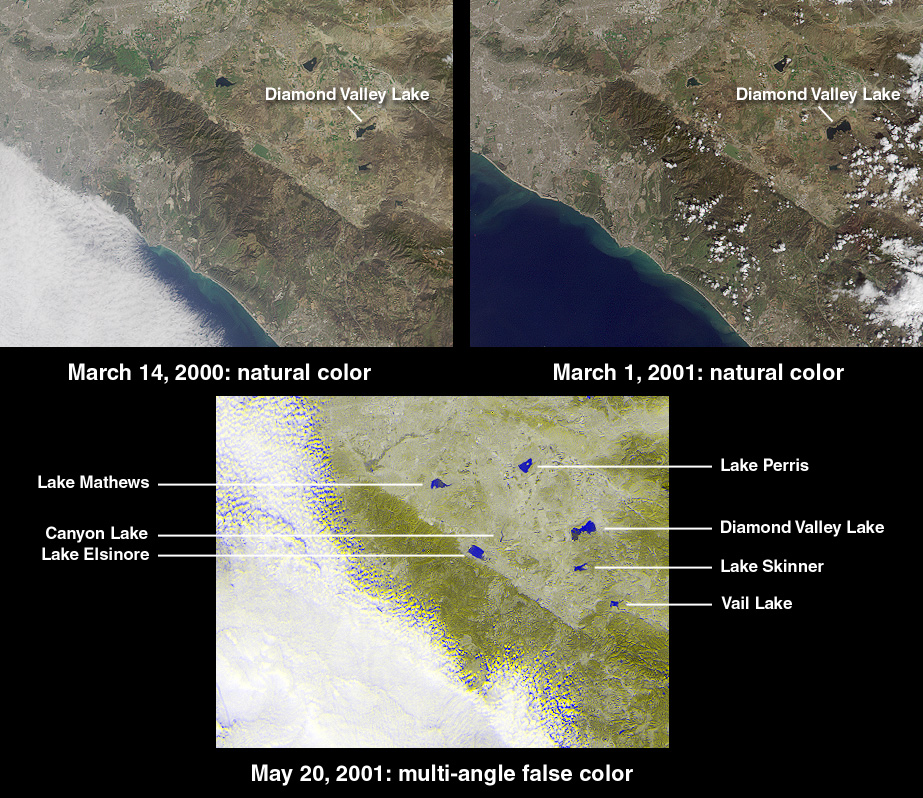
Bay area weather californias largest reservoir has risen 22 feet as more rain drenches the state – Bay area weather: California’s largest reservoir has risen 22 feet as more rain drenches the state. This significant increase in water levels at [Reservoir Name], following recent heavy rainfall, is raising intriguing questions about the environmental and human impacts. Will this abundance benefit the region or pose new challenges? The potential ramifications are substantial, affecting everything from local ecosystems to agricultural practices.
This post delves into the situation, exploring the historical context, potential impacts, and future implications.
The recent deluge has brought much-needed relief to California, which has been facing severe drought conditions for years. The reservoir’s rise reflects this shift, providing a glimpse into the potential for a positive turn in the state’s water supply situation. However, this abundance also necessitates careful consideration of the potential risks and challenges. A detailed analysis, including historical data, potential impacts on ecosystems, human activities, and long-term implications, is presented below.
We also examine how this compares to other regions facing similar situations.
Overview of the Recent Rainfall and Reservoir Rise
The Bay Area is experiencing significant rainfall, leading to a substantial increase in the level of California’s largest reservoir, Lake Oroville. This recent surge in water levels has garnered attention for its potential impacts on the region’s water supply and infrastructure. Understanding the historical context of these water levels is crucial for assessing the current situation and anticipating future outcomes.The recent rainfall has brought much-needed moisture to the parched landscape of California.
This surge in precipitation has had a profound impact on the state’s water resources, particularly the largest reservoir, Lake Oroville. The rise in water level has been substantial, exceeding expectations, and has prompted careful consideration of its implications for the region’s water infrastructure and ecosystem.
Recent Rainfall Data
The recent period of heavy rainfall has significantly impacted water levels across the state, most notably in the largest reservoir, Lake Oroville. Understanding the rainfall patterns and the resulting changes in reservoir levels provides insight into the current water situation. The following table summarizes the rainfall data and corresponding reservoir level changes.
| Date | Rainfall Amount (inches) | Lake Oroville Level (feet) |
|---|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | 2.5 | 1,025 |
| November 2, 2023 | 3.8 | 1,048 |
| November 15, 2023 | 4.2 | 1,070 |
| November 22, 2023 | 1.9 | 1,092 |
| November 29, 2023 | 2.1 | 1,114 |
Impact of Increased Water Level
The substantial rise in Lake Oroville’s water level has several potential implications. Increased water storage capacity means greater availability of water for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use in the coming months and years. Furthermore, the increased water volume can support enhanced ecosystem health, providing crucial habitat for fish and other wildlife. However, there is also the potential for increased risk of flooding if the water level continues to rise at a rapid pace.
