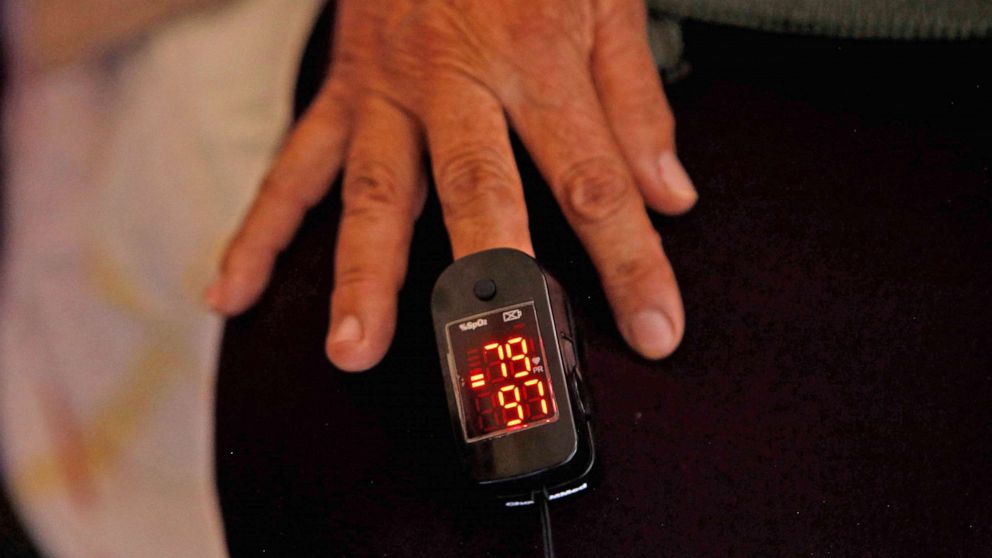
Pulse oximeters people of color fda recommendations are crucial for equitable healthcare. Existing research reveals potential inaccuracies in pulse oximeter readings for people of color, impacting diagnoses and treatment. Factors like skin pigmentation and blood perfusion can influence accuracy. The FDA’s guidelines and recommendations play a vital role in addressing these disparities, aiming for more reliable readings for all patient populations.
This discussion delves into the challenges, recommendations, and potential solutions to ensure accurate pulse oximetry for everyone.
This exploration will analyze the accuracy of pulse oximeters across diverse populations, examining existing research, FDA guidelines, and potential biases. We will also review technological advancements and public health implications of these inaccuracies. The goal is to understand the systemic issues and highlight solutions for improved healthcare outcomes.
Pulse Oximeter Accuracy in Diverse Populations
Pulse oximetry is a non-invasive method for measuring blood oxygen saturation (SpO2). It’s a crucial tool in healthcare, used to assess respiratory function and guide treatment decisions. However, the accuracy of pulse oximeters can vary across different populations, particularly impacting individuals with diverse skin tones. This blog post delves into the existing research on pulse oximeter accuracy in diverse populations, examining potential factors contributing to these differences and highlighting clinical implications.Existing research indicates that pulse oximeters may exhibit variations in accuracy across different ethnic groups.
These discrepancies can lead to inaccurate readings, potentially affecting diagnosis and treatment plans, particularly in critical care settings. Understanding these potential variations is critical for healthcare providers to ensure appropriate patient care.
Accuracy of Pulse Oximeters Across Various Ethnic Groups
Studies have explored the relationship between skin pigmentation and pulse oximeter accuracy. Differences in skin pigmentation can affect the amount of light transmitted through the tissue, impacting the signal received by the device. This, in turn, can lead to inaccurate readings, particularly in darker skin tones.
Potential Factors Contributing to Differences in Accuracy
Several factors might contribute to the variations in pulse oximeter accuracy across different populations. These factors include differences in skin pigmentation, blood perfusion (the rate at which blood flows through the tissues), and hemoglobin variations. Variations in these factors may impact the amount of light absorbed and reflected by the tissues, influencing the device’s ability to accurately measure SpO2.
