Best process management software is crucial for streamlining workflows and boosting efficiency across any industry. This guide dives deep into everything you need to know about choosing the perfect software for your needs, from understanding different types and features to evaluating options, implementing them effectively, and integrating them with your existing systems. We’ll explore real-world success stories, future trends, and specific industry applications, equipping you with the knowledge to make the right decision.
From defining core functionalities and evaluating various software solutions to implementing best practices and integrating with existing systems, this guide covers the entire process. We’ll delve into the nuances of choosing the right software for your specific needs, considering factors like budget, user-friendliness, and integration capabilities. We’ll provide valuable insights into future trends and emerging technologies shaping the process management landscape.
Introduction to Process Management Software
Process management software streamlines workflows, automates tasks, and improves efficiency across various business functions. It acts as a central hub for managing processes, ensuring consistency, and optimizing productivity. This software facilitates tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and ultimately, driving better business outcomes.By centralizing information and automating steps, process management software enables businesses to improve collaboration, reduce errors, and enhance overall operational effectiveness.
Finding the best process management software can be tricky, but it’s crucial for efficiency. Just like Steph Curry’s struggles in the Warriors’ recent loss to the Pacers at home ( steph curry struggles warriors loss to pacers at home ), sometimes a breakdown in processes can lead to disappointing results. Ultimately, the right software streamlines workflow and helps avoid similar pitfalls in your own operations.
This translates to significant cost savings and a more responsive and adaptable organization.
Definition of Process Management Software
Process management software is a category of applications designed to help businesses define, document, manage, and optimize their processes. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing workflows, tasks, and other operational aspects. They facilitate tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and ultimately, driving improvements in efficiency and effectiveness.
Key Benefits of Using Process Management Software
Process management software offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced errors, improved communication, and enhanced decision-making. These benefits are realized through streamlined workflows, automated tasks, and centralized data management. This ultimately leads to higher productivity and better business outcomes.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation of repetitive tasks frees up employees to focus on more strategic work, leading to increased productivity.
- Reduced Errors: Standardized processes and automated checks minimize human error, ensuring accuracy and consistency in operations.
- Enhanced Communication: Centralized platforms improve communication among teams, fostering better collaboration and transparency.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Tracking key metrics and performance indicators provides valuable insights for informed decision-making, leading to more effective strategies.
Industries Benefiting Most from Process Management Software
Numerous industries can significantly benefit from process management software. These include manufacturing, healthcare, customer service, and finance. The consistent and reliable nature of this software helps these industries achieve a higher level of quality and customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing: Streamlining production processes, optimizing inventory management, and tracking quality control metrics.
- Healthcare: Managing patient records, scheduling appointments, and improving communication between departments.
- Customer Service: Automating ticket resolution, tracking customer interactions, and improving response times.
- Finance: Managing transactions, automating financial reporting, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Types of Process Management Software
Various types of process management software cater to specific needs and functions. These include workflow management, task management, and project management software.
- Workflow Management Software: Designed for automating and managing sequential steps within a process. This type of software is particularly useful for industries with highly structured processes.
- Task Management Software: Focuses on organizing and assigning tasks to individuals, facilitating collaboration and tracking progress. These tools are commonly used for projects involving multiple teams or individuals.
- Project Management Software: Provides tools for planning, tracking, and managing projects, including resource allocation and progress reporting. This type of software is particularly useful for complex projects with multiple dependencies.
Comparison of Process Management Software Categories
The following table provides a comparison of different process management software categories based on their features and pricing models.
| Software Category | Key Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Management | Process visualization, task assignment, automation, and reporting. | Typically tiered pricing based on user count and features. |
| Task Management | Task assignment, deadlines, reminders, and collaboration tools. | Often a subscription-based model with varying pricing tiers. |
| Project Management | Project planning, resource allocation, progress tracking, and collaboration. | Pricing varies depending on the number of users and project features. |
Key Features of Effective Process Management Software
Choosing the right process management software is crucial for streamlining workflows and boosting overall efficiency. A robust system goes beyond simple task management; it needs to facilitate collaboration, automate repetitive steps, and provide actionable insights. This detailed look at key features will help you navigate the market and select the software best suited for your needs.Effective process management software isn’t just about organizing tasks; it’s about optimizing the entire process.
It should empower teams to work together seamlessly, identify bottlenecks, and improve performance across the board. This comprehensive approach ensures that processes are not only efficient but also adaptable to changing business needs.