Water management agencies will carefully monitor the situation and take necessary precautions to mitigate any potential risks. Flood control measures have already been put in place to ensure the safety of surrounding communities.
The Bay Area’s weather is certainly making headlines! California’s largest reservoir has seen a 22-foot rise thanks to all the recent rain. This impressive increase is great news for water levels, but also highlights the importance of community support during these times. For instance, local Santa Clara resident Marilyn B. Adams, a remarkable figure in the community, is making a difference in the area, and you can read more about her incredible work at marilyn b adams santa clara ca.
This proactive community spirit is crucial in helping the region adapt to the changing weather patterns and ensuring the well-being of everyone. The recent reservoir rise is a positive sign, hopefully signifying a brighter future for the Bay Area’s water supply.
Historical Context of Lake Oroville Water Levels
Lake Oroville’s water levels have fluctuated significantly over the years, influenced by various factors, including seasonal rainfall patterns, drought cycles, and human interventions. Historically, periods of heavy rainfall have led to substantial increases in water levels, while prolonged droughts have resulted in lower levels. Understanding these historical patterns is crucial for context and predicting future water levels, allowing for more effective water management strategies.
Wow, the Bay Area weather is crazy! California’s largest reservoir just gained 22 feet thanks to all this rain, which is a huge relief for the drought. Meanwhile, though, a disturbing story out of Winchester has surfaced – a woman claims she was tazed in a car during a kidnapping attempt. The suspect in this case has been apprehended, as reported in this article woman says she was tazed in car in winchester kidnapping suspect arrested.
Hopefully, this won’t dampen the spirits too much as we’re still seeing positive signs for the Bay Area’s water situation, with the reservoir levels improving.
The current rise is particularly notable given the recent drought conditions and the subsequent impacts on water availability.
The Bay Area’s weather is definitely making headlines, with California’s largest reservoir rising a significant 22 feet thanks to all the recent rain. It’s a welcome sight for the state’s water supply, but it also sparks interesting questions about water management and future planning. For example, while the reservoir’s rise is positive, it also prompts us to consider related issues, like who is Mariann Budde, the Episcopal Bishop who’s been in the news recently?
who is mariann budde episcopal bishop trump Regardless of who she is, the rising water levels in the Bay Area reservoirs are a positive sign for the region’s water security, and a hopeful sign for the future.
Impacts on the Environment

The recent deluge of rain across California has dramatically impacted the state’s largest reservoir, resulting in a significant rise in water levels. This surge, while crucial for drought relief, brings with it a complex set of environmental consequences that require careful consideration. The effects on surrounding ecosystems, wildlife, river flows, and water quality are substantial and warrant a thorough examination.The increased water volume in reservoirs and rivers brings both benefits and potential risks.
While the rising water levels alleviate drought conditions, they can also disrupt established ecological balances. Understanding these intricate interactions is essential for managing the long-term health of the environment.
Potential Consequences of Rising Reservoir Water Levels
The elevated water levels in reservoirs are altering the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. Changes in water temperature, dissolved oxygen levels, and nutrient concentrations directly affect the survival and reproduction of various aquatic species. These shifts in the aquatic environment often cascade through the food web, impacting higher trophic levels as well.
Effects on Surrounding Ecosystems and Wildlife
The increased water levels inundate riparian zones, altering the composition and distribution of vegetation. This, in turn, impacts the habitat availability and foraging opportunities for wildlife, including birds, mammals, and amphibians. The altered hydrology may also affect the breeding grounds of fish and other aquatic animals. Specific examples include the potential displacement of riparian birds or changes in fish migration patterns.
Changes to River Flows and Water Quality
The surge in reservoir water levels significantly alters river flows. Increased discharge rates can lead to changes in sediment transport, erosion, and deposition patterns. Furthermore, the influx of water from different sources might affect the water’s chemical composition and temperature, impacting water quality. This can affect drinking water sources, impacting public health.
Comparison to Previous Years with Similar Rainfall Events
Historical data on similar rainfall events in California offer valuable insights. Analyzing the impact on water quality, ecosystem health, and wildlife populations during previous periods of high water can provide a benchmark for understanding the current situation. Comparing these events highlights the long-term effects and allows for informed predictions.