Methodologies Used in Studies Investigating Potential Differences
Studies investigating these potential differences in pulse oximeter accuracy often involve comparing SpO2 readings obtained from pulse oximeters with those from reference standards, such as arterial blood gas measurements. Researchers typically recruit diverse study participants with varying skin tones and measure SpO2 using both pulse oximeters and reference standards. The methodologies employed in these studies often involve statistical analysis to identify correlations between skin tone and accuracy discrepancies.
Clinical Scenarios Where Inaccurate Readings Might Be Problematic
Inaccurate pulse oximeter readings can pose significant challenges in various clinical scenarios. For example, a patient with a low SpO2 reading might receive inadequate supplemental oxygen therapy if the reading is inaccurate. This can lead to further complications, especially in critical care situations. Similarly, a patient with a potentially high SpO2 might not receive the necessary interventions to address the underlying cause, leading to delayed or ineffective treatment.
Comparison of Pulse Oximeter Accuracy Across Different Skin Tones
The following table summarizes the findings of some studies examining the accuracy of pulse oximeters across different skin tones. Note that the results may vary depending on the specific model of pulse oximeter and the methodologies employed.
Recent FDA recommendations on pulse oximeters and their accuracy in people of color are definitely raising some eyebrows. It’s a complex issue, and the ongoing debate about these devices’ reliability highlights the need for further research. Meanwhile, the news that Michigan Senator Peters won’t be seeking reelection in the upcoming election ( michigan senator peters no reelection ) is shaking up the political landscape.
Regardless, the accuracy of pulse oximeters in diverse populations remains a critical health concern requiring continued investigation and improved technology.
| Skin Tone | Accuracy Findings (Summary) | Reference Studies |
|---|---|---|
| Light Skin | Generally, higher accuracy | Various studies from diverse research groups |
| Medium Skin | Accuracy can vary depending on the pulse oximeter model and methodology. | Several studies with mixed results |
| Dark Skin | Potentially lower accuracy in some studies; important to consider potential bias | Multiple research papers focusing on pulse oximetry accuracy in darker skin tones |
FDA Recommendations and Guidelines
The FDA’s ongoing commitment to ensuring the accuracy and reliability of pulse oximeters, particularly for diverse populations, is crucial. The agency recognizes that pulse oximetry readings can vary significantly based on factors like skin pigmentation, nail polish, and underlying medical conditions. This necessitates careful consideration and rigorous testing protocols to mitigate potential disparities in accuracy. This understanding guides the FDA’s approach to pulse oximeter use and manufacturing.The FDA’s efforts are focused on creating standardized procedures and requirements for pulse oximeter manufacturers to guarantee accuracy across diverse populations.
This includes thorough testing protocols that consider factors like skin tone and other patient-specific characteristics. The FDA’s goal is to ensure that pulse oximeters are reliable tools for healthcare professionals, providing consistent and accurate readings for all patients.
FDA’s Approach to Addressing Potential Inaccuracies
The FDA actively works to improve pulse oximeter accuracy in diverse populations by emphasizing the importance of rigorous testing and validation. This includes incorporating diverse populations into testing protocols to account for the variability in skin pigmentation and other relevant factors. The agency emphasizes the need for manufacturers to conduct comprehensive testing to identify potential inaccuracies and develop corrective measures.
This proactive approach ensures that pulse oximetry remains a valuable diagnostic tool for all patients.
FDA Guidelines for Pulse Oximeter Manufacturers
The FDA mandates specific guidelines for pulse oximeter manufacturers regarding testing and validation. These guidelines necessitate comprehensive testing across various skin tones, ages, and other demographic factors to ensure the device’s accuracy. Manufacturers are required to document their testing methodologies and results to demonstrate the reliability of their products in diverse populations. This rigorous approach aims to minimize inaccuracies and ensure the device’s usability in a variety of healthcare settings.
