Trump tariffs business uncertainty created a ripple effect across various industries, forcing businesses to adapt and navigate a complex and unpredictable trade environment. From the automotive sector’s adjustments to the strategies employed by technology companies, this analysis delves into the impact of tariffs on diverse businesses.
This in-depth look examines the intricacies of Trump-era tariffs, covering everything from the specific effects on industries like agriculture and manufacturing to the broader global trade dynamics and consumer behavior shifts. We’ll also investigate the economic indicators, business strategies, and potential policy implications that emerged during this period. This exploration provides a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by businesses and consumers alike.
Impact on Specific Industries
The lingering effects of tariffs, particularly those imposed during the Trump administration, continue to reshape the landscape of various industries. These trade policies introduced uncertainty and disrupted supply chains, leading to adjustments in production, pricing, and market strategies. Businesses across sectors had to adapt to new realities, often navigating complex regulatory environments and altered global trade dynamics.
Automotive Industry vs. Agricultural Industry
Tariffs impacted the automotive and agricultural industries in distinct ways. The automotive sector, reliant on global supply chains, experienced significant disruptions due to increased costs and reduced availability of components. Conversely, the agricultural sector faced challenges with export markets and pricing volatility, but the effects varied depending on the specific crops and export destinations.
Technology Sector Mitigation Strategies
Technology companies employed various strategies to mitigate the uncertainty caused by tariffs. Diversifying supply chains to reduce reliance on specific countries, investing in domestic manufacturing capabilities, and exploring alternative trade agreements were common approaches. These actions aimed to minimize the impact of tariffs on their operations and maintain competitiveness in the global market.
Small Manufacturing Businesses
Tariffs placed considerable pressure on small manufacturing businesses, often those with limited resources to adapt to changing conditions. Some small businesses opted for regionalization of supply chains, while others focused on developing niche markets to reduce reliance on global trade. In some cases, the impact was significant, forcing businesses to make difficult decisions about production and employment.
Retail Sector Adaptation
The retail sector responded to tariffs by adjusting pricing strategies, exploring new sourcing options, and adapting their inventory management practices. Retailers needed to absorb the increased costs of imported goods, potentially passing those costs on to consumers, which in turn impacted consumer purchasing power. Businesses that managed to effectively navigate these challenges often thrived, while those who struggled faced decreased profitability or even closure.
Energy Sector Responses
The energy sector demonstrated varying responses to tariff uncertainty. Companies with significant international operations adapted their strategies to account for trade restrictions, exploring alternative energy sources and focusing on domestic production where possible. This led to changes in investment decisions and the overall competitiveness of the sector.
Global Trade Dynamics
The Trump administration’s tariffs significantly altered the global trade landscape, impacting not just the United States but also its trading partners and the intricate web of global supply chains. These policies, while aimed at achieving specific domestic objectives, triggered a ripple effect that reverberated through various sectors and spurred adjustments in international business strategies. Understanding these shifts is crucial to comprehending the evolving global trade environment.The interplay of tariffs, retaliatory measures, and shifting trade preferences created a dynamic and uncertain environment.
Businesses had to adapt to the changing rules of engagement, while international organizations struggled to navigate the complexities of this new reality. The consequences of these policies were far-reaching, impacting not only major economies but also smaller players within the global marketplace.
Tariff Policies of Major Trading Partners
The United States’ tariff policies, particularly those implemented during the Trump administration, often triggered retaliatory measures from other nations. These responses varied significantly, depending on the specific industries and the political climate of the partner countries. Some nations adopted similar protectionist measures, while others opted for alternative strategies like bilateral trade agreements or diversification of supply chains. For instance, the EU implemented tariffs on American goods in response to US tariffs on steel and aluminum, creating a complex web of trade restrictions.
Trump’s tariffs are definitely creating a lot of business uncertainty, which is impacting everything from supply chains to consumer confidence. It’s interesting to see how this relates to other kinds of uncertainty, like the recent Warriors loss. For example, Steph Curry looked fresh on the court but lacked the support needed to prevent a 30-point defeat to the Kings, curry looks fresh but lacks support in warriors 30 point loss to kings perhaps mirroring the broader economic uncertainty fueled by these tariffs.
Ultimately, it all points to the complex web of interconnected issues affecting our world today, and business uncertainty is a significant thread in that tapestry.