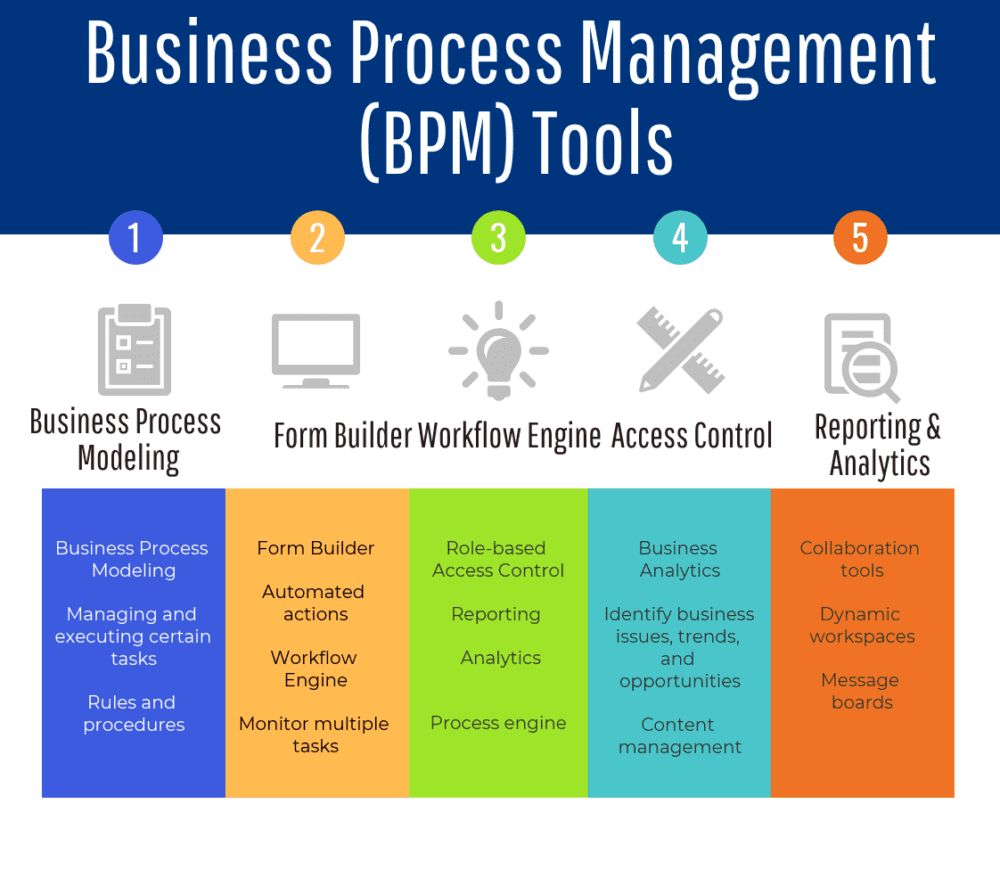
Essential Features for Efficient Workflow Management
Workflow management is the backbone of any successful process. Software should allow for the clear definition and visualization of steps, ensuring everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. This clarity prevents errors and misunderstandings, resulting in a more streamlined workflow. Furthermore, the software should support various workflow types, from simple linear sequences to complex branching logic. This flexibility is crucial for adapting to changing requirements and maintaining a responsive process.
Crucial Features for Automating Tasks and Processes
Automation is key to reducing manual errors and freeing up valuable time for more strategic work. Essential features include automated task assignments, notifications, and reminders. This ensures that tasks are completed on time and that team members are kept informed of progress. The ability to integrate with existing systems, like CRM or accounting software, is also critical for seamless data flow.
Furthermore, advanced features like robotic process automation (RPA) can automate repetitive tasks, significantly improving efficiency and reducing human error. For example, a process management tool could automatically send an email reminder to a team member when a task is due, or automatically generate reports based on collected data.
Importance of Reporting and Analytics Capabilities
Effective process management software should provide comprehensive reporting and analytics. Data-driven insights are critical for identifying bottlenecks, measuring performance, and making informed decisions. The software should allow users to generate reports on key metrics, such as task completion times, process cycle times, and resource utilization. Dashboards that visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) can further enhance understanding and decision-making.
For example, a real-time dashboard could highlight areas where processes are lagging and provide suggestions for improvement.
Features Enabling Collaboration and Communication Among Teams
Collaboration and communication are essential for successful process management. Software should provide features like shared task lists, real-time updates, and discussion forums to facilitate seamless communication between teams. This fosters a collaborative environment, ensuring that everyone is aligned on tasks and goals. Features such as version control and document sharing further enhance collaboration, especially for projects involving multiple contributors.