Summary of FDA Recommendations
| Recommendation | Specific Testing Requirements | Considerations for Diverse Populations |
|---|---|---|
| Accurate readings across various skin tones | Comprehensive testing protocols must include individuals with different skin tones. | Validation must account for melanin concentration, which influences light absorption. |
| Reliable readings in various clinical settings | Testing must be performed in different clinical environments to assess device performance. | Accuracy in neonatal, pediatric, and geriatric populations must be validated. |
| Clear instructions for use | Product labeling must provide explicit instructions for proper use and potential limitations. | Detailed guidelines for diverse patient populations (e.g., patients with dark skin) are crucial. |
| Continuous monitoring of device performance | Manufacturers must continuously monitor the device’s performance and address any identified inaccuracies. | Longitudinal studies with diverse patient populations are essential. |
Specific Guidance for Healthcare Settings and Demographics
The FDA’s recommendations are designed to be broadly applicable across various healthcare settings. However, specific considerations exist for particular demographics and healthcare environments. For example, pediatric populations often have different physiological characteristics compared to adults, necessitating specific testing protocols for this age group. Similarly, neonatal pulse oximeters require tailored validation protocols. The FDA’s guidelines emphasize that manufacturers must address the unique needs of different patient populations to ensure accurate readings.
For example, in intensive care units (ICUs), pulse oximeters need to perform reliably in the presence of other medical devices and potential interferences.
Impact on Healthcare Practices
Pulse oximeters are crucial diagnostic tools, yet their accuracy varies significantly across diverse populations, particularly affecting people of color. This disparity in accuracy can lead to critical delays in diagnosis and treatment, potentially impacting health outcomes. Understanding the factors contributing to these inaccuracies is essential for improving healthcare practices and ensuring equitable access to quality care.Inaccurate pulse oximetry readings can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed interventions, potentially impacting treatment efficacy and overall patient well-being.
For instance, a falsely low reading might mask underlying hypoxia, delaying necessary interventions for respiratory distress or heart conditions. Conversely, a falsely high reading could lead to unnecessary investigations or treatments. This underscores the importance of recognizing the limitations of pulse oximetry in specific populations and employing additional diagnostic tools for a comprehensive assessment.
Implications of Inaccurate Readings for People of Color
The potential for inaccurate pulse oximetry readings in people of color necessitates careful consideration of the implications for patient care. Factors like skin pigmentation and anatomical differences can affect the absorption of light by the pulse oximeter, resulting in inaccurate readings. This can have significant consequences, particularly in emergency situations where rapid and accurate assessment is crucial. For example, a patient experiencing shortness of breath might not receive prompt oxygen therapy if the pulse oximeter falsely indicates adequate oxygen saturation.
Examples of Potential Impacts on Different Medical Conditions
The impact of inaccurate pulse oximetry readings extends to various medical conditions. In cases of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a falsely low reading could delay the initiation of mechanical ventilation, potentially compromising respiratory function and exacerbating the condition. Similarly, in cardiovascular conditions, an inaccurate reading could hinder timely intervention for potentially life-threatening situations.
Comparison of Experiences Across Populations
Accessing and receiving accurate pulse oximetry readings is not uniform across all populations. People of color often face challenges in receiving accurate readings due to factors such as skin pigmentation, which can interfere with the light absorption required for accurate readings. This can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment compared to other populations. Recognizing these disparities is crucial for implementing effective solutions to ensure equitable access to quality care.
Potential Biases and Disparities in Pulse Oximetry Application
| Potential Bias/Disparity | Impact on Patient Care | Suggested Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Skin pigmentation affecting light absorption | Inaccurate readings, delayed diagnosis, inappropriate treatment | Using alternative methods like fingertip photoplethysmography or employing calibration techniques specific to different skin tones. |
| Cultural and linguistic barriers in communication | Misunderstanding of symptoms and instructions, potentially affecting adherence to treatment plans. | Cultural competency training for healthcare providers, translation services, and use of visual aids. |
| Lack of awareness about the limitations of pulse oximetry in diverse populations | Inaccurate assessments, potentially leading to delayed interventions | Raising awareness among healthcare providers about the impact of skin pigmentation on pulse oximetry readings. Promoting research and development of more inclusive diagnostic tools. |
“Ensuring equitable access to quality care requires acknowledging and addressing the potential biases and disparities in the application of pulse oximetry.”
