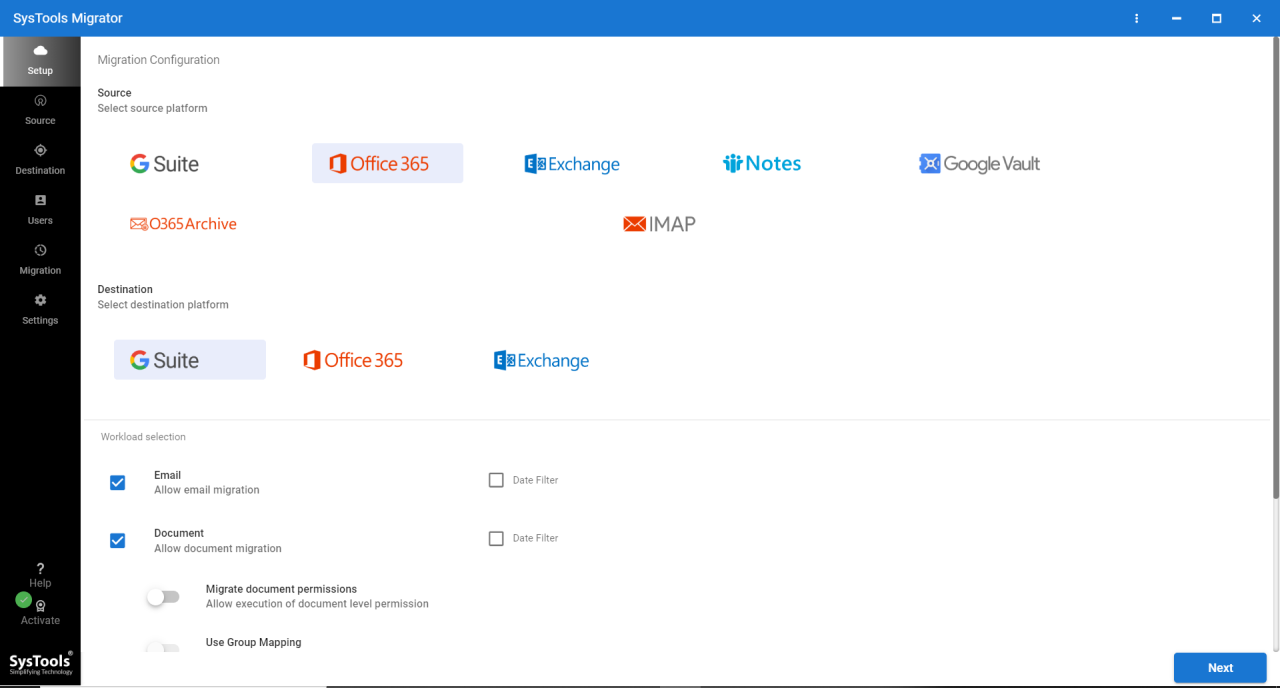
Best email migration tools are essential for smoothly transferring your email data. Whether you’re switching email providers, moving from on-premises to cloud-based systems, or simply need to archive your emails, a robust migration solution is crucial. This guide dives deep into the world of email migration, examining various tools, their features, and the key factors to consider for a successful transition.
From choosing the right tool to understanding the migration process, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate this critical task.
Choosing the best email migration tool depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Factors like the volume of emails, the complexity of the migration, and your budget all play a role. This guide explores these aspects in detail, providing a comprehensive overview of the process.
Introduction to Email Migration Tools
Email migration is the process of transferring email data from one system to another. This can involve moving emails from one email provider to another, transferring on-premises email servers to cloud-based solutions, or even migrating between different types of cloud services. Its importance stems from the need to adapt to changing technological landscapes, comply with evolving regulations, or simply improve the efficiency and security of email management.Email migration is crucial in many scenarios, such as company mergers and acquisitions, the adoption of new technologies, or the need to comply with data privacy regulations.
It ensures business continuity and avoids data loss, allowing users to seamlessly access their emails and attachments in the new system. A well-executed migration minimizes downtime and disruption to daily workflows.
