Fix File Explorer not responding. This guide dives deep into the frustrating issue of a frozen File Explorer, providing actionable steps to diagnose and resolve the problem. We’ll cover everything from simple checks to advanced troubleshooting, ensuring you get your files back in order.
A frozen File Explorer can be incredibly disruptive, preventing you from accessing essential files and potentially causing delays in your workflow. This comprehensive guide breaks down the various reasons behind this problem, from software conflicts to hardware issues, equipping you with the knowledge to fix File Explorer not responding effectively.
Understanding the Issue
File Explorer, a crucial component of the Windows operating system, is responsible for managing files and folders. A “File Explorer not responding” error can significantly impact productivity, making it impossible to access, manage, or interact with files. This issue often arises due to various factors, and understanding these causes can lead to effective solutions.The “File Explorer not responding” error manifests as a complete or partial freeze in the File Explorer window.
Users may notice their mouse cursor becoming unresponsive, the inability to open or close folders, or the absence of any visual updates in the Explorer window. This problem can occur unexpectedly, during seemingly benign tasks like browsing folders, or under more demanding circumstances like large file transfers or software installations. Understanding the possible causes and symptoms will help in diagnosing the issue and implementing the appropriate solution.
Common Causes of File Explorer Freezing
Several factors can contribute to File Explorer becoming unresponsive. These range from corrupted system files to conflicting software, and sometimes even simple memory constraints.
- Corrupted System Files: Windows relies on a collection of system files for its core functions. Damage or corruption in these files can lead to various errors, including File Explorer freezing. This corruption can stem from improper shutdowns, virus infections, or even system updates gone awry. A corrupted system file often needs to be replaced or repaired through system file checker tools.
- Conflicting Software: Some software applications, especially those dealing with file systems, might have compatibility issues or conflicts with Windows’ File Explorer. These conflicts can manifest as instability, including the “File Explorer not responding” error. The conflict might arise from a recent software installation, or a previously installed program causing issues.
- Insufficient System Resources: File Explorer, like any other application, requires system resources such as memory and processing power. If these resources are insufficient, particularly during large file operations, File Explorer may become unresponsive. This can be a result of running too many applications simultaneously or low RAM.
- Hardware Issues: In rare cases, hardware problems, such as failing hard drives or faulty memory modules, can cause File Explorer to freeze. These issues often lead to more widespread system instability and are usually accompanied by other performance problems. This includes checking disk space for errors.
- Virus or Malware Infections: Malware or viruses can corrupt system files or overload system resources, causing File Explorer to freeze. Regular antivirus scans and software updates are crucial to prevent such infections.
Symptoms and Potential Solutions
The following table summarizes common causes, symptoms, and potential solutions for File Explorer not responding issues.
| Common Cause | Symptoms | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Corrupted System Files | File Explorer freezes, hangs, or displays error messages, often during file operations. | Run System File Checker (SFC) scan, Windows Update. If the issue persists, consider a system restore to a previous point. |
| Conflicting Software | File Explorer becomes unresponsive after installing or updating a specific program. | Uninstall or update the recently installed program. If possible, disable or uninstall potentially conflicting services. |
| Insufficient System Resources | File Explorer freezes, especially during large file operations. System performance may also be slow overall. | Close unnecessary programs, increase virtual memory, or consider upgrading RAM. |
| Hardware Issues | File Explorer freezes intermittently, accompanied by other system instability issues like hard drive errors or blue screen errors. | Run hard drive diagnostics, check for failing memory modules. Seek professional assistance if hardware issues are suspected. |
| Virus or Malware | File Explorer freezes or behaves erratically. System performance may be significantly degraded. | Run a full antivirus scan, remove any detected malware. Update antivirus definitions. |
Troubleshooting Steps
File Explorer not responding can be a frustrating issue, often stemming from a variety of underlying problems. This section provides a structured approach to diagnosing and resolving the problem, starting with basic checks and progressing to more advanced solutions. Understanding the root cause is key to effective troubleshooting.Troubleshooting file explorer issues requires a methodical approach. Begin by assessing system resources and processes, then delve into potential conflicts with other applications or outdated drivers.
By following these steps, you can identify and address the specific problem causing File Explorer to freeze or become unresponsive.
