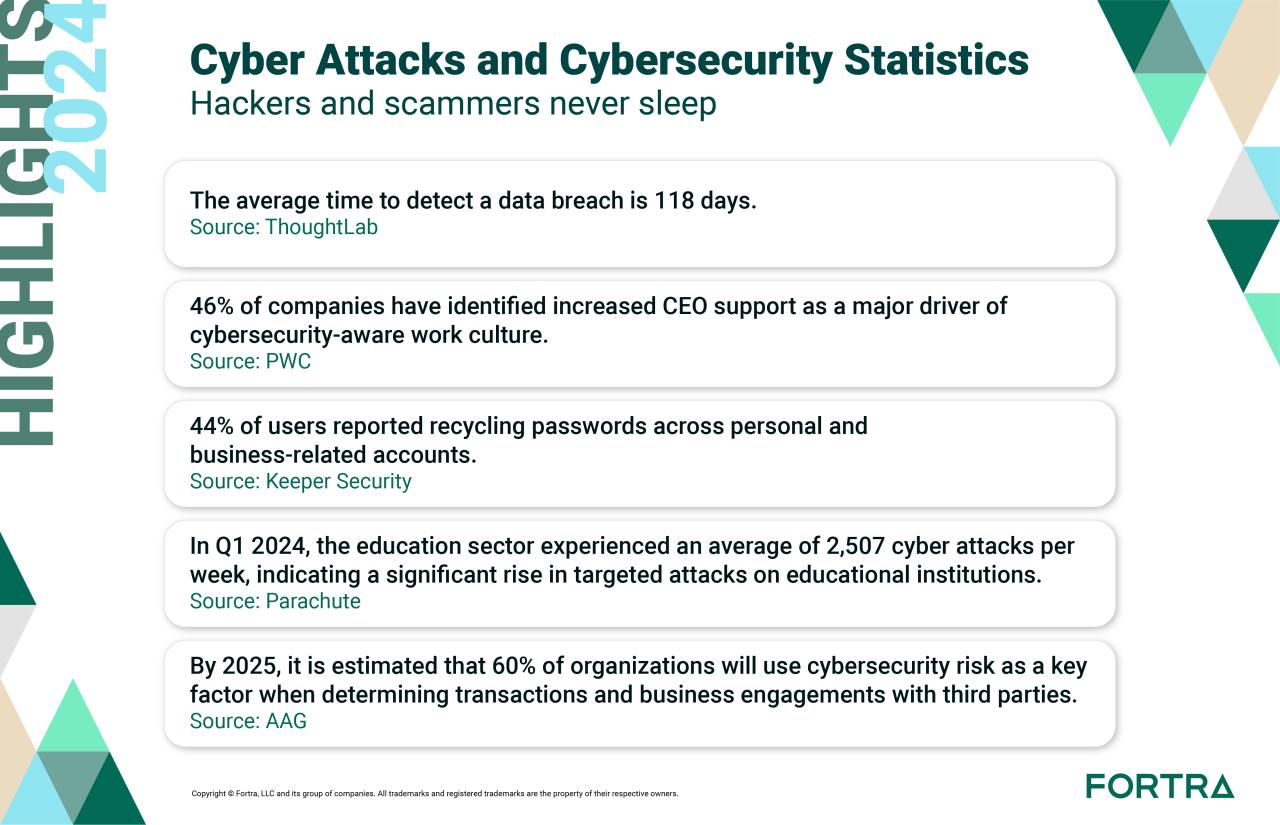
Cybersecurity data and statistics paint a stark picture of the evolving threat landscape. From the global rise in sophisticated attacks to the escalating financial costs of breaches, understanding these trends is critical for navigating the digital age. This deep dive examines key data points, exploring global cybersecurity trends, breach statistics, spending patterns, skills gaps, and the impact of emerging technologies.
We’ll analyze the increasing sophistication of attack vectors, the financial implications of data breaches across various industries, and the crucial role of cybersecurity investment in mitigating these risks. The content will present data in a clear, concise manner, utilizing tables and charts to highlight key comparisons and insights. Furthermore, we will discuss the emerging cybersecurity skills gap and explore how training and development can address these challenges.