For instance, a project management tool with a built-in messaging system can keep teams informed about updates and issues, leading to better collaboration and quicker problem-solving.
Table Outlining Features That Distinguish Top-Tier Process Management Software
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Visualization | Clearly depicts the steps and stages of a process. | Ensures everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. |
| Task Automation | Automates repetitive tasks like assignments, notifications, and reminders. | Reduces manual errors and frees up time for strategic tasks. |
| Reporting & Analytics | Provides comprehensive reports and dashboards on key metrics. | Enables data-driven decision-making and performance improvement. |
| Collaboration Tools | Facilitates communication, shared task lists, and real-time updates. | Enhances teamwork and ensures everyone is on the same page. |
| Integration Capabilities | Integrates with existing systems like CRM and accounting software. | Ensures seamless data flow and avoids data silos. |
Evaluating Software Options: Best Process Management Software
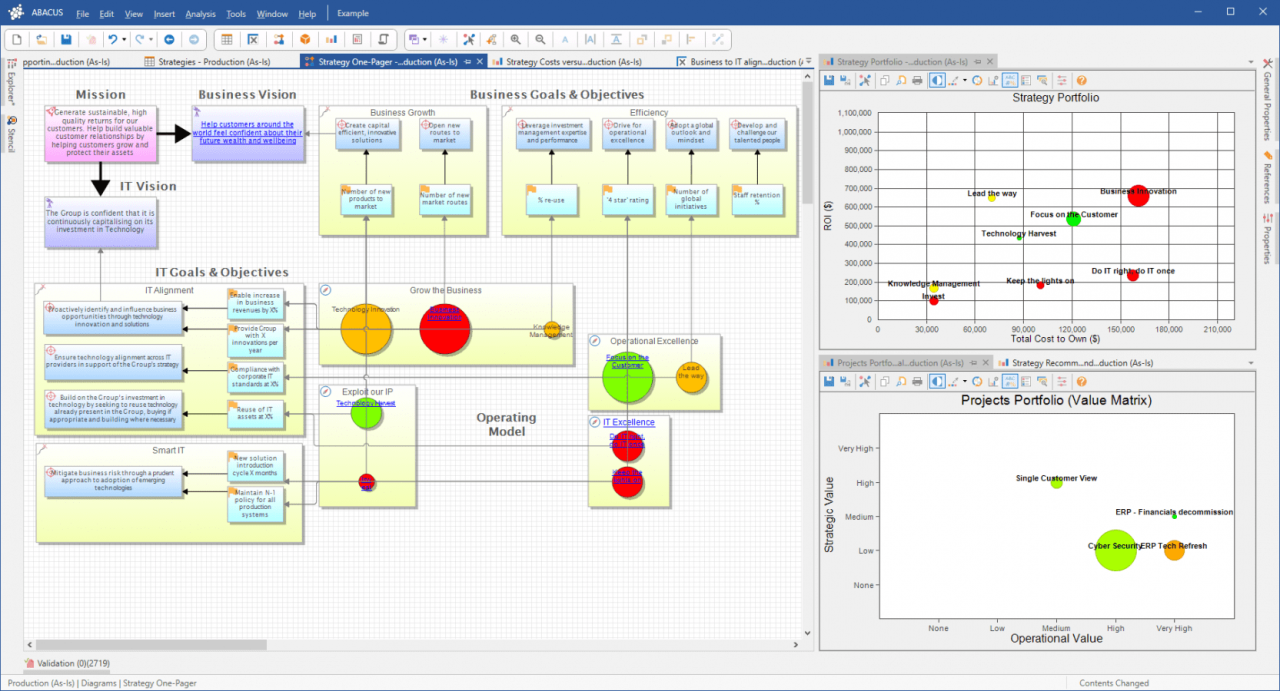
Choosing the right process management software is crucial for streamlining operations and achieving desired outcomes. A poor fit can lead to wasted resources and decreased efficiency. Thorough evaluation, considering various factors, is paramount before making a commitment. This involves comparing leading solutions, understanding pricing models, and assessing the software’s usability.Evaluating process management software isn’t just about finding the cheapest option; it’s about finding the best solution for your specific needs.
The most effective software will integrate seamlessly with existing systems, offer a user-friendly interface, and provide robust reporting features. This process requires careful consideration of not only the features but also the vendor’s reputation, customer support, and the overall value proposition.