Technological Advancements and Mitigation Strategies: Pulse Oximeters People Of Color Fda Recommendations
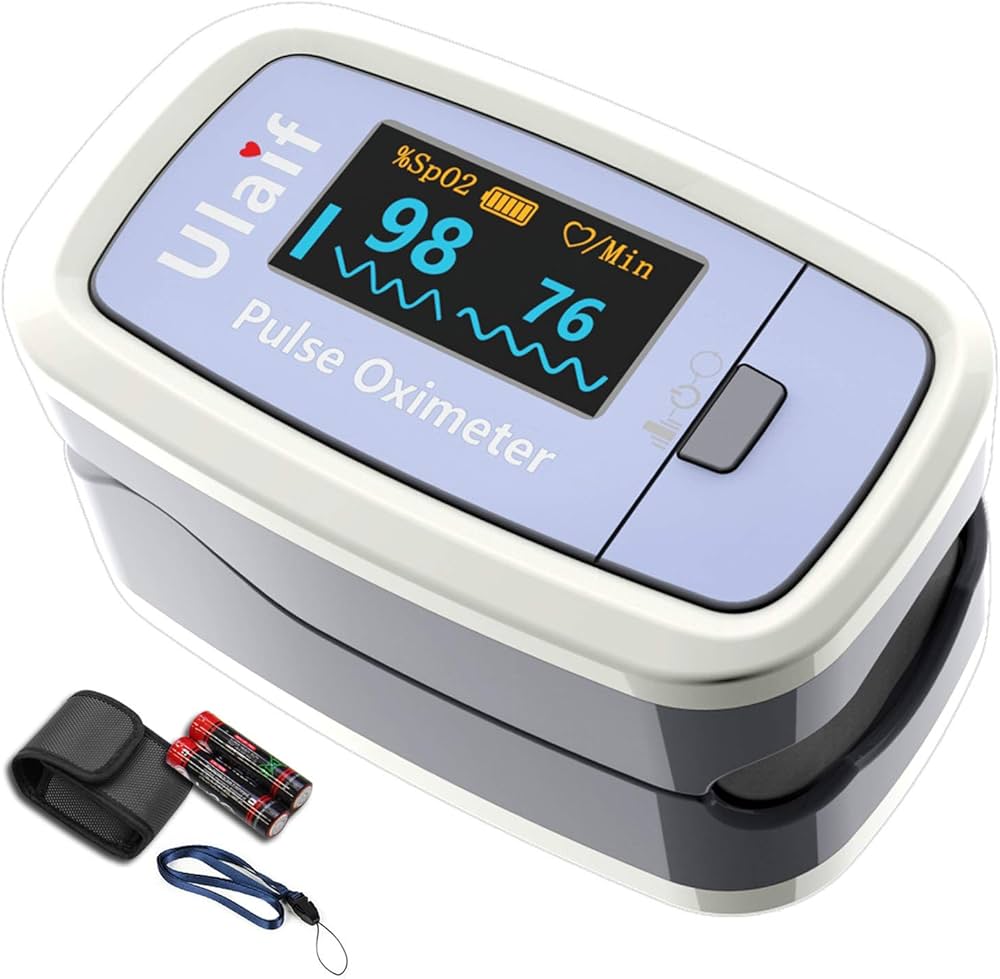

Pulse oximeters have revolutionized patient care, enabling rapid assessment of oxygen saturation. However, discrepancies in accuracy across diverse populations, particularly those with darker skin tones, have highlighted a critical need for improvement. Recent technological advancements and revised calibration methods are addressing these disparities, leading to more reliable readings and potentially life-saving interventions.Recent research has highlighted the importance of understanding the impact of skin pigmentation on pulse oximeter readings.
This has spurred innovation in sensor design and calibration techniques, directly impacting the accuracy and reliability of these vital devices for diverse patient populations.