Global Cybersecurity Trends
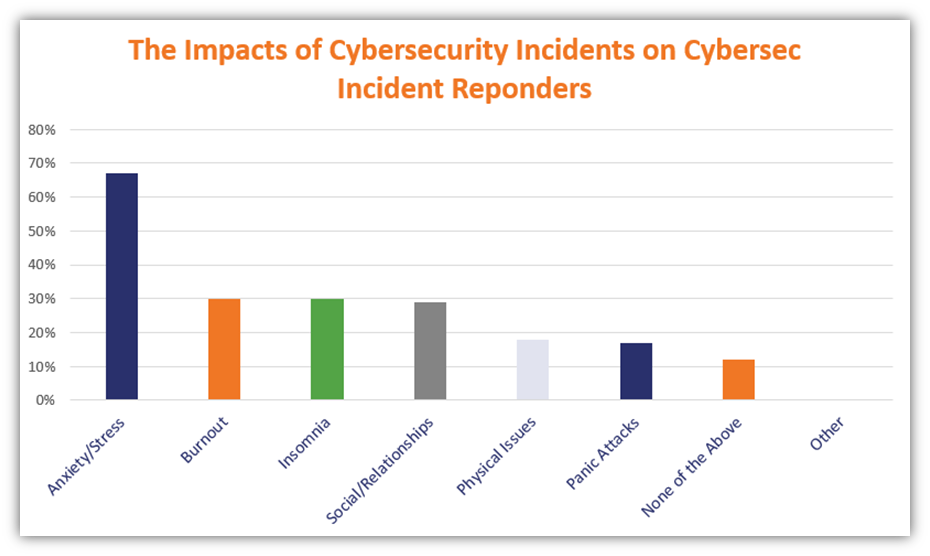
The digital landscape has become increasingly intertwined with our daily lives, making cybersecurity a paramount concern. Over the past five years, a concerning trend of evolving threats has emerged, demanding proactive measures and adaptable strategies. This evolution underscores the constant need for vigilance and the importance of staying ahead of sophisticated attack methods.
Prevalence of Cybersecurity Threats
Global cybersecurity threats have shown a significant increase in sophistication and frequency over the past five years. Phishing attacks, malware campaigns, and ransomware attacks have been particularly prevalent, exploiting vulnerabilities in software and human behavior. Ransomware attacks, in particular, have become a major concern, targeting critical infrastructure and demanding significant financial payments for data recovery.
Evolution of Attack Vectors
Attack vectors have evolved significantly, moving beyond simple email phishing to more complex and targeted approaches. Spear phishing, social engineering, and supply chain attacks are now more common, demonstrating the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals. For example, a well-crafted spear phishing email can convincingly impersonate a trusted entity, luring victims into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software. Supply chain attacks, targeting software vulnerabilities within software development pipelines, pose a significant threat, impacting multiple organizations simultaneously.
Rising Trends in Data Breaches, Cybersecurity data and statistics
Data breaches are escalating in frequency and impact, compromising various types of data. Personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, and intellectual property are all prime targets, leading to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions for organizations. The potential impact of data breaches can extend to individuals, impacting their financial security and privacy. For example, a breach of a major retailer’s database could expose millions of customer credit card numbers, leading to widespread financial fraud.
Changing Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding cybersecurity is evolving rapidly. Increased governmental regulations and industry standards are demanding greater security measures from organizations. These evolving standards mandate robust security protocols, data protection measures, and incident response plans. For example, GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California have significantly influenced data protection practices, requiring organizations to be more transparent about data collection and usage.
Regional Cybersecurity Challenges
| Region | Primary Threats | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Ransomware, supply chain attacks, advanced persistent threats (APTs) | Financial losses, operational disruption, reputational damage | Investment in robust security infrastructure, employee training, incident response plans |
| Europe | Phishing, data breaches, GDPR compliance | Financial penalties, legal liabilities, loss of customer trust | Enhanced data security protocols, improved cybersecurity awareness training, adherence to GDPR regulations |
| Asia Pacific | Malware, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, data breaches | Financial losses, reputational damage, operational disruptions | Stronger cybersecurity measures, improved incident response protocols, increased investment in security solutions |
| Latin America | Phishing, ransomware, malware | Financial losses, data breaches, operational disruptions | Investment in cybersecurity infrastructure, employee training, improved incident response |
The table above highlights the varying cybersecurity challenges faced by different regions, underscoring the need for tailored mitigation strategies. Different regions have varying levels of maturity and resources for cybersecurity. These factors influence the type and frequency of attacks, along with the impact they have.