My File Explorer keeps freezing? It’s a frustrating tech issue, and honestly, sometimes it feels like a wildfire ripping through my digital files. It’s a constant battle, but thankfully, there are usually fixes. Thinking about how all California homeowners could be on the hook for the LA wildfire costs, this article really highlights the complex financial picture, which made me wonder if my computer’s data loss issues were even a small drop in the bucket compared to the sheer scale of this disaster.
Hopefully, some of these tech fixes will help my File Explorer act a bit less like a wildfire in my digital space.
Initial Checks
A crucial first step in troubleshooting is to perform a series of basic checks. These preliminary steps often reveal simple solutions without the need for more complex procedures.
- Restart your computer. A simple restart often resolves temporary glitches and clears any minor conflicts in system processes. This is a quick and easy method to try before resorting to more involved solutions.
- Check for any error messages. Windows often displays error messages when a problem arises. Carefully examine any error messages that appear on the screen, as these can provide valuable clues about the nature of the issue. Note any specific error codes or descriptions, as these can help pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
- Close unnecessary applications. Running too many programs simultaneously can overload system resources, leading to performance issues. Identify and close any programs that are not currently in use, especially if they are known to be resource-intensive.
System Resource Monitoring
Ensuring adequate system resources is critical to avoiding performance issues. Low memory, insufficient disk space, or high CPU usage can all contribute to the problem.
- Check CPU usage. Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and monitor the CPU usage. High CPU usage for extended periods can indicate a problem with a particular application or process. If a specific program is consistently consuming high CPU resources, it might be causing File Explorer to become unresponsive.
- Monitor RAM usage. Observe RAM usage in Task Manager. Insufficient RAM can lead to performance issues, impacting File Explorer’s responsiveness. If RAM usage is consistently high, consider adding more RAM to the system or closing unnecessary programs.
- Verify disk space. Ensure there’s sufficient free disk space. Low disk space can lead to performance slowdowns, including issues with File Explorer. Delete unnecessary files or folders to free up disk space and improve system performance.
Process Monitoring
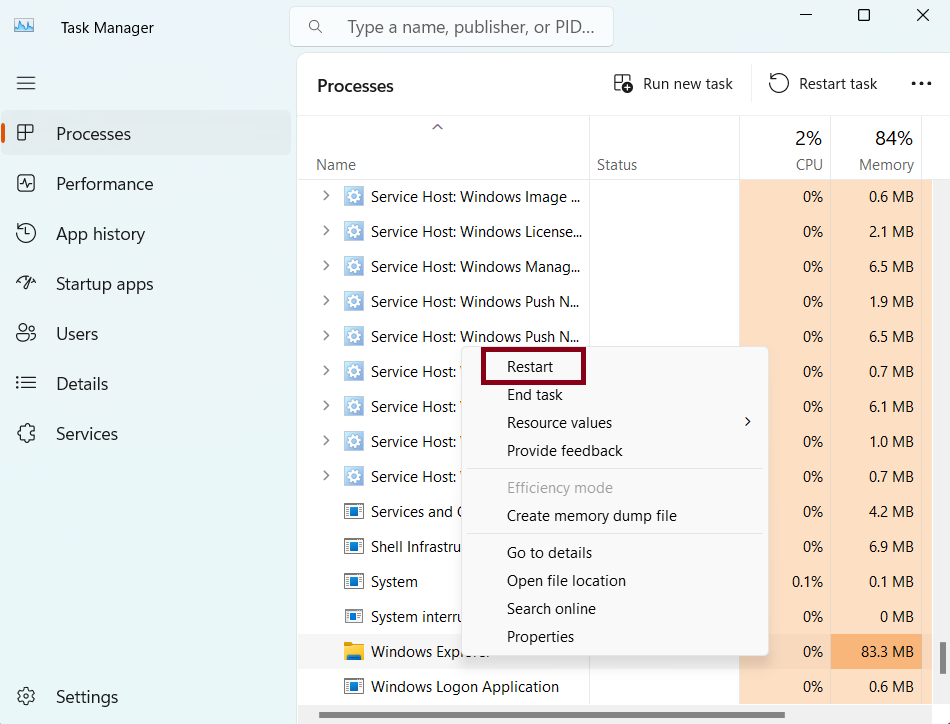
Identifying processes that might be interfering with File Explorer’s operation is crucial. Task Manager offers tools for examining and controlling system processes.
- Identify potentially problematic processes. In Task Manager, carefully review running processes to pinpoint any unusually high resource consumption or unexpected behaviors. Look for any programs that are unexpectedly using a significant amount of CPU, RAM, or disk I/O. Potentially problematic processes should be noted and investigated.