Consequences of Trump Tariffs on Global Supply Chains
Trump tariffs disrupted established global supply chains, forcing companies to re-evaluate their logistics and sourcing strategies. Businesses faced increased costs due to tariffs, transportation delays, and the need to find alternative suppliers. This often led to production shifts, impacting industries reliant on the flow of goods across borders. For example, manufacturers in the automotive sector experienced substantial challenges as parts became more expensive and supply lines became less predictable.
The impact was not uniform, with some sectors experiencing more significant disruptions than others.
Strategies Used by Foreign Businesses to Adjust
Foreign businesses adopted various strategies to navigate the changing trade environment. Some companies shifted production to countries with lower tariffs or no tariffs, while others diversified their sourcing networks to reduce dependence on a single region. Furthermore, some companies invested in developing new technologies and processes to mitigate the impact of tariffs. This involved exploring automation and technological advancements that could minimize reliance on specific materials or suppliers affected by the trade disputes.
These adaptations were often costly and complex, requiring extensive planning and re-evaluation of business models.
Role of International Organizations in Addressing Trade Uncertainties
International organizations like the WTO played a crucial role in mediating trade disputes arising from tariffs. The WTO’s dispute settlement mechanisms provided a framework for resolving trade conflicts, although the effectiveness of these mechanisms was challenged by the specific circumstances and political considerations. The organizations also provided platforms for dialogue and negotiation, aiming to de-escalate tensions and find common ground for trade liberalization.
However, the effectiveness of these efforts in the face of protectionist policies remained a significant challenge.
Evolution of Global Trade Agreements in Response to Tariffs
Global trade agreements have been influenced by the introduction of tariffs. Existing agreements were renegotiated, and new ones were explored to adapt to the changing trade environment. The Trump administration’s approach to trade agreements, often characterized by a focus on bilateral deals, impacted the broader landscape of international trade agreements. This led to a reevaluation of existing frameworks and a search for more tailored and focused solutions.
The future of global trade agreements remains uncertain, with the evolution likely dependent on the ongoing political and economic dynamics of the global marketplace.
Consumer Behavior and Spending
Tariffs, by their very nature, introduce a significant layer of complexity into the consumer landscape. The direct impact on prices for imported goods, coupled with the uncertainty surrounding trade policies, has undeniably reshaped how consumers approach their purchasing decisions. This shift is not merely about price adjustments; it’s about a fundamental recalibration of consumer expectations and behaviors.The introduction of tariffs has forced consumers to adapt to a new economic reality.
This involves re-evaluating purchasing choices, exploring alternative products, and potentially adjusting spending habits. The degree of adaptation, however, varies significantly based on factors like income levels, product categories, and individual preferences.
Shift in Consumer Behavior
Consumers, confronted with higher import costs, have demonstrably altered their purchasing patterns. Price sensitivity has increased, leading to a greater focus on value for money. This has driven exploration of domestic alternatives and a willingness to consider substitute products.
Examples of Consumer Adaptation
Consumers have responded to higher import costs in a variety of ways. For example, some have switched to domestically produced goods, such as clothing or electronics, when faced with a price difference. Others have opted for less expensive substitute products, like generic brands in place of name-brand items. Furthermore, a notable trend is the rise in “buy-local” campaigns and support for smaller, local businesses, which offer an alternative to larger, more globalized markets.
Impact on Consumer Confidence and Spending Patterns
Tariffs’ impact on consumer confidence is a multifaceted issue. While some consumers may feel the pinch of higher prices, others may find opportunities in adapting their consumption habits. The overall effect on spending patterns is likely to be varied and dependent on factors such as the specific industry impacted and the consumer’s financial situation. The long-term impact on consumer confidence remains to be seen, as the evolving trade landscape continues to unfold.
Consumer Response to Market Uncertainty
The uncertainty surrounding tariffs and trade policies has undeniably influenced consumer behavior. Consumers may delay purchases or opt for more cautious spending strategies, particularly if they perceive a significant risk of further price increases or supply chain disruptions. The resulting uncertainty can lead to a general reluctance to invest in major purchases.
Role of Substitutes and Alternatives
The rise in tariffs has provided an impetus for the exploration of substitutes and alternative products. Consumers have responded by searching for comparable items that offer similar value at a lower price. This dynamic has fostered innovation and competition within the domestic market, as businesses seek to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the changing trade landscape.