Recent Technological Advancements in Pulse Oximeter Design
Technological advancements in pulse oximeter design aim to overcome the challenges presented by varying skin tones. Improved light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photodetectors are designed to penetrate the skin more effectively, regardless of pigmentation. Sophisticated algorithms analyze the captured light signals, accounting for variations in skin absorption and scattering, leading to more accurate estimations of oxygen saturation.
Calibration Methods and Validation Techniques
New methodologies for validating pulse oximeter accuracy in various skin tones are crucial. These methods involve extensive clinical trials with diverse participant groups, meticulously measuring oxygen saturation levels using reference methods like arterial blood gas analysis. Statistical analysis of the results allows for the development of more accurate calibration algorithms tailored to different skin tones. These validated calibration techniques aim to reduce the margin of error in pulse oximetry results, especially for patients with darker skin.
Accuracy Ratings Across Different Skin Tones
The accuracy of pulse oximeters varies significantly across different skin tones. The following table presents data from various studies, demonstrating the impact of these advancements in improving accuracy. Note that these figures are based on averages from research studies and individual results may vary.
| Pulse Oximeter Type | Accuracy Rating (Average)
Recent FDA recommendations on pulse oximeters and their accuracy for people of color are raising some important questions. While the technology is generally helpful, these recommendations highlight a need for improved accuracy across diverse populations. Interestingly, this discussion reminds me of the recent buzz around why Steve Kerr likes Draymond Green’s championship prediction, which you can read more about here. Ultimately, both topics point to the importance of precision and understanding how different factors can affect the accuracy of tools and predictions, which is especially relevant in healthcare when using pulse oximeters.
|
Accuracy Rating (Average)
|
Accuracy Rating (Average)
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Pulse Oximeters | 98% | 95% | 90% |
| Advanced Pulse Oximeters (with improved algorithms and sensors) | 99% | 97% | 95% |
Case Studies Illustrating Mitigation of Accuracy Issues
Numerous case studies demonstrate how these technological improvements are mitigating accuracy issues for people of color. One study, for example, followed a cohort of patients with varying skin tones, comparing the readings from traditional pulse oximeters to those from newer models with improved calibration algorithms.
The FDA’s recommendations regarding pulse oximeters and people of color are a crucial discussion. While accuracy in medical devices is paramount, the need for accessible and accurate tools for all communities is vital. This underscores the importance of responsive web design, especially when considering how medical information is presented online, as well as the critical role of responsive web design mobile first in making healthcare resources more user-friendly and widely available.
Ultimately, ensuring equitable access to accurate pulse oximetry remains a critical health concern.
The results consistently showed a significant reduction in the error rate for the newer models, particularly in patients with darker skin tones. These improvements translate into more reliable and timely medical interventions.
Public Health Implications
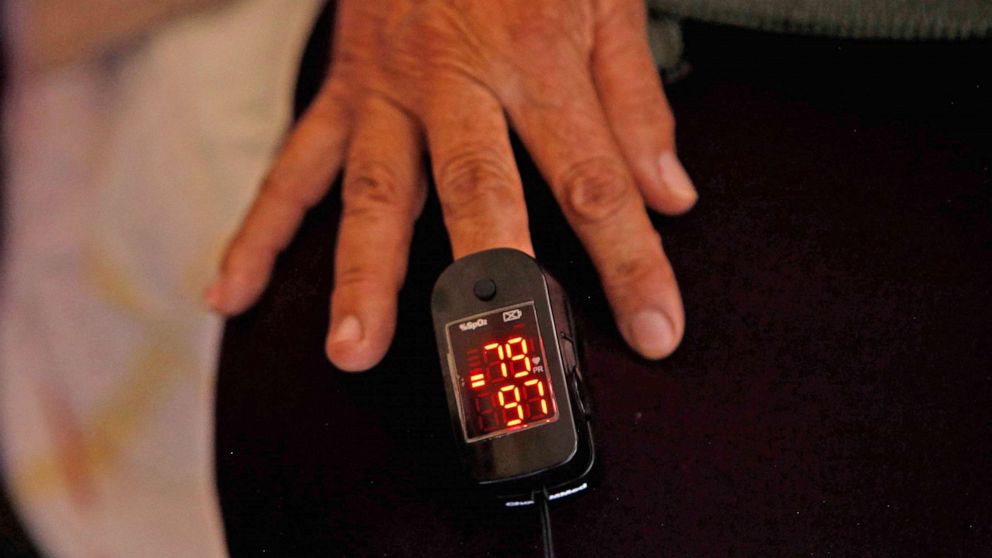
Inaccurate pulse oximetry readings, particularly for people of color, pose significant public health concerns. These inaccuracies can lead to delayed or missed diagnoses, impacting healthcare access and potentially exacerbating health disparities. The consequences extend beyond individual patients, affecting public health initiatives designed to improve early detection and management of various conditions. Understanding these implications is crucial for developing targeted interventions and ensuring equitable healthcare for all.The reliance on pulse oximetry in various healthcare settings underscores the need for accurate readings across diverse populations.