- End processes if necessary. If a specific process is causing File Explorer to freeze, you can try ending the process in Task Manager. This can be a temporary solution, but if the problem persists, the root cause might lie elsewhere.
Driver Checks
Outdated or conflicting drivers can also contribute to File Explorer issues. Ensure that drivers are up-to-date and compatible.
- Check for outdated drivers. Outdated or incompatible device drivers can sometimes lead to system instability and unexpected behavior, including File Explorer not responding. Visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest drivers for all connected devices.
- Verify driver compatibility. Ensure that the drivers you install are compatible with your operating system version. Installing incorrect or incompatible drivers can lead to further issues and complications.
Application Conflicts
Conflicts with other applications can lead to File Explorer not responding. Identify and resolve these conflicts.
- Identify potential conflicts. Consider whether recently installed or updated applications might be interfering with File Explorer’s operation. A recent program update might introduce a conflict, so consider uninstalling or updating problematic programs.
- Uninstall or disable problematic applications. If a specific application is suspected of causing the problem, temporarily uninstall or disable it to determine if the issue resolves. If the problem is resolved, the application might be the source of the issue.
Troubleshooting Table
| Troubleshooting Step | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Restarting the computer | Resolves temporary issues, clears conflicts |
| Checking for error messages | Provides clues about the nature of the problem |
| Closing unnecessary applications | Reduces system resource usage |
| Monitoring system resources | Identifies resource bottlenecks |
| Checking for outdated drivers | Ensures compatibility |
| Identifying application conflicts | Resolves conflicts and improves performance |
Software Conflicts
File Explorer’s responsiveness can be hampered by conflicts with other installed software. These conflicts can manifest in various ways, from sluggish performance to complete crashes. Identifying and resolving these conflicts is often crucial in restoring normal functionality. This section delves into potential software conflicts and provides actionable steps to diagnose and address them.Software conflicts can stem from a multitude of sources.
Recently installed programs, outdated or corrupted system files, and even conflicts between different versions of the same program can all contribute to File Explorer instability. Understanding these potential sources empowers users to take proactive steps toward resolving these issues.
Identifying Software Conflicts
Recent software installations are frequently a source of File Explorer problems. A newly installed program might have conflicting components or libraries, interfering with File Explorer’s operations. Thorough examination of recent installations is crucial.
Managing Conflicts with Recently Installed Programs
To identify potential conflicts, carefully review the software installed shortly before the File Explorer issue arose. Uninstall the most recently installed program, and observe if the problem persists. If the issue is resolved, the newly installed program was likely the culprit. Reinstall the program if necessary, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Corrupted or Outdated System Files
Corrupted or outdated system files can also cause File Explorer issues. These files are essential for Windows’ core functionality, and their corruption can lead to unpredictable behavior. Windows provides tools to scan and repair these files.
Checking and Fixing Corrupted System Files
Windows offers the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt as an administrator, and run the command `sfc /scannow`. This process might take some time, and it’s important to allow it to complete.
Figuring out how to fix File Explorer not responding can be a real pain, especially when you’re in the middle of something important. Thankfully, there are some pretty straightforward solutions. Meanwhile, the recent news about the fatal Piedmont Cybertruck crash, as detailed by witness details fatal piedmont cybertruck crash , highlights the importance of reliable technology in everyday life.
Hopefully, once you’ve sorted out your File Explorer woes, you can get back to your tasks without any further hiccups.
Updating or Reinstalling Relevant Software
Outdated software, including drivers and other applications, can also be a source of conflicts. Outdated drivers can disrupt communication between hardware and the operating system. Keeping drivers up-to-date is essential. Check the manufacturer’s websites for the latest drivers for your hardware. Reinstalling a program that’s known to have caused issues is also an option.