Comparing Leading Process Management Software Solutions
Different process management software solutions cater to varying needs and budgets. Some focus on specific industries, while others offer a more generalized approach. Key considerations include the software’s capabilities in automating tasks, tracking progress, and facilitating collaboration among teams. This analysis helps to narrow down the options to those most appropriate for your organization’s requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Software
Several critical factors influence the selection of process management software. These include scalability, customization options, integration capabilities, and security measures. Consider how the software will adapt to future growth, the level of flexibility required for modifications, and its ability to integrate with existing systems. The security of sensitive data is paramount, and the chosen software should adhere to industry best practices.
- Scalability: The software should be capable of accommodating future growth in terms of users, data volume, and process complexity. Look for solutions with modular designs to enable easy expansion and adaptation to changing business needs.
- Customization Options: Process workflows are often unique to each organization. The software should allow for customization to fit specific needs and procedures. The ability to tailor forms, fields, and workflows is crucial for optimal efficiency.
- Integration Capabilities: Smooth integration with existing systems, such as CRM, ERP, and other business applications, is vital for data consistency and process flow. Poor integration can lead to redundant data entry and wasted time.
- Security Measures: Data security is paramount. The chosen software should implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information and comply with industry regulations.
Pricing Models for Process Management Software
Process management software pricing varies significantly based on features, user licenses, and support packages. The most common models include per-user licensing, tiered pricing plans, and subscription models.
- Per-user licensing: This model charges a fee for each user accessing the software. It’s straightforward but can be costly for organizations with a large workforce.
- Tiered pricing plans: These models offer different packages with varying features and user limits. The price increases with the addition of advanced features and user capacity.
- Subscription models: This model charges a recurring fee for access to the software and its updates. This provides predictable costs and ensures access to the latest versions.
Importance of User-Friendliness and Intuitive Interfaces
A user-friendly interface is essential for efficient adoption and sustained usage of the software. Complex interfaces can lead to user frustration and decreased productivity. Intuitive design reduces the learning curve and empowers users to quickly master the software’s functionality.
Software Solutions Comparison Table
| Software Solution | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Solution A | Excellent integration capabilities, robust reporting features, and a user-friendly interface. | Limited customization options and higher price point compared to some competitors. |
| Solution B | Highly customizable, offering extensive features for complex processes. | Steeper learning curve, potentially requiring more training and support for users. |
| Solution C | Affordable pricing model, suitable for smaller teams, good basic features. | Limited customization and integration options, potentially lacking advanced reporting capabilities. |
Implementing Process Management Software
Successfully implementing process management software is a critical step in optimizing workflows and achieving business goals. It’s not just about purchasing the software; it’s about seamlessly integrating it into your existing operations, training your team, and managing the inevitable change. This requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and a commitment to ongoing improvement.Effective implementation isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. The specific strategies depend on the complexity of your existing processes, the size of your organization, and the chosen software’s capabilities.
However, certain best practices consistently contribute to smooth transitions and successful outcomes.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Careful planning and preparation are crucial for a smooth implementation. This involves a detailed assessment of current processes, identifying areas for improvement, and aligning the software’s features with specific business needs. A phased approach, starting with pilot projects or specific departments, can be invaluable in testing the software and mitigating risks before a full-scale deployment.
Migrating Existing Processes to the New System
A crucial aspect of implementation is transferring existing processes into the new software. This involves mapping out current workflows, identifying key stakeholders, and documenting detailed procedures. Thorough documentation ensures clarity and consistency during the transition. Using templates and guides will help standardize the documentation and facilitate the migration process.
Training Users on the New Software
Comprehensive user training is vital for successful software adoption. Tailored training programs, incorporating hands-on exercises and real-world scenarios, can significantly improve user proficiency. Training should cover both the fundamental features of the software and how they apply to specific job roles. This includes practical demonstrations, interactive tutorials, and ongoing support.
The Role of Change Management in the Implementation Process
Change management plays a significant role in ensuring a positive user experience and minimizing resistance. Communication is key. Regular updates and transparent communication about the project’s progress, benefits, and challenges are vital. Addressing concerns and providing ample support during the transition phase are critical to securing buy-in from all stakeholders.
Integrating the Software with Other Systems
Integrating the process management software with existing systems like CRM, ERP, or accounting software is essential for streamlining operations and achieving a holistic view of business processes. A detailed integration strategy should Artikel the specific data points to be transferred, the methods for data exchange, and the potential technical challenges. A well-defined API (Application Programming Interface) and a clear understanding of the data formats used by each system are critical.
This step often requires collaboration between IT and business process owners. Using pre-built connectors or custom integrations depending on the software’s capabilities can be beneficial in facilitating data exchange.
- A well-defined API (Application Programming Interface) is crucial for seamless integration with other systems.