Email Migration Scenarios
Different types of email migration scenarios exist, each requiring specific approaches and tools. Migrating from one email provider to another (e.g., from Gmail to Outlook) involves transferring user accounts, emails, and potentially calendars and contacts. Migrating on-premises email to the cloud (e.g., from an Exchange server to Office 365) involves transferring data to a cloud-based platform. There’s also the scenario of migrating between different cloud platforms, each with unique configurations and data structures.
For instance, migrating from a legacy on-premises system to a newer cloud-based platform can involve significant technical complexities and require careful planning.
Examples of Crucial Email Migration Situations
Email migration is essential in numerous business situations. For example, when a company acquires another, consolidating email accounts is necessary to maintain a unified communication system. The adoption of new technologies, such as a switch from a legacy on-premises system to a cloud-based solution, often necessitates migrating email accounts and data to ensure seamless operations. Similarly, regulatory compliance mandates, like GDPR, might require organizations to migrate email data to platforms with enhanced security measures.
These scenarios underscore the critical role of email migration in maintaining business continuity and minimizing disruptions.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an Email Migration Tool
Several factors are crucial when selecting an email migration tool. The tool’s ability to handle the volume and type of data to be migrated is paramount. Scalability, in terms of accommodating future growth, is also essential. Compatibility with the source and target email systems is a prerequisite for seamless data transfer. Security features, such as encryption and data protection, are essential to safeguard sensitive information during the migration process.
Finally, the tool’s ease of use and support are critical for a smooth migration experience.
Comparison of Email Migration Tools
| Category | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-based | Hosted on a provider’s servers. | Ease of access, scalability, automatic updates. | Potential vendor lock-in, dependence on internet connectivity. |
| On-premises | Installed and managed on company servers. | Greater control over security and infrastructure, customization options. | Requires IT expertise, higher maintenance costs, limited scalability. |
| Third-party | Independent software solutions. | Specific features, often tailored for particular migration needs. | Potential compatibility issues, vendor lock-in, potentially higher cost. |
This table provides a general overview of the different categories of email migration tools. Each category has its own strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial to assess your specific needs and resources before making a decision.
Evaluating Email Migration Tools
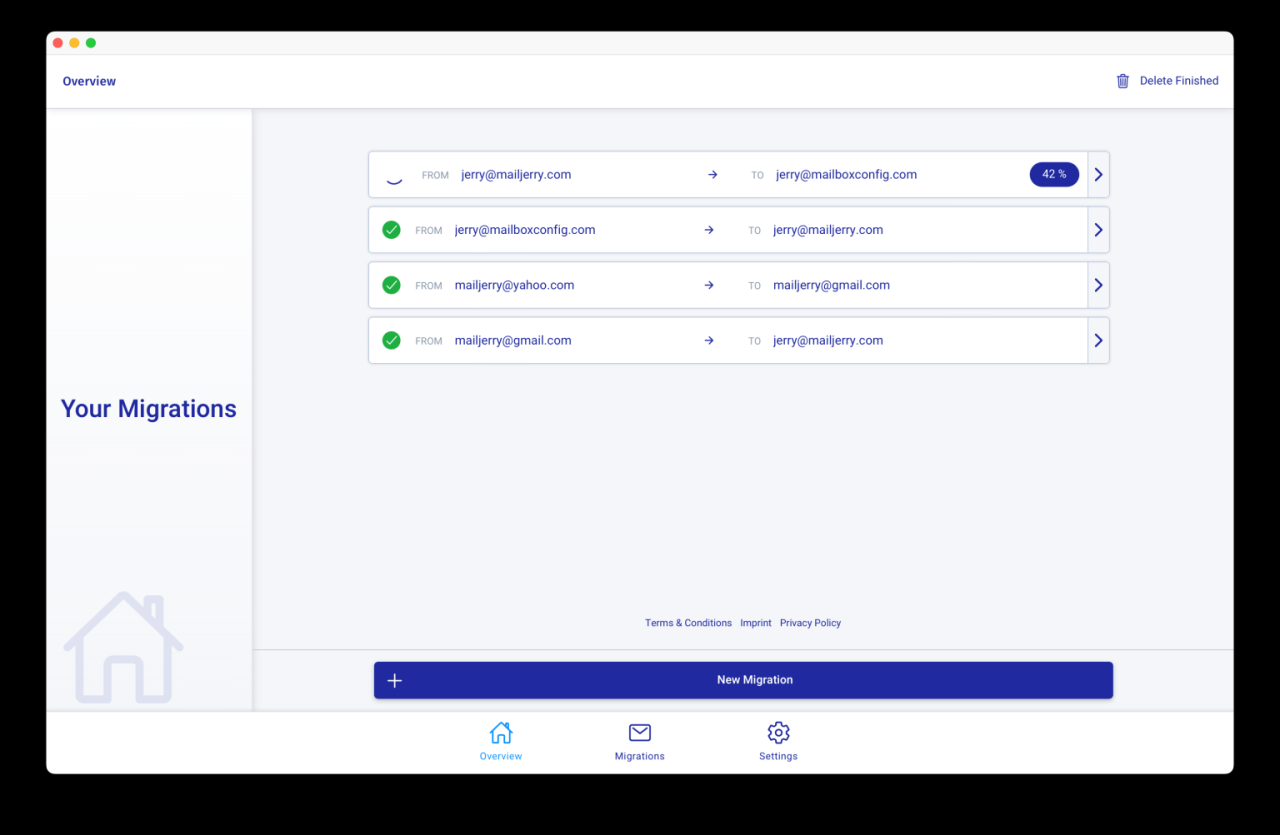