Software Conflict Resolution Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Uninstall Recently Installed Programs | Temporarily uninstall the most recently installed software to isolate potential conflicts. | Often effective for identifying the source of the problem. |
| Run System File Checker (SFC) | Use the built-in SFC tool to scan and repair corrupted system files. | Effective in resolving issues caused by corrupted system files. |
| Update Drivers | Ensure all drivers are up-to-date to prevent hardware conflicts. | Crucial for maintaining stability and functionality. |
| Reinstall Software | Reinstall programs that are known to be problematic, following the manufacturer’s instructions. | Can resolve conflicts and ensure program integrity. |
System Configuration Issues
File Explorer’s erratic behavior can often stem from underlying problems within your system’s configuration. These issues, ranging from corrupted registry entries to compromised file system integrity, can manifest as sluggish performance, missing files, or the dreaded “not responding” error. Understanding these potential culprits is crucial for effective troubleshooting.System configurations are intricate networks of settings and data structures. Minor inconsistencies or errors can disrupt the smooth operation of File Explorer, leading to a cascade of issues.
Corrupted registry entries, for example, can interfere with File Explorer’s ability to locate and access files, while file system integrity problems can result in missing or inaccessible data.
My File Explorer keeps freezing? Ugh, frustrating! Sometimes a simple restart fixes it, but other times, you need a deeper dive. Luckily, the Warriors are facing a similar challenge, needing to adjust their approach to the game, and this article on GUI Santos isn’t what the Warriors need; he’s what the Warriors need to do better highlights a crucial element.
If all else fails, maybe a system file check is in order to troubleshoot further. Hopefully, a quick fix will resolve this File Explorer issue soon.
Registry Errors and File Explorer
Registry errors can significantly impact File Explorer’s functionality. The registry acts as a central database for Windows settings, and incorrect entries can cause File Explorer to misbehave. Problems in the registry keys responsible for file system access, user settings, or shell extensions can lead to unexpected behaviors, including the “not responding” error. Registry errors are often insidious, subtly impacting performance before becoming blatant problems.
Identifying and Fixing Registry Problems
To identify and fix registry problems, utilize the Registry Editor (regedit.exe). Carefully examine keys related to file system operations and user settings. Look for unusual or corrupted entries. Remember, modifying the registry improperly can lead to system instability. Back up the registry before making any changes.
If unsure about a particular entry, consult online resources or seek professional assistance.
System Settings and File Explorer
Correct system settings are vital for File Explorer’s optimal performance. Incorrect or outdated settings can lead to performance issues or unexpected behavior. Ensure that the system’s indexing settings are properly configured. Overly aggressive indexing can lead to slower response times and resource consumption. Adjusting these settings may improve responsiveness.
Check that the file system is set to the correct access mode. Incorrect access settings can prevent File Explorer from interacting with certain files or folders correctly.
File System Integrity Issues
File system integrity is essential for File Explorer’s stability. Corrupted or damaged file system structures can lead to missing files, incorrect file paths, and File Explorer crashes. Physical damage to storage devices, improper shutdowns, or malware attacks can compromise the integrity of the file system. It’s crucial to monitor for signs of file system corruption, such as frequent errors or unexpected data loss.
Repairing or Restoring the File System
Repairing or restoring the file system involves various methods, depending on the nature of the damage. If the damage is minor, running a file system check (chkdsk) can often resolve the problem. However, more significant issues may necessitate a system restore or even a complete reinstall of Windows. Consult system administrators or specialists for complex situations involving significant file system damage.
Potential System Configuration Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Corrupted Registry Entries | Use Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with caution, back up the registry before making changes, and seek professional help if necessary. |
| Incorrect System Settings | Review and adjust indexing settings, access permissions, and other relevant settings. |
| File System Corruption | Run a file system check (chkdsk), restore from a backup, or seek professional help for severe corruption. |
| Software Conflicts | Uninstall or update conflicting software or drivers. |
Hardware Issues: Fix File Explorer Not Responding
File Explorer’s responsiveness can be significantly impacted by underlying hardware problems. While software glitches are common culprits, faulty or failing hardware components can also cause the explorer to freeze, crash, or become unresponsive. Understanding the potential hardware issues is crucial for effective troubleshooting.Often, issues with the hard drive or RAM are the root cause of File Explorer’s erratic behavior.
These components are essential for storing and accessing files, and any malfunction can lead to the explorer’s performance degradation or complete failure. Properly identifying and addressing these problems can restore normal functionality.
Hard Drive Errors
Hard drive errors are a frequent source of File Explorer problems. Physical damage, logical errors, or wear and tear can disrupt the drive’s ability to read and write data. This disruption manifests as the explorer freezing, failing to load files, or even preventing the system from booting.
Identifying hard drive errors involves checking for errors and evaluating performance metrics. This process allows for proactive measures and preventative maintenance.