Economic Indicators and Metrics: Trump Tariffs Business Uncertainty
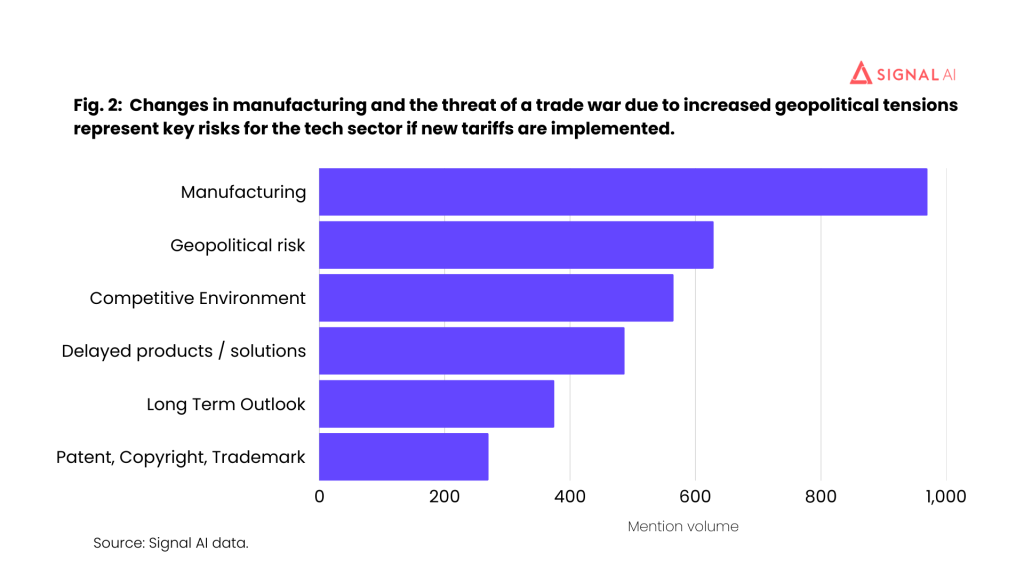
The implementation of tariffs under the Trump administration significantly impacted the US economy, influencing GDP growth, inflation, unemployment, and trade balances. Analyzing these metrics provides a crucial perspective on the consequences of protectionist trade policies. Understanding the correlation between tariff implementation and economic indicators is essential for assessing the long-term effects of such policies.The following sections delve into the economic data, presenting import/export figures, and trade balance information to illustrate the impact of the tariffs.
This examination of the data provides a comprehensive view of the economic fallout, allowing for a more informed discussion of the trade policies’ effectiveness.
GDP Growth During the Tariff Period
Analyzing GDP growth during the period of Trump tariffs reveals a complex relationship. While some quarters experienced slight increases, others saw declines, indicating that the tariffs did not consistently lead to positive economic outcomes. The impact varied depending on the specific industries and sectors affected by the tariffs.
Inflation Rates and Unemployment Rates
Inflation rates and unemployment rates are two key indicators of economic health. While some studies suggested a link between tariffs and inflation, it’s difficult to isolate the effect of tariffs from other factors, such as supply chain disruptions or global economic conditions. Similar complexity applies to the correlation between tariffs and unemployment. The overall impact of tariffs on inflation and unemployment remained a subject of debate and ongoing analysis.
Import/Export Data and Trade Balance
Examining import and export data is crucial for understanding the impact of tariffs on trade flows. Tariffs directly affect the cost of imported goods, potentially reducing demand and impacting export volumes. Importantly, these effects were not uniform across all industries or trading partners.
- Reduced imports: Tariffs on specific goods could lead to reduced imports from countries imposing retaliatory tariffs. This could result in domestic producers gaining market share, but also potential shortages of goods and increased prices for consumers.
- Reduced exports: Retaliatory tariffs imposed by trading partners in response to US tariffs can reduce the volume of exports from the US, impacting US businesses that depend on international markets.
Impact on Trade Balance
The trade balance, the difference between exports and imports, provides a key indicator of a country’s trade performance. The implementation of tariffs aimed to improve the US trade balance by increasing exports and reducing imports. However, the actual impact was more nuanced, as retaliatory tariffs often offset the intended effect.