Data Breach Statistics and Patterns
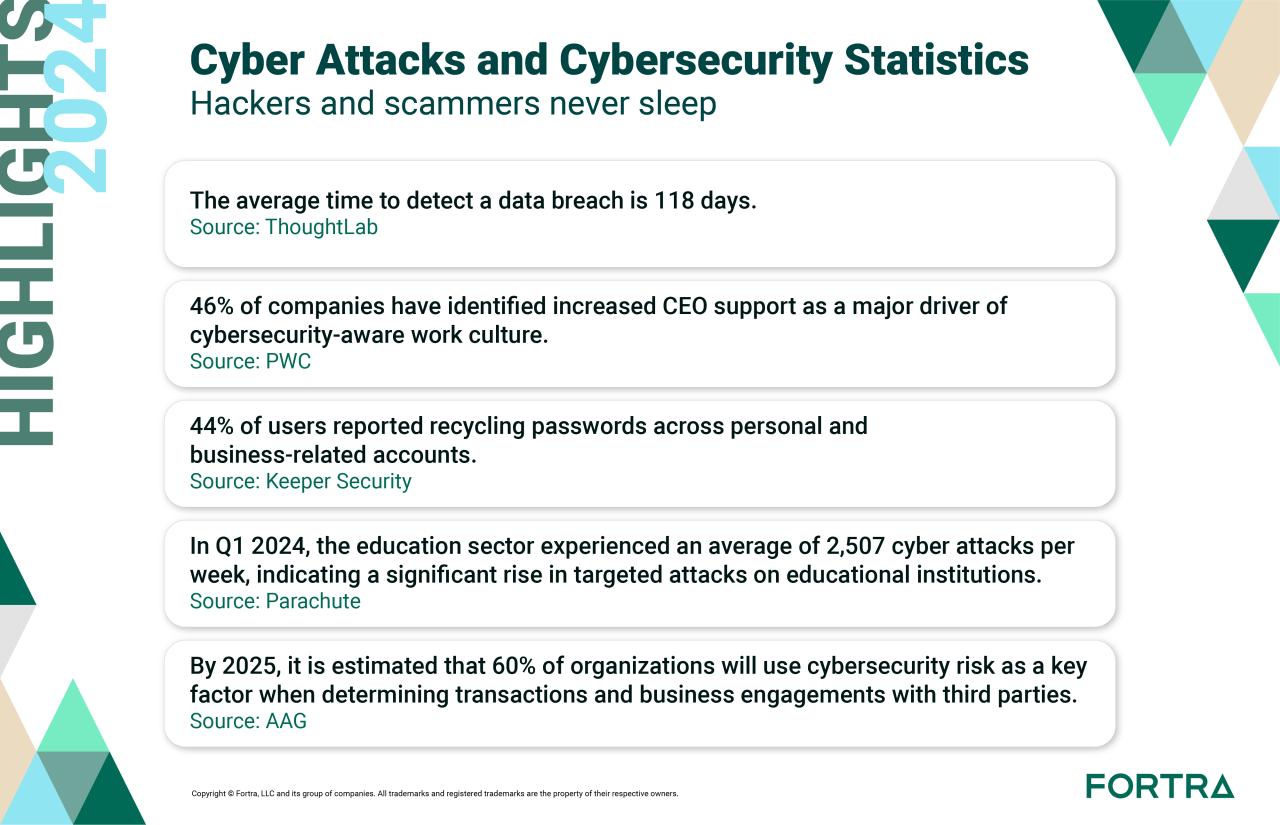
Data breaches are a pervasive threat to organizations of all sizes, impacting their financial stability, reputation, and customer trust. Understanding the patterns and statistics surrounding these incidents is crucial for developing effective preventative measures. This analysis delves into the financial consequences, common vulnerabilities, attack methodologies, the human element, and strategies for mitigating these risks.The financial consequences of data breaches extend far beyond immediate costs.
Beyond the direct expenses of investigation and remediation, organizations face reputational damage, legal liabilities, and lost customer confidence. The erosion of trust can have long-term effects on a company’s market value and profitability.
Financial Impact of Data Breaches
Data breaches inflict significant financial damage across various industries. The costs encompass immediate expenses like forensic analysis, notification procedures, and regulatory fines. Long-term repercussions include lost revenue, legal settlements, and the expense of bolstering security measures.