Checking Hard Drive Health and Performance
Various tools are available to assess hard drive health. These tools scan the drive for errors, and report on read/write speeds. The built-in Windows tools (e.g., CHKDSK) are a first step, and third-party applications can offer more comprehensive diagnostics.
- Windows built-in tools: The command-line tool CHKDSK can check for and repair errors on the hard drive. Running this utility is a straightforward approach to identifying potential issues. Remember to run it with the /f switch to force the repair if errors are detected.
- Third-party tools: Applications like CrystalDiskInfo or Hard Disk Sentinel provide detailed information about the hard drive’s health, including temperature, SMART status, and performance metrics. These tools can provide deeper insights than built-in diagnostics.
Memory Issues
Insufficient or faulty RAM can also hinder File Explorer’s performance. When the system struggles to allocate enough memory to handle tasks, File Explorer might become unresponsive or freeze. Identifying and addressing potential memory issues is crucial to maintaining system stability.
Checking and Troubleshooting RAM
Diagnosing RAM problems involves a multi-step process. This process begins with checking for physical damage or loose connections and then proceeds to testing RAM functionality.
- Physical inspection: Carefully examine RAM modules for any visible damage, bent pins, or loose connections. Ensuring the modules are securely seated in the slots is essential.
- RAM testing: Utilize dedicated RAM testing tools (like Memtest86+) to run comprehensive memory tests. These tools identify errors and malfunctions in the RAM modules. If the tests reveal problems, replacing the RAM is often necessary.
Common Hardware Issues and Their Effects on File Explorer
| Hardware Issue | Potential Effect on File Explorer |
|---|---|
| Hard drive errors | File Explorer freezes, crashes, or fails to load files. Slow response times. |
| Insufficient RAM | File Explorer becomes unresponsive, freezes, or displays frequent errors. |
| Faulty RAM modules | File Explorer crashes, displays random errors, or operates erratically. |
| Hard drive malfunction | Inability to access files, system instability, and complete system failure. |
Advanced Solutions
When basic troubleshooting steps fail to resolve File Explorer’s “not responding” issue, more advanced techniques may be necessary. These methods delve deeper into the system’s configuration and files, potentially identifying and rectifying underlying conflicts. This section explores such procedures, offering a structured approach to resolve the problem.Advanced troubleshooting often requires a systematic approach, moving from general system checks to more specific file and configuration manipulations.
This ensures a comprehensive resolution, aiming to identify the root cause of the issue and implement the appropriate solution.
System File Checker (SFC)
The System File Checker (SFC) tool is a vital diagnostic tool for Windows. It scans for and repairs corrupted system files. Corrupted system files can often lead to unexpected behaviors, including File Explorer freezing or not responding. Using SFC can often restore stability and functionality.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator. This elevated privilege is crucial to modify system files.
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. This command initiates the scan and repair process. - Allow the scan to complete. This process can take several minutes or even hours, depending on the system’s resources and the extent of the corruption.
- After completion, restart your computer. This step ensures that the changes made by SFC take effect.
System Restore
System Restore is a built-in feature that allows you to revert your system to a previous state, effectively rolling back changes that might have caused the issue. This is particularly helpful if you recently installed software or made significant configuration changes that might have introduced the File Explorer problem.
- Access the System Restore utility. This can usually be found through the Control Panel or search.
- Select a restore point. Choose a point in time before the issue started to ensure you’re restoring to a stable state.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the restore process. This will revert the system to the selected point, potentially resolving the problem.
- Important Note: System Restore will undo recent changes. Be sure to back up any important data before proceeding.
Clean Boot
A clean boot is a diagnostic process that starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This helps to isolate whether a third-party application or driver is causing the File Explorer issue.
- Search for “msconfig” in the Start menu and open the System Configuration utility.
- Select the “Services” tab and check the box that says “Hide all Microsoft services.” This ensures only third-party services are visible.
- Click “Disable all.” This disables all non-Microsoft services.
- Select the “Startup” tab and click “Open Task Manager.” This will open the Task Manager, where you can disable startup programs.
- In Task Manager, disable all startup programs. This isolates any startup conflicts.
- Restart your computer. A clean boot environment has been established.
- Attempt to reproduce the File Explorer issue. If the issue does not occur, it indicates a third-party application or driver is likely the culprit. Gradually re-enable services and programs to identify the specific cause.