Choosing the right email migration tool is crucial for a smooth transition and minimal disruption to your workflow. A poorly implemented migration can lead to significant downtime, data loss, and a decline in user productivity. Careful evaluation of potential tools is essential to ensure a seamless and secure process.Robust email migration tools offer a wide array of features, exceeding simple file transfer.
This evaluation delves into essential features, data security considerations, and the varying capabilities of different tools.
Essential Features of a Robust Email Migration Tool
Careful selection of a migration tool requires understanding the key features. A robust tool should not only transfer emails but also handle attachments, calendars, contacts, and other associated data seamlessly. This includes maintaining the original formatting and metadata of the emails, ensuring data integrity throughout the process.
- Data Integrity: The tool should preserve the original formatting and metadata of emails, ensuring accurate representation of the data.
- Attachment Handling: Support for various file types and sizes is critical, preventing data loss or corruption during migration.
- Contact Management: The tool should migrate contact lists efficiently, ensuring accurate and complete data transfer.
- Calendar Integration: Efficient migration of calendar events, appointments, and schedules is essential for continuity.
- Customizable Settings: Flexibility in configuring the migration process allows for tailoring to specific needs and user requirements.
Data Security and Integrity During Migration
Data security is paramount during any migration. A secure tool employs encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information. Data integrity ensures that the migrated data remains accurate and complete. This involves verification steps to confirm the successful transfer of all data components.
- Encryption: Sensitive data should be encrypted both during transit and at rest, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Rigorous access controls limit access to the migrated data to authorized personnel only.
- Data Validation: Thorough validation procedures confirm the accuracy and completeness of the migrated data, detecting and rectifying any errors or inconsistencies.
Comparing Migration Tool Capabilities
Different tools exhibit varying capabilities in handling file sizes, message volumes, and data conversion. Some tools excel in large-scale migrations, while others are better suited for smaller projects. Thorough research is needed to identify the tool that best meets your specific needs.
Finding the best email migration tools can be tricky, especially when you’re juggling a lot of different accounts. Right now, importers are scrambling to stockpile Italian Prosecco, due to new tariffs. This situation highlights the importance of efficient processes , and that’s something excellent email migration tools can help with. Luckily, there are many robust options available to ensure a smooth transition of your emails to a new system.
- File Size Handling: The tool should handle large files and attachments without compromising speed or integrity.