Average Breach Cost by Company Size
The cost of a data breach varies significantly based on the size of the organization. Smaller companies often lack the resources and expertise to manage the aftermath of a breach, resulting in higher relative costs.
Cybersecurity data and statistics are constantly evolving, reflecting the ever-changing threat landscape. Recent funding news for self-driving startups, like the self driving startup nuro raises 106 million at lower valuation 2 , highlight the need for robust security measures in emerging technologies. This, in turn, emphasizes the importance of understanding and analyzing these data points to better protect against future vulnerabilities and potential breaches.
| Company Size | Average Breach Cost | Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Small (1-100 employees) | $3.88 million | Financial Services |
| Medium (101-500 employees) | $4.79 million | Retail |
| Large (501+ employees) | $8.45 million | Healthcare |
Note: These figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on the specific industry, the nature of the breach, and the response time.
Common Vulnerabilities Exploited in Data Breaches
Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities in software and systems to gain unauthorized access. These vulnerabilities can stem from outdated software, misconfigurations, or inadequate security protocols. A lack of security awareness among employees also plays a significant role.
Methods Used by Attackers to Gain Access
Attackers employ various methods to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive data. Phishing scams, malware infections, and exploiting software vulnerabilities are common tactics. Social engineering, where attackers manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information, is another prevalent technique.
Role of Human Error in Data Breaches and Prevention
Human error is a significant factor in many data breaches. Employees may inadvertently expose sensitive data through negligent actions, such as clicking on malicious links or sharing passwords. Security awareness training and robust security policies are crucial in mitigating the risk of human error.
Data Breach Prevention Strategies for Different Sectors
Effective data breach prevention requires tailored strategies for different sectors. These strategies should include multi-factor authentication, robust access controls, regular security audits, and employee training programs. Specific security protocols must be tailored to the industry’s unique data handling and regulatory requirements.
- Financial Services: Implementing strong encryption protocols, regularly updating security systems, and conducting rigorous background checks for employees are essential.
- Healthcare: Strict adherence to HIPAA regulations, robust data encryption, and secure data storage protocols are crucial for safeguarding patient information.
- Retail: Implementing secure payment gateways, robust cybersecurity measures for point-of-sale systems, and educating employees about phishing attacks are critical.
Cybersecurity Spending and Investment
Global cybersecurity spending has been steadily increasing over the past decade, driven by a rising number of sophisticated cyberattacks and the growing reliance on digital infrastructure. Organizations of all sizes are recognizing the critical need to protect their valuable data and systems from malicious actors, leading to substantial investments in security technologies and personnel. This evolution reflects the evolving threat landscape and the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals.Cybersecurity budgets are not uniformly distributed across the globe.
Factors such as economic conditions, regulatory environments, and the prevalence of specific threats significantly influence spending patterns. This variance is apparent in the differing approaches to security by nations and organizations, highlighting the need for tailored strategies. Understanding these trends and factors is crucial for effective cybersecurity planning and resource allocation.
Global Cybersecurity Spending Trends
Cybersecurity spending has shown a consistent upward trajectory over the past decade. This growth is fueled by the increasing number and complexity of cyberattacks, as well as the growing dependence on digital infrastructure across industries. The rise of ransomware attacks, data breaches, and sophisticated phishing campaigns has directly influenced the increase in investment. This escalation of threats compels organizations to enhance their defenses.
Comparison of Cybersecurity Budgets
| Country/Organization | Budget (USD) | Year |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $170 Billion | 2023 |
| China | $100 Billion | 2023 (estimated) |
| European Union | $50 Billion | 2023 (estimated) |
| Large Financial Institutions (e.g., JP Morgan Chase) | $1 Billion | 2022 |
| Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs) | $10,000 – $100,000 | 2023 |
The table illustrates the diverse range of cybersecurity budgets across different countries and organizations. The substantial difference in spending reflects variations in national security priorities, economic capabilities, and the prevalence of specific threats. The disparity between large institutions and small businesses underscores the importance of tailoring security strategies to the unique needs and resources of each entity.
Factors Driving Cybersecurity Spending
Several factors contribute to the increase in cybersecurity spending. The growing reliance on cloud computing, the proliferation of IoT devices, and the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks all necessitate enhanced security measures. Furthermore, regulatory mandates and compliance requirements, such as GDPR and CCPA, drive investment in security infrastructure. These pressures create a constant need for companies to adapt and invest in cybersecurity.