Advanced Solutions Summary
| Advanced Solution | Procedure | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| System File Checker (SFC) | Scans and repairs corrupted system files. | Fixes corrupted system files, potentially resolving various system issues. |
| System Restore | Reverts the system to a previous state. | Undos recent changes, crucial for recovering from software conflicts. |
| Clean Boot | Starts Windows with minimal drivers and programs. | Identifies if third-party applications or drivers are causing the issue. |
Prevention Strategies
File Explorer not responding can be frustrating, but proactive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of these issues. By understanding the common causes and implementing preventive strategies, you can maintain a smooth and efficient operating system. A well-maintained system not only prevents these problems but also enhances overall performance and stability.Preventing File Explorer issues involves a multi-faceted approach, combining good system hygiene with responsible software management.
A healthy system is a robust system, capable of handling everyday tasks without hiccups. Proactive measures, like regular backups and maintenance, will pay dividends in the long run.
Maintaining System Health and Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal system performance and to avoid File Explorer issues. This includes keeping drivers updated, running disk cleanup utilities, and managing startup programs. Keeping your system clean and efficient will prevent File Explorer from being overloaded, thereby minimizing the risk of crashes.
- Regularly update drivers: Outdated drivers can lead to instability and conflicts, potentially causing File Explorer to malfunction. Checking and updating drivers through Device Manager is a simple yet effective preventative measure.
- Run disk cleanup utilities: Over time, temporary files and unnecessary data accumulate on your hard drive, slowing down performance and potentially causing issues with File Explorer. Utilizing built-in disk cleanup tools can free up space and improve system responsiveness.
- Manage startup programs: Excessive startup programs can strain system resources. Review and disable unnecessary programs that launch automatically on boot. This reduces the initial load on the system, thereby reducing the potential for File Explorer to become unresponsive.
- Defragmenting hard drives (for older systems): For older systems with mechanical hard drives, defragmentation can improve file access times, which in turn enhances system responsiveness. However, for modern SSDs, defragmentation is often unnecessary and may even be counterproductive.
Avoiding Software Conflicts, Fix file explorer not responding
Software conflicts are a common source of File Explorer issues. Incompatible or poorly designed programs can interfere with system functions, leading to unexpected behavior.
- Install software from reputable sources: Downloading and installing software from trusted sources significantly reduces the risk of encountering malware or poorly written programs that may conflict with File Explorer.
- Check for software compatibility: Before installing new software, verify its compatibility with your operating system and existing applications. Look for system requirements and reviews to assess compatibility.
- Use a reliable antivirus program: A robust antivirus program helps identify and remove malicious software that can cause system instability and software conflicts. This is essential for protecting the system from potentially harmful software that could interfere with the normal operation of File Explorer.
Regular Data Backup Strategies
Data loss can be devastating. Establishing a regular backup routine is a critical preventive measure against File Explorer issues and other potential system problems.
- Implement a scheduled backup routine: Schedule automatic backups of important files and folders to an external hard drive, cloud storage, or another reliable location. This routine ensures that critical data is protected from potential system failures or unexpected data loss.
- Choose a reliable backup solution: Select a backup solution that suits your needs and offers a robust method of data protection. Consider factors like data encryption and restoration capabilities.
- Verify backup integrity: Regularly test the integrity of your backups to ensure that they can be successfully restored in case of data loss or system failure. Verify that the backup can be restored without any issues to maintain the reliability of the data protection.
Scheduling Regular System Maintenance
Regular system maintenance is key to preventing File Explorer issues and keeping your system running smoothly.
- Utilize built-in maintenance tools: Most operating systems include built-in maintenance tools for tasks like disk cleanup and defragmentation. Leverage these tools to ensure that your system remains optimized and efficient.
- Establish a maintenance schedule: Create a schedule for performing routine maintenance tasks, such as checking for updates, running disk cleanup, and scanning for malware. Regular maintenance will help ensure that File Explorer and the entire system remain in optimal working condition.
- Consider using system optimization software (with caution): Some third-party system optimization software can help maintain system performance. However, exercise caution when using such software, as some tools may be harmful or contain malware. Always research and select reputable software from trusted sources.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, fixing a not-responding File Explorer can involve various approaches, from basic checks to more intricate system-level adjustments. Understanding the potential causes and implementing the appropriate troubleshooting steps is key to restoring File Explorer’s functionality. Remember to prioritize preventative measures to maintain a smooth and reliable system experience. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for you to confidently navigate and resolve this common Windows issue.