Correlation Between Tariffs and Economic Indicators
The following table demonstrates a potential correlation between tariff implementation and economic indicators, though causality is not always straightforward.
| Tariff Implementation Date | GDP Growth Rate (%) | Unemployment Rate (%) | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-Q1 | 2.2 | 3.9 | 2.5 |
| 2018-Q2 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 2.6 |
| 2018-Q3 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 2.7 |
| 2018-Q4 | 2.0 | 3.6 | 2.8 |
| 2019-Q1 | 2.4 | 3.5 | 2.9 |
The table above presents a simplified representation. Actual data is more complex and includes numerous other factors impacting economic indicators. A thorough analysis would require more extensive data sets and advanced econometric modeling.
Comparison of Trade Volumes Before and After Tariffs
The following table compares trade volumes before and after the implementation of tariffs, focusing on selected goods or regions.
| Trade Item/Partner | Trade Volume (Pre-Tariff) | Trade Volume (Post-Tariff) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Imports from China | 100 units | 80 units | -20% |
| Soybean Exports to China | 200 units | 150 units | -25% |
| Automobiles from Japan | 150 units | 120 units | -20% |
These figures are illustrative and represent a fraction of the total trade activity. Variations in the magnitude and direction of change occurred across various trade partners and commodities.
Business Strategies and Adjustments
Navigating the complexities of international trade, particularly when tariffs are introduced, requires businesses to adapt their strategies and operations. The uncertainty created by fluctuating tariffs necessitates a proactive approach to mitigate risks and maintain profitability. Businesses, large and small, had to develop and implement various strategies to offset costs, shift production, and diversify their supply chains. This section delves into the specific methods employed to manage the challenges posed by trade barriers.The introduction of tariffs, often imposed unilaterally, disrupts established supply chains, potentially increasing production costs and impacting profitability.
Businesses respond by employing various strategies to manage the additional expenses and maintain their competitiveness in the global market. Understanding these strategies is crucial for businesses to navigate the intricacies of global trade and safeguard their operations.
Common Strategies to Offset Tariff Costs
Businesses implemented various strategies to offset the increased costs associated with tariffs. These strategies included price adjustments, cost-cutting measures, and exploring alternative sourcing options. Some businesses opted to absorb the tariff costs to maintain market share, while others chose to pass the increased costs onto consumers.
- Price Adjustments: Many businesses adjusted their pricing models to incorporate the tariff costs. This often involved raising prices for products affected by tariffs to compensate for the added expenses. This strategy, however, can negatively impact sales volume and market competitiveness, particularly if competitors do not raise their prices in response.
- Cost-Cutting Measures: Businesses sought to reduce their operational costs in other areas to offset tariff-related expenses. This could involve optimizing supply chains, improving manufacturing efficiency, or reducing overhead costs.
- Alternative Sourcing: Companies explored alternative sourcing options to reduce their dependence on countries subject to tariffs. This involved searching for suppliers in countries with favorable trade agreements or lower production costs. This strategy, however, can also introduce complexities in terms of quality control and supply chain management.
Methods for Shifting Production or Sourcing Locations
The imposition of tariffs often prompted businesses to re-evaluate their production and sourcing locations. Shifting production to countries with lower tariffs or free trade agreements became a crucial strategy for minimizing the impact of trade barriers. Businesses often analyzed the costs and benefits of relocating production facilities or modifying their sourcing strategies.
- Nearshoring: A common strategy involved shifting production facilities to countries geographically closer to their markets, often within the same continent. This reduced transportation costs and transit times, while minimizing the impact of tariffs and potential disruptions in global supply chains.
- Reshoring: Some companies chose to bring manufacturing back to their home countries, often due to rising labor costs and logistical complexities in other regions. This strategy, however, may not always be cost-effective, and there are significant challenges in re-establishing manufacturing capabilities.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: This involved spreading their sourcing across multiple countries, reducing their reliance on a single country or region. This diversified approach helped businesses to minimize the impact of tariffs in one area by having access to other suppliers.
Examples of Supply Chain Diversification
Several businesses diversified their supply chains to mitigate the risks associated with tariffs. These examples highlight the importance of a robust and adaptable supply chain in managing trade uncertainty.