- Data mapping ensures accurate and consistent data transfer between systems.
- Testing the integration thoroughly, including validation of data transfer, is essential to prevent errors and disruptions.
- Ongoing monitoring and maintenance of the integration are vital to ensure its continued effectiveness.
Case Studies and Success Stories
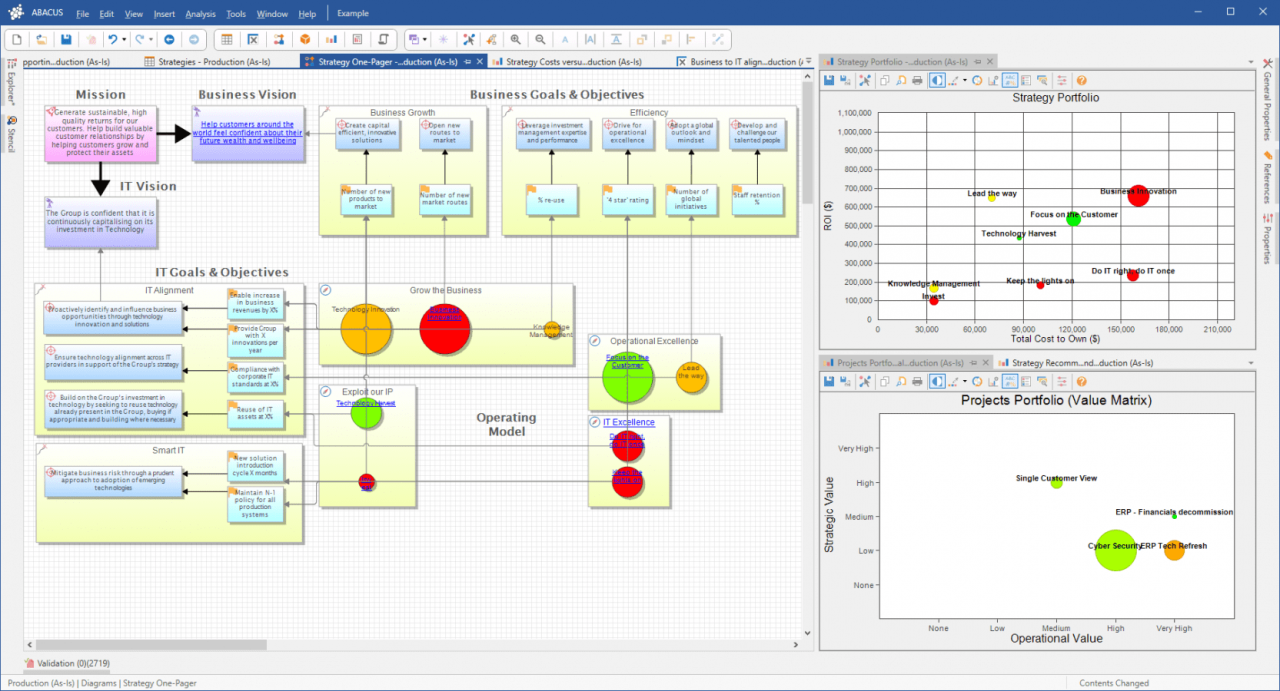
Seeing is believing, right? Real-world examples of how process management software has improved businesses are crucial for understanding its potential. These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits, from streamlined workflows to enhanced collaboration, showcasing how the right software can transform an organization.
Finding the best process management software can be tricky, but it’s crucial for streamlining workflows. Just like the San Jose Giants’ promise of renovation won’t destroy the ballpark’s charm, renovating your processes shouldn’t erase the good parts. Ultimately, the right software will help maintain a smooth, efficient operation, ensuring your team can focus on what matters most.
Successful Process Improvement Projects
Process management software isn’t just about installing a program; it’s about implementing a strategic shift in how work gets done. Successful projects leverage the software to identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and ultimately, improve efficiency. For instance, a manufacturing company using this software might pinpoint inefficiencies in their order fulfillment process, leading to significant reductions in delivery times and increased customer satisfaction.
Another example might be a customer service department, noticing delays in resolving customer inquiries, and using the software to create standardized protocols and allocate resources more effectively.
Measurable Improvements in Efficiency and Productivity
Quantifiable results are the best way to demonstrate the software’s impact. A retail company, for example, could measure a 15% reduction in order processing time after implementing the process management software. This directly translates into increased productivity and a corresponding boost in profitability. The software allows for meticulous tracking of metrics like task completion rates, cycle times, and resource utilization.