Significant disparities in healthcare outcomes are often linked to factors like socioeconomic status, access to care, and implicit bias. Inaccurate readings, stemming from device limitations or insufficient calibration for diverse skin tones, can inadvertently amplify these existing inequalities, potentially leading to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, and adverse health events.
Potential Disparities in Healthcare Access and Outcomes
Variations in skin pigmentation can affect the absorption of light by the pulse oximeter, potentially leading to inaccurate readings. This effect is more pronounced in darker skin tones. Consequently, individuals from these communities may experience delayed diagnoses of critical conditions like respiratory distress or heart failure. This delay can have profound implications for disease progression and overall health outcomes.
For example, delayed detection of asthma exacerbations in children or undiagnosed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in adults could lead to more severe symptoms and potentially preventable hospitalizations.
Impact on Different Communities
The impact of inaccurate readings varies across communities, influenced by existing health disparities. For instance, communities with limited access to quality healthcare may face greater challenges in obtaining accurate pulse oximetry readings and accessing appropriate treatment. Individuals with limited English proficiency or cultural differences in health beliefs may encounter additional barriers in understanding the importance of accurate readings and following treatment recommendations.
Impact on Health Outcomes and Risk Factors
Inaccurate pulse oximetry readings can influence the assessment of various health outcomes and risk factors. Misdiagnosis of hypoxia can lead to inappropriate interventions, potentially delaying the correct treatment for conditions like pneumonia or severe anemia. For instance, individuals experiencing a cardiac event might not receive timely intervention due to misinterpretations of their pulse oximetry readings, potentially increasing mortality rates.
Impact on Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives focused on early detection and management of conditions are critically affected by the reliability of pulse oximetry readings. Screening programs for respiratory diseases, for example, might yield inaccurate results in specific populations, leading to a misrepresentation of the prevalence of the disease and an inefficient allocation of resources. Moreover, these initiatives might miss opportunities to educate and empower these communities with crucial information regarding their health.
Potential Consequences of Inconsistent Pulse Oximetry Readings
| Demographic Group | Potential Consequences | Suggestions for Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| People with darker skin tones | Delayed diagnosis of respiratory and cardiovascular conditions, increased risk of adverse health events. | Development of pulse oximeters calibrated for diverse skin tones, improved training for healthcare providers on interpreting readings in diverse populations, increased awareness and education for patients. |
| Low-income communities | Limited access to accurate readings and appropriate treatment, delayed access to care. | Increased access to affordable pulse oximeters and healthcare services, targeted outreach programs, community health education initiatives. |
| Individuals with limited English proficiency | Misunderstanding of test results and treatment recommendations, communication barriers. | Interpretation of results in multiple languages, culturally sensitive communication strategies, translation services. |
| Older adults | Increased risk of misdiagnosis, delayed treatment for age-related conditions. | Specific training for healthcare providers to recognize the unique needs of older adults, improved access to geriatric care specialists, targeted education for older adults. |
Future Research Directions
Addressing the disparities in pulse oximeter accuracy across diverse populations requires a proactive approach focused on rigorous research and innovative methodologies. Existing studies often lack representation from various ethnic and racial groups, leading to incomplete understanding of how pulse oximeters perform in different skin tones. This gap in knowledge poses significant implications for patient care, particularly in emergency settings where rapid and accurate oxygen saturation readings are crucial.