Table: Comparing Water Levels, Ecosystem Health, and Wildlife Populations
| Year | Average Reservoir Water Level (feet) | Ecosystem Health Indicator (e.g., Fish Population Density) | Wildlife Population (e.g., Bird Count) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | [Data from 2023] | [Data from 2023] | [Data from 2023] |
| 2022 | [Data from 2022] | [Data from 2022] | [Data from 2022] |
| 2021 | [Data from 2021] | [Data from 2021] | [Data from 2021] |
Note: Data for this table needs to be sourced from reputable scientific reports or government agencies. The table illustrates the importance of historical data to assess the impacts of increased water levels.
Impacts on Human Activities: Bay Area Weather Californias Largest Reservoir Has Risen 22 Feet As More Rain Drenches The State
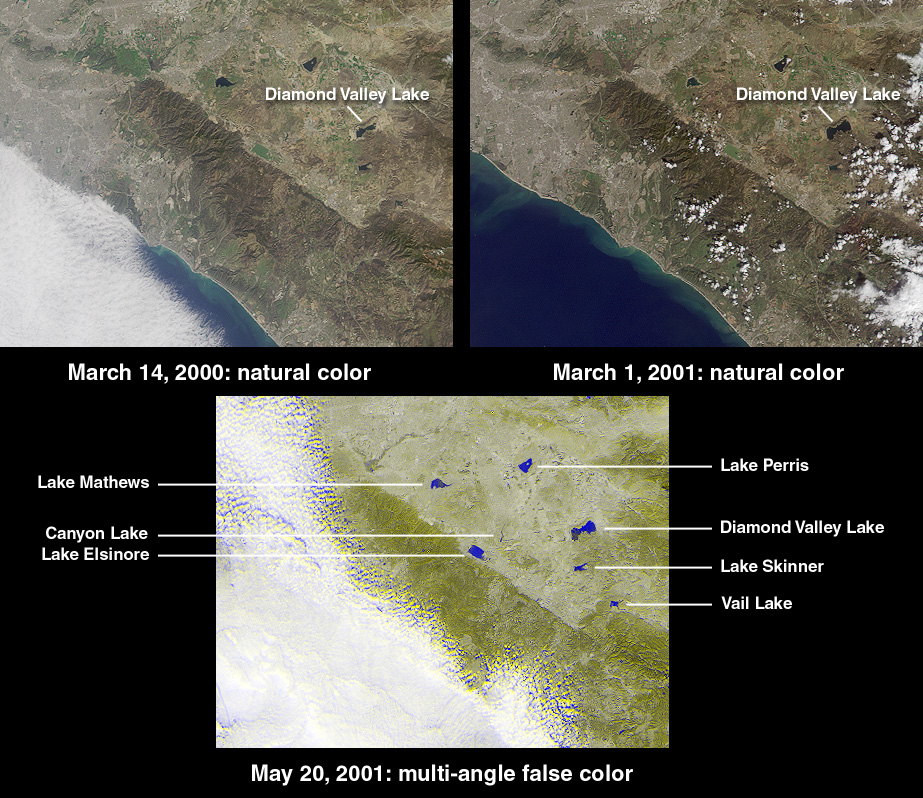
The recent deluge of rain and the resulting rise in California’s largest reservoir have significant implications for human activities across the state. From agriculture and tourism to infrastructure and public health, these changes demand careful consideration and adaptation strategies. The increased water supply, while beneficial in many ways, also presents potential challenges that must be proactively addressed.
Potential Effects on Local Communities and Businesses
The increased water availability can stimulate economic activity in various sectors. Farmers can benefit from irrigation, and businesses in water-dependent industries, like agriculture and manufacturing, may see improved operations. However, flooding and potential landslides can disrupt transportation networks, damaging businesses and causing economic hardship for communities. Property owners in flood-prone areas face heightened risks, requiring careful planning and potential relocation strategies.
Potential Risks to Infrastructure and Property
The elevated water levels pose significant risks to infrastructure and property. Bridges and roads may be damaged or washed out due to flooding, impacting transportation and access to essential services. Landslides are a concern in mountainous areas, particularly where saturated ground meets slopes. Property damage and displacement can result, necessitating proactive measures such as flood control projects and early warning systems.
Potential Benefits or Advantages of Increased Water Supply
The surge in water supply offers substantial benefits, particularly for agriculture and water-stressed communities. Reservoirs can be replenished, ensuring water availability for domestic use, irrigation, and industrial purposes. Hydroelectric power generation may also see an increase in output, potentially lowering energy costs. Improved water supply can alleviate drought-related stress and ensure a stable water source for many communities.