These metrics, combined with a clear understanding of the processes involved, help organizations optimize their workflow. Furthermore, organizations can monitor these metrics and make adjustments as needed, leading to continuous process improvement.
Impact on Team Collaboration and Communication
Improved collaboration and communication are often overlooked benefits of process management software. A team managing a complex project can utilize the software to share information, track progress, and assign tasks. This transparency fosters a more collaborative environment and improves team communication, resulting in better outcomes. For instance, a software development team using the software can easily share project updates, track individual contributions, and resolve conflicts proactively, ultimately leading to a smoother and more productive development process.
Summary of Key Case Studies
| Company | Process Improved | Measurable Outcome | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acme Manufacturing | Order Fulfillment | 15% reduction in order processing time, 10% increase in on-time deliveries | Clear task assignment and automated reminders improved efficiency. |
| BrightSparks Solutions | Project Management | 20% decrease in project completion time, 15% increase in team satisfaction | Transparent communication and shared task management fostered better collaboration. |
| Zenith Retail | Customer Service | 12% reduction in average resolution time, 8% increase in customer satisfaction scores | Standardized protocols and automated workflows improved response times and quality of service. |
This table summarizes key aspects of the successful implementation of process management software across various industries. Each case highlights a specific process that was improved and the measurable outcome achieved. The lessons learned provide valuable insights into the practical application of the software and how it can be tailored to specific business needs.
Future Trends in Process Management Software
The landscape of process management software is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-increasing need for efficiency and automation. This dynamic environment demands adaptability and foresight to stay ahead of the curve. This section delves into emerging trends and technologies reshaping the field, highlighting the pivotal role of AI and machine learning, and anticipating the future features that will define process management software.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Process Management
The evolution of process management software is intertwined with the broader technological advancements, including cloud computing, big data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly prevalent, offering scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Big data analytics enables a deeper understanding of process performance and identifies areas for optimization, while IoT integration provides real-time data insights from connected devices, facilitating proactive process adjustments.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Process Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming process management by automating complex tasks, identifying bottlenecks, and predicting potential issues. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, leading to process improvements and increased efficiency. Machine learning algorithms can learn from historical data to predict future outcomes, enabling proactive decision-making and risk mitigation.
For example, a software might analyze historical order fulfillment data to predict potential delays, enabling the company to adjust its inventory levels or shipping schedules in advance.
Emerging Features for Enhanced Automation and Integration
The future of process management software will prioritize seamless automation and integration with other business systems. This includes features like robotic process automation (RPA) for handling repetitive tasks, intelligent process discovery to automate processes without prior documentation, and advanced integration capabilities to connect with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. These integrated solutions provide a holistic view of business operations, enabling better coordination and communication across departments.
Predictions about the Future of Process Management Software
Process management software will increasingly rely on AI and machine learning for predictive analytics and proactive issue resolution. The integration of various business systems will become more seamless, fostering a holistic view of business operations. User-friendly interfaces and intuitive dashboards will become more important for accessibility and widespread adoption. For example, companies might utilize process mining tools that automatically discover and visualize workflows, enabling process improvements without extensive manual effort.
Predicted Advancements in Process Management Software
- Predictive analytics will become even more sophisticated, allowing for proactive identification and mitigation of potential process bottlenecks and issues. This will involve advanced machine learning models analyzing large datasets to anticipate problems and optimize resource allocation.
- AI-powered process discovery will automate the identification and documentation of existing processes, enabling the development of optimized workflows without extensive manual effort. This will involve AI algorithms that can analyze existing data and identify patterns to automatically model and document processes.
- Enhanced integration with other business systems, including ERP, CRM, and supply chain management systems, will lead to more holistic and interconnected views of business operations. This will facilitate real-time data sharing and communication across departments.
- Increased emphasis on user-friendly interfaces and intuitive dashboards will improve accessibility and encourage broader adoption of process management software across different roles and skill levels within an organization.
- Greater emphasis on process mining, using automated tools for discovering, visualizing, and analyzing workflows to enable process improvements. This will involve the integration of AI algorithms to identify inefficiencies and suggest optimization strategies.
Choosing the Right Process Management Software
Selecting the right process management software is crucial for optimizing workflows and achieving business goals. A poorly chosen solution can lead to wasted resources, frustrated employees, and ultimately, decreased efficiency. Carefully evaluating your needs and comparing potential options is paramount to a successful implementation.