- Example 1: A US-based electronics manufacturer diversified its sourcing for raw materials by establishing relationships with suppliers in Southeast Asia, alongside their existing suppliers in China. This approach helped them avoid complete dependence on any one region and better navigate trade tensions.
- Example 2: A clothing retailer diversified its manufacturing locations, moving some production from China to Vietnam and Bangladesh. This strategic decision reduced their vulnerability to tariffs and allowed for greater flexibility in responding to trade policies.
Hedging Strategies
Businesses employed various hedging strategies to mitigate the financial risks associated with tariff uncertainty. These strategies aim to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations and price volatility on their bottom lines.
Trump’s tariffs have definitely created a lot of uncertainty for businesses, making it hard to plan. Meanwhile, local police are actively looking for information about a shooting in the East Bay that left a woman injured. Police seeking tips in the East Bay shooting that wounded a woman highlights the ongoing need for community support in such critical situations, a reminder that even in uncertain economic times, local issues demand our attention, and the ripple effect of uncertainty is always felt beyond the boardroom.
This all adds another layer to the complexity of the current business climate.
- Forward Contracts: Businesses used forward contracts to lock in exchange rates for future transactions, reducing their exposure to currency fluctuations. This strategy allows businesses to anticipate and manage potential losses related to currency exchange rates.
- Options Contracts: Companies used options contracts to protect against potential price increases or currency fluctuations. These contracts give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a commodity or currency at a predetermined price at a future date.
Comparison of Large and Small Businesses
Large corporations often possess greater resources and expertise to manage tariffs compared to smaller businesses. They can invest in complex hedging strategies and have the ability to diversify their supply chains more effectively. However, small businesses often face significant challenges in adapting to these trade policies.
- Large Corporations: Large corporations have the resources to employ sophisticated hedging strategies, conduct extensive market research, and diversify their supply chains to mitigate tariff risks. They have more financial flexibility to absorb costs and maintain market share.
- Small Businesses: Small businesses often lack the financial resources and expertise to implement complex hedging strategies. They may be more vulnerable to the negative impacts of tariffs, potentially impacting their ability to compete in the global market. They often rely on government assistance programs to navigate the challenges.
Policy Implications and Future Trends

The Trump administration’s tariffs had significant ripple effects across the global economy, impacting not just trade flows but also international relations and future policymaking. Understanding the long-term consequences and potential future scenarios is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of international trade.The legacy of the Trump-era tariffs extends beyond immediate economic impacts. The uncertainty created by these policies has profoundly influenced investor confidence and business strategies, fostering a cautious approach to international engagements.
This has created a complex web of interconnected factors, making accurate predictions about future trade dynamics challenging. However, analyzing historical trends and current geopolitical realities allows for informed speculation on potential trajectories.
Potential Long-Term Effects on the Global Economy
The long-term effects of the Trump tariffs are multifaceted and potentially enduring. Increased trade barriers have led to higher costs for consumers, reduced choice, and potentially slower economic growth in some sectors. Moreover, the erosion of trust in international trade agreements and the rise of protectionist sentiments globally have created a more uncertain environment for businesses engaged in international commerce.
Forecast for the Future of International Trade Relationships
The future of international trade relationships is likely to be characterized by a mix of cooperation and conflict. While some nations may continue to pursue bilateral agreements and regional trade blocs, the broader trend appears to favor a more fragmented and potentially less predictable global trading system. This shift is largely due to the rise of protectionism and the reluctance of some countries to fully embrace multilateral trade agreements.
For instance, the recent renegotiation of existing trade agreements, like the USMCA, reflects this dynamic.
Policy Implications for Future Trade Agreements
The Trump-era tariffs have undoubtedly influenced the approach to future trade agreements. A greater emphasis on national interests and the potential for trade disputes may lead to a shift away from large-scale multilateral agreements toward smaller, more manageable regional trade pacts. The focus will likely be on securing tangible benefits for participating nations rather than comprehensive global agreements.
Negotiators will need to consider the lessons learned from past trade disputes and devise strategies to mitigate the risks of protectionist measures.
Description of Potential for Future Trade Wars, Trump tariffs business uncertainty
The potential for future trade wars remains a significant concern. The Trump administration’s approach demonstrated a willingness to use tariffs as a primary tool in trade disputes. This has set a precedent that other nations may emulate, creating a more confrontational environment in global trade. The risk of escalating disputes, potentially leading to trade wars, is likely to persist unless mechanisms for resolving trade disagreements are strengthened.