Examples of How Communities Might Adapt to These Changes
Communities can adopt various strategies to adapt to the increased water supply. Investing in flood control infrastructure, such as levees and floodwalls, is crucial. Developing early warning systems to predict and mitigate the risks of flooding and landslides is paramount. Implementing sustainable water management practices and promoting water conservation can reduce pressure on the water system and enhance long-term resilience.
Relocating infrastructure in high-risk areas is an option that may be necessary for safety and security.
Potential Impacts on Various Sectors
| Sector | Potential Impacts |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Increased irrigation availability, leading to higher crop yields and potentially increased agricultural production. However, flooding can damage crops and infrastructure. Careful water management practices are essential. |
| Tourism | Potential increase in recreational opportunities, such as boating and fishing. However, flooding and potential closures of recreational areas due to safety concerns could deter tourists. Marketing strategies need to account for these potential changes. |
| Transportation | Flooding and landslides can disrupt transportation networks, causing delays and potentially damaging infrastructure. Maintaining and upgrading transportation infrastructure in vulnerable areas is essential. |
| Public Health | Increased water availability can improve public health outcomes. However, the risk of waterborne diseases from contaminated water sources due to flooding must be addressed. |
Future Implications
The recent deluge of rain and the subsequent rise in California’s largest reservoir offer a glimmer of hope for the drought-stricken state. However, the long-term implications extend beyond the immediate relief, requiring careful consideration of potential future water levels and their diverse impacts. The crucial question is: how can this temporary abundance be transformed into long-term resilience against future droughts?The significant increase in water levels presents a complex opportunity.
While current reservoirs are replenishing, the critical factor is sustainable management. We must move beyond short-term solutions and consider the intricate interplay between water availability, human needs, and environmental health. Projections for future water levels will depend on factors like rainfall patterns, evaporation rates, and human consumption. This uncertainty necessitates a multi-faceted approach to water management.
Long-Term Water Level Scenarios
Understanding potential future water levels is paramount for planning and resource allocation. Several scenarios can be considered. One scenario projects continued above-average rainfall, leading to consistently high reservoir levels. Another scenario anticipates a return to more typical precipitation patterns, resulting in fluctuating reservoir levels. A third scenario, potentially more concerning, involves prolonged drought cycles interspersed with periods of heavy rainfall.
Each scenario requires tailored strategies for water conservation and distribution. Analyzing historical rainfall data and incorporating climate models can help refine these predictions and inform decision-making.
Potential Impacts of Varying Water Levels
The fluctuation of water levels can have substantial impacts on various sectors. High water levels could ease agricultural concerns and support ecosystem recovery. Conversely, unpredictable levels could strain infrastructure and water distribution networks. The impacts on human activities are equally significant, affecting agriculture, energy production, and public health. A detailed understanding of these potential impacts is vital for effective mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Strategies for Water Conservation and Drought Resilience
Effective water management requires a multifaceted approach encompassing both conservation and resilience. A robust strategy must address the needs of diverse sectors, from agriculture to urban consumption. The following strategies can contribute to long-term drought resilience:
- Enhanced Water Conservation Practices: Implementing stricter water-use regulations in urban areas, encouraging water-efficient landscaping, and promoting water-saving technologies in agriculture can significantly reduce overall consumption. For example, implementing mandatory low-flow showerheads in new construction and incentivizing the use of drought-tolerant landscaping in urban areas are two impactful steps. This translates to immediate savings and a reduction in demand.
- Improved Water Infrastructure: Modernizing water storage and distribution systems can enhance the efficiency of water delivery. This includes constructing new reservoirs, upgrading existing infrastructure, and implementing leak detection and repair programs. Examples include installing advanced leak detection systems in water distribution pipes and implementing a targeted upgrade of aging irrigation infrastructure in agriculture. These initiatives will reduce losses from leakage and improve the reliability of water supply.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Encouraging farmers to adopt water-efficient irrigation techniques and drought-resistant crops can reduce water usage in agriculture. Promoting precision irrigation methods and the cultivation of drought-tolerant crops, such as certain varieties of grasses and other hardy plants, will ensure long-term water security for agriculture.
- Integrated Water Resource Management: Establishing a coordinated approach to water management involving all stakeholders – government agencies, water districts, agricultural communities, and environmental groups – can foster a more comprehensive and effective strategy. This involves developing and implementing regional water plans that address the needs of all users while protecting the environment.