Impact of Automation on Cybersecurity Spending
Automation is significantly impacting cybersecurity spending. Automated tools and systems are used for tasks such as threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident response. While automation reduces the workload for security personnel, it also necessitates investment in advanced security tools and platforms. The need to integrate automation with existing security infrastructure is crucial, and this integration can influence the required budget.
Breakdown of Cybersecurity Investments
Cybersecurity investments are distributed across various technologies, including:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions are crucial for monitoring and responding to threats on individual devices. The rise in remote work necessitates robust endpoint security, driving demand and investment in this area.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources to identify threats. The increased volume of security data requires sophisticated SIEM systems, leading to investment in these solutions.
- Cloud Security Platforms: The expanding adoption of cloud services necessitates dedicated security solutions to protect cloud environments. Companies are investing heavily in cloud security to address the unique security challenges presented by cloud deployments.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of threat intelligence to proactively identify and respond to emerging threats. Investment in threat intelligence platforms is essential to maintain a proactive security posture.
These technologies are essential components of modern cybersecurity strategies, and the investments in them reflect the ever-changing threat landscape. The need for a multi-layered approach to security is reflected in the investment strategies of organizations.
Cybersecurity data and statistics paint a pretty grim picture, highlighting vulnerabilities in our digital world. Recent news about celebrities, like the recent buzz surrounding asking Eric Thomas having their baby , often overshadows the real-world threats to our personal information. Still, understanding these statistics is crucial to staying safe online. The numbers behind data breaches and cyberattacks are a constant reminder of the need for stronger security measures.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap and Training
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, demanding a workforce with specialized skills to combat sophisticated threats. This necessitates continuous investment in training and development programs to bridge the growing skills gap. The gap is not just about the number of qualified professionals; it also encompasses the specialized expertise needed for emerging technologies and threat vectors.The current cybersecurity talent shortage is impacting organizations’ ability to adequately protect their assets.
Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses education, practical experience, and certifications. Organizations must proactively invest in developing the necessary skills within their existing teams and also attract top talent.
Current Cybersecurity Skills Gap
The cybersecurity skills gap spans across various roles, from penetration testers and security analysts to incident responders and cloud security engineers. The demand for these professionals often outpaces the supply, creating a critical shortage. This gap is particularly acute in areas like cloud security, IoT security, and artificial intelligence-related security. This lack of qualified professionals can lead to significant security vulnerabilities and increase the risk of data breaches.
Demand and Supply of Cybersecurity Professionals
The table below illustrates the disparity between demand and supply for key cybersecurity roles. The data is indicative and may vary depending on region and specific industry.
| Role | Demand | Supply | Training Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Analyst | High | Low | Advanced threat intelligence, incident response, and security monitoring |
| Penetration Tester | High | Moderate | Hands-on experience with various attack methodologies, vulnerability assessment tools, and ethical hacking |
| Incident Responder | High | Low | Expertise in handling security incidents, incident response frameworks, and collaboration with stakeholders |
| Cloud Security Engineer | Very High | Low | Deep understanding of cloud security architectures, best practices, and compliance regulations |
| Security Architect | High | Low | Experience designing and implementing robust security systems, understanding of various security models, and knowledge of complex security technologies |
| IoT Security Specialist | Growing | Very Low | Understanding of IoT protocols, security vulnerabilities, and threat models specific to IoT devices |
| AI/ML Security Engineer | Emerging | Non-existent | Knowledge of AI/ML systems, understanding of potential security threats specific to these systems, and ability to detect anomalies |
Importance of Continuous Cybersecurity Training
Continuous cybersecurity training is essential to address the ever-evolving threat landscape. Cybercriminals are constantly developing new techniques, and security professionals need to stay updated with the latest threats and vulnerabilities. This ensures that organizations can proactively mitigate risks and adapt to new threats, keeping pace with the ongoing evolution of cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity data and statistics often highlight the vulnerabilities in our digital world. For example, the recent Big 12 MBB power ratings examining BYU’s narrow path into the NCAA tournament here reveal how even seemingly successful teams can face unexpected challenges. Ultimately, these statistics remind us of the importance of robust cybersecurity measures in our increasingly connected lives.