Factors Influencing Software Selection, Best process management software
Several factors play a significant role in determining the ideal process management software for a company. These factors include the specific industry, the company’s size and structure, the complexity of existing processes, and the desired level of automation. The software should seamlessly integrate with existing systems and align with the company’s overall strategic objectives. Furthermore, the software’s scalability and future adaptability must be considered to ensure its effectiveness in the long term.
A thorough understanding of these factors is essential for a successful selection process.
Criteria for Selecting the Best Solution
Choosing the right process management software necessitates a clear set of selection criteria. These criteria should reflect the specific needs and priorities of the company. Key criteria include features like workflow automation, reporting capabilities, user interface intuitiveness, and security protocols. The software’s ability to handle data volumes and the flexibility to adapt to future changes are also important considerations.
A robust system will allow for the evolution of processes as the company grows and expands.
Decision Matrix for Evaluating Software Options
A decision matrix provides a structured approach to evaluating different process management software options. This matrix should include columns for key criteria such as cost, features, scalability, integration capabilities, and vendor support. Each software option can then be scored based on its performance against each criterion. This allows for a quantifiable comparison of the various options.
| Criteria | Software Option A | Software Option B | Software Option C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Medium | Low |
| Features | Excellent | Good | Average |
| Scalability | High | Medium | Low |
| Integration | Excellent | Good | Average |
| Vendor Support | Excellent | Good | Average |
| Overall Score | 4.5 | 3.8 | 2.7 |
Creating a Software Evaluation Checklist
Developing a comprehensive checklist is vital for a thorough evaluation of potential process management software. This checklist should encompass all the key features and functionalities required by the company. The checklist should include specific questions regarding user interface, data security, and integration with existing systems. It should also address potential issues such as support options, training materials, and ongoing maintenance costs.
The checklist should be tailored to the company’s unique requirements.
- Identify specific needs and requirements. This includes detailed analysis of current processes, desired improvements, and the types of data to be managed. Each item should be documented with supporting evidence.
- List key features and functionalities. Consider aspects such as workflow automation, reporting, data storage, user access controls, and security protocols.
- Establish evaluation criteria. Quantify criteria with ratings or scoring systems to facilitate objective comparisons. Examples of criteria include ease of use, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and integration capabilities.
- Develop a structured evaluation process. This could involve demonstrations, trials, and consultations with the vendor.
- Document findings and recommendations. Compile detailed notes about each software option, including pros and cons, and provide clear recommendations for selection.
Potential Software Providers
Evaluating potential software providers requires an in-depth analysis of their strengths and weaknesses. This table provides a comparison of some prominent providers in the market.
| Provider | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Robust features, excellent scalability, strong support | High pricing, complex setup |
| Company B | User-friendly interface, affordable pricing, good integration capabilities | Limited features, potentially less robust support |
| Company C | Highly customizable, adaptable to various industries, comprehensive documentation | Steeper learning curve, potential for slow implementation |
Integrating Process Management Software with Other Systems
Connecting your process management software to other crucial business systems is key to unlocking its full potential. A siloed system limits the visibility and efficiency of your entire operation. Seamless integration with CRM, ERP, and other tools creates a unified view of your processes, allowing for real-time data flow and improved decision-making. This is not just about plugging things together; it’s about creating a streamlined, data-driven workflow.
Finding the best process management software can be tough, but it’s crucial for efficiency. It’s inspiring to see how dedicated coaches like the ones leading the Mitty girls volleyball team, who just recently stepped down after a remarkable run leading the Monarchs to consecutive state finals ( mitty girls volleyball coach steps down after leading monarchs to consecutive state finals ), demonstrate meticulous planning and execution.
Ultimately, the right software can streamline any process, just like a successful coaching strategy.
Methods for Integration with CRM, ERP, and Other Systems
Integrating process management software with CRM, ERP, and other business systems often involves leveraging Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). APIs act as translators between systems, allowing them to exchange data seamlessly. This facilitates the flow of information, such as customer data from CRM, order details from ERP, or project progress updates from other platforms, into your process management system.
Different systems have varying API structures, so understanding these structures is crucial for successful integration.
Importance of API Connections and Data Synchronization
API connections are vital for data synchronization. Without them, data remains isolated in individual systems, hindering comprehensive process analysis and reporting. Real-time data synchronization ensures all systems have the most current information, preventing discrepancies and errors. This synchronized data allows for a holistic view of operations, making data-driven decisions easier and faster. For example, a customer service ticket in the process management software can automatically update the CRM record, keeping everyone informed.
Best Practices for Seamless Integration
Implementing best practices is critical for a smooth integration process. This includes careful planning, thorough testing, and continuous monitoring. A well-defined integration strategy, mapping the data flows between systems, is paramount. This will prevent conflicts and ensure that the integration meets the specific needs of the business. Robust testing in a staging environment before full implementation is crucial for identifying and resolving potential issues before impacting live operations.