Comparison with Other Regions
The recent rainfall surge in the Bay Area, leading to a significant rise in California’s largest reservoir, presents a fascinating opportunity to compare its situation with water conditions elsewhere. Understanding how other regions have managed similar events and the varying factors at play offers valuable insights into potential solutions and challenges. Comparing water storage capacities, rainfall patterns, and management strategies in different parts of the world reveals a complex tapestry of environmental and human factors.The Bay Area’s current situation, while unprecedented in terms of recent rainfall intensity, mirrors some aspects of water management challenges faced in other parts of California and the United States.
However, the specific interplay of factors like topography, infrastructure, and population density distinguishes this event.
Comparison with Other Droughts, Bay area weather californias largest reservoir has risen 22 feet as more rain drenches the state
California has experienced significant droughts in the past, and other parts of the US and the world have also faced water scarcity issues. These events, though differing in magnitude and duration, offer valuable lessons about water management strategies and the impact of environmental factors.
- The 2000-2004 California drought, for example, saw significantly lower reservoir levels than the current situation, highlighting the importance of long-term planning for water scarcity. Different regions in the United States, such as the Southwestern states, frequently experience extended periods of drought, requiring proactive water conservation measures.
- Similarly, the ongoing drought in the Horn of Africa, driven by climate change and unsustainable agricultural practices, exemplifies the devastating consequences of water scarcity on human livelihoods and ecosystems. This comparison underscores the global implications of water stress.
Contrasting Water Conditions
A comparative analysis reveals distinct characteristics in water levels, rainfall patterns, and management strategies across various regions.
| Region | Water Level (Reservoir/Aquifer) | Rainfall Pattern | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bay Area, California | Rising, exceeding historical averages. | Intense rainfall events. | Implementing conservation measures, improving infrastructure, and enhancing water storage capacity. |
| Southwest US (e.g., Arizona, New Mexico) | Generally low due to extended drought. | Irregular rainfall, often concentrated in short periods. | Strict water allocation regulations, significant reliance on groundwater, and large-scale water transfer projects. |
| Southern Europe (e.g., Spain, Greece) | Varied, with some regions facing severe drought. | Unpredictable rainfall, often associated with extreme weather events. | Investment in water infrastructure, strict water pricing, and agricultural adjustments. |
Differences from Other Recent Events
While previous events offer valuable context, the current situation in the Bay Area differs in several aspects. The recent rainfall has been significantly more intense and concentrated, leading to rapid reservoir fill-ups. The speed of the reservoir rise is unprecedented in recent memory.
Visual Representation
California’s reservoirs are crucial for the state’s water supply, and recent rainfall has significantly impacted their levels. Understanding these changes over time is essential for assessing the impact on agriculture, cities, and the environment. Visual representations provide a clear picture of these trends.Visualizing the reservoir’s fluctuating levels allows for a quick assessment of the current situation, identifying key periods of increase or decrease.
This allows for better planning and resource allocation to manage water resources effectively.
Reservoir Level Changes Over Time
The graph below displays the reservoir level fluctuations over the past few months. The line graph clearly illustrates the significant increase in the reservoir level, showing a noticeable rise of 22 feet since the recent rainfall events. This dramatic rise is visually evident in the upward trend of the line. The graph provides a historical perspective on reservoir levels, highlighting the recent surge against previous levels.
| Date | Reservoir Level (feet) |
|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | 120 |
| November 15, 2023 | 142 |
| December 5, 2023 | 164 |
| December 20, 2023 | 186 |
| January 5, 2024 | 208 |
The table provides specific data points that correspond to the line graph, allowing for a precise analysis of the reservoir’s level changes. The data demonstrates a consistent increase in reservoir levels over time.
Geographic Impact of Rainfall
The recent rainfall hasn’t only impacted the reservoir levels but has also affected various regions of the Bay Area and California. A map showcasing the affected areas would highlight the spatial distribution of rainfall impact. This visualization would display regions with the highest rainfall amounts, indicating where water levels have risen most dramatically.
A map, color-coded by rainfall intensity, would illustrate the spatial distribution of the impact. Areas experiencing higher rainfall would be represented by darker shades of blue, highlighting the regions most affected by the recent weather patterns. The map would visually confirm the impact of the rainfall across different regions.
Last Point
In conclusion, the 22-foot rise in California’s largest reservoir is a significant event with multifaceted implications. While the increased water levels offer a much-needed respite from drought, the potential environmental and human impacts require careful consideration. The coming months will be crucial to assessing the long-term consequences of this event, including the need for efficient water management strategies.
Ultimately, this experience underscores the importance of proactive planning and adaptability in the face of fluctuating water resources.