- Message Volume: Tools should be capable of migrating large volumes of emails efficiently, preventing processing delays.
- Data Conversion: Support for various email formats (e.g., PST, MBOX, Exchange) is crucial for seamless migration.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Features
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) features within a migration tool are crucial for protecting sensitive data. Implementing DLP measures during migration prevents unauthorized data exposure and ensures compliance with regulations. This feature is critical in preventing sensitive information from being accidentally leaked or transferred to incorrect destinations.
- Data Filtering: Tools with filtering capabilities can identify and exclude sensitive data during migration, preventing its accidental transfer.
- Data Redaction: Tools can redact or mask sensitive data elements to comply with privacy regulations.
- Audit Trails: Detailed audit trails provide a record of all actions taken during the migration process, aiding in troubleshooting and compliance.
Comparative Analysis of Migration Tool Categories
| Category | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud-based | Scalability, accessibility, lower initial investment | Potential for vendor lock-in, reliance on internet connectivity |
| On-premises | Greater control over infrastructure, data security | Higher initial investment, management overhead, scalability limitations |
| Third-party | Specialized expertise, customized solutions, potentially advanced features | Potential cost, integration challenges, less control over data |
Features and Capabilities of Migration Tools
Choosing the right email migration tool is crucial for a smooth transition. Beyond the basic functionalities of moving data, a robust tool should offer a comprehensive suite of features to ensure a seamless process and minimal disruption to users. Understanding the specific capabilities of various tools is essential for evaluating their suitability for a particular organization’s needs.
Data Accuracy During Migration
Ensuring data accuracy is paramount during any migration process. Errors in the transfer can lead to lost information, compromised data integrity, and operational inefficiencies. Reputable migration tools employ robust validation and error-handling mechanisms to minimize the risk of data loss or corruption. They often provide comprehensive reporting features, allowing users to track the migration progress and identify any discrepancies early on.
This proactive approach helps maintain data integrity throughout the entire migration cycle.
Email Archiving and Recovery
Email archiving and recovery capabilities are critical components of a migration tool. A reliable tool should allow users to archive their email data in a secure and accessible manner, often using industry-standard formats. This feature enables organizations to comply with regulatory requirements and retain crucial business information. The recovery aspect is equally important; the tool should facilitate easy retrieval of archived emails when needed, providing a streamlined process for accessing historical information.
For example, a tool might allow for search functionality across archived data, enabling users to locate specific emails based on s or dates.
Email Filtering and Categorization
Email filtering and categorization during migration are essential for maintaining organizational structure and productivity. Migration tools that offer robust filtering options enable users to organize their emails according to various criteria, such as sender, subject, or s. This functionality ensures that important emails are easily accessible and that unwanted or irrelevant emails are automatically filtered. Furthermore, effective categorization during migration allows users to maintain their existing email organization structure in the new system, preventing confusion and disruption.
Comparative Analysis of Migration Tools
The table below provides a comparison of specific features offered by different email migration tools, focusing on crucial aspects like email filtering options, file size limits, and data volume limits. This comparative analysis helps users make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
Finding the best email migration tools can be tricky, but it’s definitely doable! With so many options out there, it’s important to consider your needs. Thinking about recent weather events like the flood watch for the Bay Area inland regions until Saturday night here , you might need a tool that’s reliable and fast for getting your important emails safely transferred.
Ultimately, the right tool will depend on your specific situation, but doing your research is key for a smooth transition.
| Feature | Tool A | Tool B | Tool C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Email Filtering Options | Advanced filters based on sender, subject, s, and more | Basic filters based on sender and subject | Customizable filters with complex logic |
| File Size Limits | 100 MB per email | Unlimited per email | 50 MB per email, with an option to increase for a fee |
| Data Volume Limits | 5 GB per migration | 10 GB per migration | Unlimited data volume with tiered pricing |
| Archiving Formats | PST, EML, MBOX | PST, EML, MBOX, and custom formats | PST, EML, MBOX, and cloud-based archiving |
| Recovery Options | Basic search functionality | Advanced search and metadata retrieval | Full-text search and advanced filtering |
Migration Process and Implementation
Successfully migrating emails involves careful planning, meticulous execution, and rigorous testing. Choosing the right email migration tool is just the first step; the process itself demands a structured approach to ensure minimal disruption and data integrity. A well-executed migration minimizes downtime, preserves user productivity, and ensures a seamless transition to the new system.The process of migrating emails is not a one-size-fits-all affair.