Thorough documentation of the integration process, including data mapping and API calls, is vital for future maintenance and updates.
How Integration Improves Overall Workflow Efficiency
Integrating process management software with other systems significantly enhances workflow efficiency. By connecting disparate systems, businesses can automate tasks, reduce manual data entry, and eliminate data silos. This leads to faster processing times, reduced errors, and a more streamlined workflow. For example, an order placed through the ERP system can automatically trigger a production process in the process management software, eliminating manual handoffs and delays.
Detailed Flowchart Illustrating a Typical Integration Process
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+ | ERP System |------>| Process Management |------>| CRM System | +-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+ | Order Placed | | Process Initiated | | Order Updated | | | | | | | | | | Data Synchronized| | | | | | | | | +-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
This flowchart depicts a simplified integration process.
The ERP system initiates an order, which triggers a process in the process management software. The process management software then updates the relevant data in the CRM system, keeping all stakeholders informed and on the same page. This streamlined process significantly improves operational efficiency.
Process Management Software for Specific Industries
Process management software is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses across various sectors. Understanding the unique needs and challenges of each industry is crucial for selecting the right software solution. Tailored software solutions can significantly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance compliance, leading to increased profitability and competitive advantage. By addressing specific industry challenges, process management software can streamline operations and unlock new opportunities.
Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry faces unique challenges in maintaining patient safety, regulatory compliance, and managing complex workflows. Process management software can automate tasks such as appointment scheduling, electronic health records (EHR) management, and claims processing, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Implementing robust software solutions can enhance patient care and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare organizations are subject to numerous regulations, including HIPAA and others. Process management software can help ensure compliance by automating documentation and tracking processes, providing audit trails, and facilitating regulatory reporting. Software tools designed for this industry often include features that automate the generation of compliance reports.
- Patient Safety: Streamlined processes and automated workflows reduce errors and improve patient safety. For example, medication dispensing systems integrated with process management software can track medication administration and prevent errors.
- Cost Reduction: Streamlined workflows and automation can reduce administrative overhead, freeing up staff to focus on patient care. Process management software can identify bottlenecks in existing procedures and recommend improvements for cost reduction.
Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry benefits from process management software in optimizing production lines, tracking inventory, and managing quality control. Effective software solutions can reduce production time, improve product quality, and minimize waste.
- Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking and forecasting enable manufacturers to optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency. Process management software often integrates with warehouse management systems for a holistic view of inventory.
- Production Optimization: Software can monitor machine performance, predict maintenance needs, and schedule repairs proactively. This reduces downtime and improves overall production efficiency. Examples include software for scheduling machine maintenance based on usage data.
- Quality Control: Process management software can track quality metrics, identify defects, and implement corrective actions. This ensures higher quality products and reduces rework costs. Tracking and reporting on quality issues and their resolutions are crucial in the manufacturing sector.
Financial Services Industry
The financial services industry requires robust process management software to manage risk, ensure compliance, and improve customer service. Effective solutions help financial institutions comply with regulations and reduce operational risks.
- Compliance Management: Financial institutions are subject to stringent regulatory requirements. Process management software can help automate compliance checks, track regulatory changes, and ensure consistent adherence to standards. Software often integrates with compliance management systems.
- Risk Management: Process management software can identify and mitigate financial risks by automating fraud detection, monitoring transactions, and ensuring compliance with internal policies. These tools often leverage machine learning algorithms for advanced risk assessment.
- Customer Service: Streamlined processes can enhance customer service by automating tasks such as account opening, loan processing, and claim settlements. This leads to quicker response times and increased customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table of Industry-Specific Software
| Industry | Key Challenges | Software Features | Examples of Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Regulatory compliance, patient safety, cost reduction | Automated workflows, EHR integration, compliance reporting | Epic, Cerner, Meditech |
| Manufacturing | Inventory management, production optimization, quality control | Real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, quality control dashboards | SAP, Oracle, Infor |
| Financial Services | Compliance, risk management, customer service | Automated compliance checks, fraud detection, customer relationship management | Salesforce, SAP, Temenos |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, selecting the best process management software is a strategic investment that can significantly improve efficiency and productivity. By carefully considering your specific needs, evaluating available options, and understanding the implementation process, you can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of this powerful tool. Remember to prioritize user-friendliness, integration capabilities, and long-term value when making your decision.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights to help you find the perfect solution.