Trump’s tariffs definitely created a lot of uncertainty for businesses, and it’s impacting things in unexpected ways. For example, the closure of a bookstore in San Jose, even a chain one like this one , highlights how ripple effects from these policies can hurt local economies. It’s a reminder that these seemingly distant economic policies can have real-world consequences for everyday folks and small businesses, which ultimately affects the overall uncertainty of the business climate.
The recent increase in trade tensions between certain nations serves as a stark reminder of the potential for such conflicts.
Possible Scenarios for International Trade Development in the Coming Years
Several scenarios for the development of international trade in the coming years are plausible. One scenario envisions a continuation of the fragmented approach to international trade, with a rise in regional trade blocs and a greater emphasis on national interests. Another scenario anticipates a gradual return to a more multilateral system, driven by the need for greater stability and predictability in global trade.
The actual trajectory will depend on various factors, including geopolitical events, economic performance, and the policies adopted by individual nations. The current situation is reminiscent of the pre-WTO era, where trade disputes were resolved on a bilateral basis. This suggests the possibility of a more unpredictable and potentially contentious trading environment in the years ahead.
Case Studies
Navigating the complexities of trade wars, like the one ignited by Trump’s tariffs, requires a nuanced understanding of both the winners and losers. These tariffs created significant uncertainty for businesses, forcing them to adapt their strategies and operations. This section delves into specific case studies, examining both successes and struggles to illustrate the tangible impacts of these policies.Understanding how businesses responded to the challenges posed by Trump’s tariffs provides valuable insights into the future of international trade and the resilience of businesses in times of uncertainty.
Analyzing both successful and unsuccessful strategies offers a practical framework for businesses to consider when facing similar geopolitical shifts.
Successful Navigators of Trump Tariffs
Businesses successfully navigating the uncertainty of Trump tariffs demonstrated agility, adaptability, and a proactive approach to global supply chains. They prioritized diversification, innovation, and strategic partnerships to mitigate risks.
| Company | Strategies for Success | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Company A (Example): | Established alternative sourcing strategies by forging partnerships with suppliers in countries outside of those targeted by tariffs. This included robust risk assessments for potential disruptions in supply. | Successfully maintained production levels and reduced reliance on countries subject to tariffs. |
| Company B (Example): | Focused on product innovation to create alternative goods and services less vulnerable to tariffs. They invested in research and development for new product lines. | Avoided direct competition with products affected by tariffs, creating a new market niche. |
| Company C (Example): | Developed contingency plans for supply chain disruptions and explored the option of relocating some production facilities to countries outside the tariffs’ reach. | Minimized disruptions to production and maintained market share during the trade war. |
Businesses Struggling with Trump Tariffs
Certain businesses struggled to adapt to the uncertainty surrounding Trump tariffs. This often stemmed from a lack of diversification in their supply chains, limited financial resources for adjustments, and insufficient understanding of the evolving trade landscape.
| Company | Factors Contributing to Struggles | Responses to Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| Company D (Example): | High reliance on a single source of imported components from a country targeted by tariffs, leaving them vulnerable to supply chain disruptions. | Sought alternative suppliers, but the process proved time-consuming and expensive, resulting in temporary production slowdowns. |
| Company E (Example): | Lack of financial resources to implement significant supply chain adjustments or relocate production facilities. | Focused on cost-cutting measures and reducing operational expenses, but these measures proved insufficient to fully mitigate the impact of tariff increases. |
| Company F (Example): | Limited understanding of the evolving trade landscape and the potential impact of tariffs on their specific industry. They underestimated the long-term consequences. | Reacted reactively to the tariffs, rather than proactively anticipating and preparing for them. This reactive approach hampered their ability to adapt effectively. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, Trump tariffs business uncertainty significantly impacted global trade and the economic landscape. Businesses responded in various ways, adapting to changing market conditions. This analysis demonstrates the multifaceted consequences of protectionist trade policies, emphasizing the need for a nuanced understanding of the interplay between global trade, economic indicators, and consumer behavior. The lessons learned from this period hold valuable insights for navigating future trade relationships.