Different tools offer varying approaches, but the fundamental steps remain consistent. Understanding these steps and the importance of meticulous planning and testing will ensure a smooth transition.
Step-by-Step Migration Process
The email migration process typically involves several key stages, each crucial for a successful transition. Proper planning, detailed setup, and thorough testing are vital to minimize potential issues. A phased approach, clearly defined in each step, is recommended.
- Planning: A thorough assessment of the current email system, including user counts, email volume, and data storage capacity, is critical. This phase also involves identifying the target email system, outlining specific requirements, and establishing timelines. Defining success metrics, such as the desired migration completion time and the acceptable level of downtime, is crucial for effective planning.
- Setup: This stage involves configuring the chosen email migration tool and setting up the destination email system. Careful configuration of the tool’s settings, including data filters and mapping rules, is essential. This phase also encompasses setting up user accounts and permissions in the new system. Properly setting up the target email system and the migration tool is fundamental to ensuring a smooth migration.
- Migration: This phase is where the actual migration takes place. The migration tool transfers emails from the source system to the destination system. Monitoring the migration process closely is essential to identify and resolve any issues promptly. Real-time progress reports are helpful to track the migration and assess its pace.
- Testing: Before the actual migration, a pilot test should be conducted using a small subset of users or a limited number of emails. This test allows for the detection and resolution of potential issues in the migration process. This critical step is where the system’s performance and stability can be thoroughly assessed. It helps to validate the setup, migration process, and potential issues.
- Verification: This crucial stage involves validating the integrity of the migrated data. A comprehensive verification process should include verifying email delivery, account accessibility, and the accuracy of all migrated emails. This phase also entails checking for any data loss or corruption.
Importance of Testing
Testing the migration process before the actual migration is vital. It allows for the identification and resolution of potential issues in the migration process, minimizing the risk of downtime and data loss during the live migration. Testing, with a small portion of data or users, enables adjustments and fixes before the full migration, ensuring a smoother and more reliable migration.
Finding the best email migration tools can be tricky, but it’s crucial for smooth transitions. With recent news of Trump cabinet member Hegseth being sworn in , it’s a reminder that keeping your email organized is important no matter the political landscape. Ultimately, the right tool can save you a lot of headaches and ensure a seamless email transfer.
User Training and Support
Providing adequate user training and support during the migration is crucial. Users need clear instructions on the new email system and how to access and use their migrated emails. Providing user guides, FAQs, and direct support channels will help ease user anxiety and encourage a smooth transition.
Post-Migration Verification
Post-migration verification is essential to ensure the successful completion of the migration process. It involves validating that all emails have been transferred correctly, that users can access their accounts, and that all functions are working as expected. Thorough verification is a final step in guaranteeing data integrity and a seamless user experience.
Migration Process Phases
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Planning | Defining scope, identifying resources, and establishing timelines. |
| Setup | Configuring the migration tool and destination system. |
| Migration | Transferring emails from the source to the destination system. |
| Testing | Validating the migration process with a small subset of data. |
| Verification | Confirming the integrity and accessibility of the migrated data. |
User Experience and Support
Choosing the right email migration tool isn’t just about features; it’s crucial to consider how easy the process is for your team. A smooth user experience, coupled with robust support, can significantly impact the success of your migration. Poorly designed interfaces or inadequate support can lead to delays, errors, and ultimately, a frustrating experience for everyone involved.A user-friendly interface is key to a successful email migration.
The best tools offer intuitive dashboards, clear instructions, and visual representations of progress. This reduces the learning curve for your team, enabling them to focus on the migration itself rather than struggling with the tool.