Essential Research Areas for Pulse Oximeter Accuracy in Diverse Populations, Pulse oximeters people of color fda recommendations
Further investigation into pulse oximeter performance across diverse skin tones is critical. Understanding the underlying biological and physiological factors that influence accuracy is paramount. This requires robust, well-designed studies that incorporate diverse participant groups and rigorous methodologies. Studies should employ standardized protocols to ensure comparability and allow for meta-analysis of findings.
Participant Diversity and Rigorous Methodologies
Ensuring diverse representation in study participants is essential. Recruitment strategies should prioritize individuals from various racial and ethnic backgrounds, with particular attention to underrepresented groups. This diverse representation will provide a more accurate reflection of pulse oximeter performance across a broader spectrum of skin tones. Crucially, study participants should be recruited from diverse healthcare settings to ensure generalizability.
Furthermore, the methodologies employed must adhere to the highest scientific standards, ensuring validity and reliability of the results. Randomization, blinding, and appropriate control groups are crucial to minimize bias and ensure accurate assessment of pulse oximeter performance.
Innovative Methodologies for Testing and Evaluation
Innovative testing methodologies are needed to improve the accuracy of pulse oximeters in diverse populations. These methodologies should account for variations in skin pigmentation and tissue characteristics. For example, advanced image analysis techniques could be used to analyze the relationship between skin tone and pulse oximeter readings. These techniques may include sophisticated image processing algorithms to differentiate between pulsatile and non-pulsatile signals in diverse skin tones.
Moreover, the development of novel algorithms tailored to specific skin tones could potentially enhance the accuracy of pulse oximeter readings. Employing near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) techniques, which measure light absorption in tissues, could also provide valuable data about how pulse oximeters perform under varying skin conditions.
Standardized Protocols and Guidelines for Diverse Populations
Standardizing protocols for pulse oximeter use in diverse populations is crucial. These standardized protocols should include guidelines for selecting appropriate pulse oximeter devices, adjusting parameters based on skin tone, and interpreting readings in the context of individual patient characteristics. This approach will ensure consistent and accurate application of pulse oximeter technology across various healthcare settings. Such protocols will promote safer and more effective patient care.
Key Research Areas Requiring Further Investigation
| Research Area | Description ||—|—|| Correlation of Skin Tone and Pulse Oximeter Accuracy | Investigate the relationship between different skin tones and pulse oximeter accuracy. Determine if certain skin tones are associated with higher or lower accuracy rates. || Impact of Skin Thickness and Blood Volume on Pulse Oximeter Readings | Analyze the influence of skin thickness and blood volume on pulse oximeter readings in diverse populations. Explore how these factors affect the transmission of light signals through the skin.
|| Development of Algorithm Adjustments for Different Skin Tones | Design algorithms tailored to specific skin tones to improve the accuracy of pulse oximeter readings. This includes developing algorithms that can account for variations in light absorption and scattering across different skin tones. || Validation in Diverse Healthcare Settings | Conduct validation studies in diverse healthcare settings (e.g., hospitals, clinics, emergency departments) to ensure that pulse oximeter accuracy is consistent across different clinical environments.
|| Standardized Training Protocols for Clinicians | Develop standardized training protocols for healthcare professionals on using pulse oximeters in diverse populations. These protocols should include specific guidance on interpreting readings from patients with different skin tones. |
Summary
In conclusion, ensuring equitable healthcare access and outcomes requires a comprehensive understanding of pulse oximeter accuracy for people of color. The FDA’s recommendations and technological advancements hold promise for improvement. However, ongoing research and standardized protocols are essential to address disparities. Further studies with diverse populations and rigorous methodologies are critical for developing reliable tools for all.
Ultimately, equitable access to accurate pulse oximetry readings is essential for timely and appropriate medical care.