Successful Cybersecurity Training Programs
Numerous organizations and institutions offer effective cybersecurity training programs. Some examples include:
- Industry-recognized certifications: CompTIA Security+, Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), and GIAC certifications are valuable for professionals seeking to advance their careers.
- Corporate training programs: Many organizations offer internal training programs focused on specific security risks, vulnerabilities, and policies to enhance employee awareness and improve overall security posture.
- Online learning platforms: Platforms like Cybrary, SANS Institute, and Udemy offer a vast array of cybersecurity courses, allowing individuals to acquire knowledge and skills at their own pace.
- Hands-on labs and simulations: Practical experience is crucial for developing real-world skills. Training programs often include hands-on labs and simulations that allow participants to practice their skills in a safe environment, mirroring real-world scenarios.
Bridging the Cybersecurity Skills Gap
Several strategies can help bridge the cybersecurity skills gap:
- Invest in educational programs: Funding educational initiatives at universities and colleges focused on cybersecurity can create a pipeline of qualified professionals.
- Support and encourage cybersecurity career paths: Creating awareness about the career opportunities in cybersecurity can attract talented individuals to the field.
- Implement mentorship programs: Experienced cybersecurity professionals can guide and mentor aspiring security professionals.
- Incentivize and reward security certifications: Offering incentives for obtaining cybersecurity certifications can encourage professionals to acquire the necessary skills.
Emerging Technologies and Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity Data And Statistics
The rapid advancement of technologies like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various sectors. However, these innovations also introduce novel cybersecurity challenges that require proactive strategies and robust defenses. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate security measures are critical for mitigating risks and ensuring the continued safety and reliability of these transformative technologies.
Impact of Cloud Computing on Cybersecurity Practices
Cloud computing has fundamentally altered how data is stored and processed, offering scalability and flexibility. However, this shift brings new security considerations. Organizations must carefully manage access controls and ensure data encryption within the cloud environment. Security breaches in cloud infrastructure can have devastating consequences for businesses and individuals. Implementing robust security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and regular security audits, is crucial for protecting sensitive data residing in the cloud.
The shared responsibility model between cloud providers and customers necessitates clear understanding of each party’s security obligations.
Cybersecurity Challenges Posed by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming industries, but their use also introduces unique cybersecurity challenges. Malicious actors can leverage these technologies to create sophisticated attacks, making detection and response more complex. AI-powered tools can enhance threat detection and response, but they also require careful development and deployment to avoid unintended consequences or biases. Examples include the creation of deepfakes for fraudulent activities or the development of AI-driven malware.
The potential for AI to be used for both good and evil necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its implications for cybersecurity.
Importance of Blockchain Technology in Enhancing Data Security
Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature presents opportunities for enhancing data security. Its cryptographic principles can ensure data integrity and transparency. Secure data storage and transfer are possible with blockchain, and it can strengthen trust between parties in digital transactions. Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology can prevent single points of failure, making systems more resilient to attacks. However, blockchain is not a panacea, and vulnerabilities in smart contracts or consensus mechanisms can still pose risks.
A robust security framework is necessary to leverage the benefits of blockchain while mitigating its inherent risks.
Cybersecurity Implications of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices has expanded the attack surface, creating new avenues for cybercriminals. The interconnected nature of these devices means a breach in one can potentially compromise the entire network. Vulnerabilities in poorly secured IoT devices can be exploited to gain access to sensitive data or disrupt critical infrastructure. Security protocols must be built into the design and development of IoT devices from the outset.
Regular updates and patches are essential to address known vulnerabilities. Securing IoT devices requires a layered approach, including device-level security, network security, and cloud security.
Different Approaches to Securing Emerging Technologies
Various approaches are being employed to secure emerging technologies. One approach focuses on developing robust security protocols and standards for each technology. Another approach emphasizes proactive threat intelligence and vulnerability assessment. A third approach involves fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders, researchers, and policymakers to address the evolving challenges. A comparative analysis of different approaches highlights the need for a multi-faceted strategy that combines technical solutions, proactive security measures, and international cooperation.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the cybersecurity landscape is dynamic and complex, demanding constant vigilance and proactive measures. Understanding the statistics and trends presented here is paramount for organizations and individuals alike. This overview underscores the importance of staying informed, investing in robust security measures, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness. The future of cybersecurity requires a collaborative effort, combining technological advancements with human ingenuity to combat the ever-evolving threat landscape.