User-Friendly Interfaces
Different migration tools employ various approaches to user interface design. Some tools use drag-and-drop functionality to simplify the mapping of email folders, while others provide detailed spreadsheets for complex configurations. A good example of a user-friendly interface might be one that allows users to visualize the migration process in real-time, showing the progress of each email being transferred.
Another example is a tool that clearly displays the mapping between source and destination folders, making it simple to review and adjust settings before proceeding. These features contribute to a more streamlined migration process.
Comprehensive Documentation and Support Resources
Thorough documentation is vital for a successful migration. Excellent documentation should cover every aspect of the migration process, from initial setup to troubleshooting potential issues. This includes detailed tutorials, FAQs, and step-by-step guides, making the entire migration journey less daunting. Comprehensive user guides are crucial for users who might encounter unforeseen challenges during the process. Well-organized support resources ensure that users can readily find answers to their questions, minimizing delays and maximizing efficiency.
Customer Support Availability and Quality, Best email migration tools
The quality and availability of customer support are critical factors. A responsive support team can provide assistance during any hurdles encountered during the migration. This might include phone support, email support, or online chat. The availability of 24/7 support can be particularly beneficial for global teams or those working across time zones. The responsiveness of the support team and their ability to provide helpful solutions are crucial factors to consider when choosing a migration tool.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Support
Post-migration support is equally important. Even after the migration is complete, monitoring the new system and addressing any lingering issues is crucial. Post-migration support often includes regular check-ins to ensure the email system is functioning correctly. Tools offering this ongoing support provide an additional layer of assurance and minimize the risk of issues arising later.
Comparison of Support Options
| Email Migration Tool | FAQs | Tutorials | Phone Support | Email Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool A | Extensive, covering common and uncommon scenarios | Comprehensive video tutorials and written guides | Available during business hours | Responsive, with quick turnaround times |
| Tool B | Limited, focusing on basic questions | Limited tutorials, primarily text-based | Available during specific hours | Delayed responses, potentially lengthy wait times |
| Tool C | Good coverage of common issues | Interactive online tutorials | Available 24/7 | Prompt responses and clear solutions |
This table highlights the varying support options provided by different tools. Consider which level of support best suits your needs and budget when making your decision. Tools with comprehensive documentation and responsive support can greatly improve the overall migration experience.
Cost and Scalability
Choosing the right email migration tool hinges significantly on its pricing model and scalability. A tool that works well for a small business might prove inadequate (or prohibitively expensive) as the company grows. Understanding these aspects upfront is crucial for avoiding costly surprises down the road. A transparent pricing structure and the ability to handle increasing email volume are key factors in long-term email migration success.
Pricing Models
Various pricing models exist for email migration tools, each catering to different needs and budgets. Understanding these models is essential to aligning the tool with your specific requirements.
- Per-user pricing: This model charges a fixed fee per user who will be accessing the migrated emails. It’s often a straightforward option for smaller organizations with a predictable user base. For example, a tool might charge $5 per user per month for a basic migration package, scaling to higher costs for premium features.
- Per-message pricing: This model charges based on the number of emails migrated. It’s suitable for projects with a known email volume, such as migrating a specific project or team’s correspondence. This model can be unpredictable for large-scale migrations where the email volume is unknown or fluctuates significantly.
- Subscription-based pricing: This model provides access to the tool’s features for a recurring monthly or annual fee. This is often the most common approach for email migration tools. The subscription tier typically determines the features available and the support level included. A higher tier might unlock features like advanced filtering or custom scripting.
Scalability
Scalability is a critical consideration when selecting an email migration tool. The ability to handle increasing email volume is paramount as the organization grows. A tool lacking in scalability could significantly hinder operations during or after the migration.
- Importance of Scalability: Email volume can fluctuate significantly. A tool should be capable of managing peak loads without compromising performance. A tool that can adjust its resources to handle a surge in email traffic is vital for seamless migration and continued smooth operation.
- Impact of Email Volume: The sheer volume of emails to be migrated can dramatically affect the cost and duration of the project. Tools that struggle with large volumes can lead to extended migration periods, potentially impacting productivity and workflow.
- Scalability Considerations: Look for tools with robust infrastructure capable of handling a wide range of email volumes. A tool’s ability to adjust processing power, storage capacity, and bandwidth is essential to its scalability.
Pricing Model Examples
To illustrate the differences, let’s consider some examples of email migration tools and their pricing models. Note that specific pricing details can vary significantly and should be verified with the vendor directly.
| Tool | Pricing Model | Scalability Options |
|---|---|---|
| Mail Migration Pro | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Supports increasing user count and email volume through different tiers. |
| FastEmailMigrate | Per-message pricing | Scalable, but cost can be unpredictable depending on the volume of emails. |
| EmailMover | Per-user pricing | Good for organizations with predictable user numbers. May become expensive for large user bases. |
Security and Compliance: Best Email Migration Tools
Choosing the right email migration tool is crucial, but equally important is ensuring the security and compliance of your data during and after the migration process. Robust security measures and adherence to industry standards are paramount for protecting sensitive information and avoiding costly penalties. This section delves into the security protocols implemented by various migration tools and the importance of compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.Implementing a secure email migration process is critical for protecting sensitive data, safeguarding your organization’s reputation, and adhering to industry regulations.
A well-structured approach to security encompasses data encryption, access controls, and adherence to industry standards. This careful planning and execution will protect sensitive information from unauthorized access during the transition.
Security Measures Implemented by Migration Tools
Various email migration tools employ a range of security measures to safeguard data during the migration process. These measures typically include encryption of data both in transit and at rest. Access controls, such as user authentication and authorization, are also vital for restricting access to sensitive information. Regular security audits and penetration testing are often incorporated to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Significance of Compliance with Industry Standards
Adherence to industry standards and regulations is essential for maintaining data integrity and avoiding potential legal repercussions. Compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) ensures that sensitive data is handled responsibly and in accordance with legal obligations. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage.
For example, a healthcare organization that does not comply with HIPAA regulations during an email migration could face substantial penalties.
Examples of Tools Complying with Security Standards
Several email migration tools demonstrate commitment to security standards. Some tools offer encryption capabilities for both data in transit and at rest, ensuring confidentiality throughout the migration process. Tools that integrate with secure storage systems or use secure communication protocols further enhance data protection. Specific certifications or compliance audits may be publicly available for certain tools. Investigating these certifications can help ensure a tool’s alignment with your organization’s security requirements.
Data Encryption During Migration
Data encryption is crucial during the migration process to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. End-to-end encryption of emails and other data during transmission is vital. Additionally, ensuring data is encrypted at rest, in storage, helps prevent unauthorized access if a system were compromised. This encryption protects confidential data during both the transfer and storage phases of the migration.
Robust encryption protocols, like AES-256, are commonly employed by reputable migration tools.
Table of Security Features and Compliance Certifications
| Email Migration Tool | Encryption (Transit/Rest) | Compliance Certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2) | Access Controls | Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | |---|---|---|---|---| | Tool A | Yes/Yes | ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II | Multi-factor authentication, Role-based access control | Advanced DLP features | | Tool B | Yes/Yes | HIPAA, SOC 2 Type I | Strong user authentication, granular permissions | Basic DLP features | | Tool C | Yes/No | ISO 27001, GDPR | User-level access controls, audit logs | Limited DLP |
Note: This table is a simplified representation.
Specific features and certifications may vary based on the specific tool and plan selected. Consult the vendor’s documentation for precise details.
Final Review
In conclusion, migrating your emails efficiently requires careful consideration of various factors. From evaluating features and security to understanding pricing models and support, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of best email migration tools. Ultimately, the best tool for you will depend on your unique situation. Remember to prioritize security, consider scalability, and thoroughly test the migration process before initiating the actual transfer.
By following this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to choose the perfect email migration tool and ensure a seamless transition.