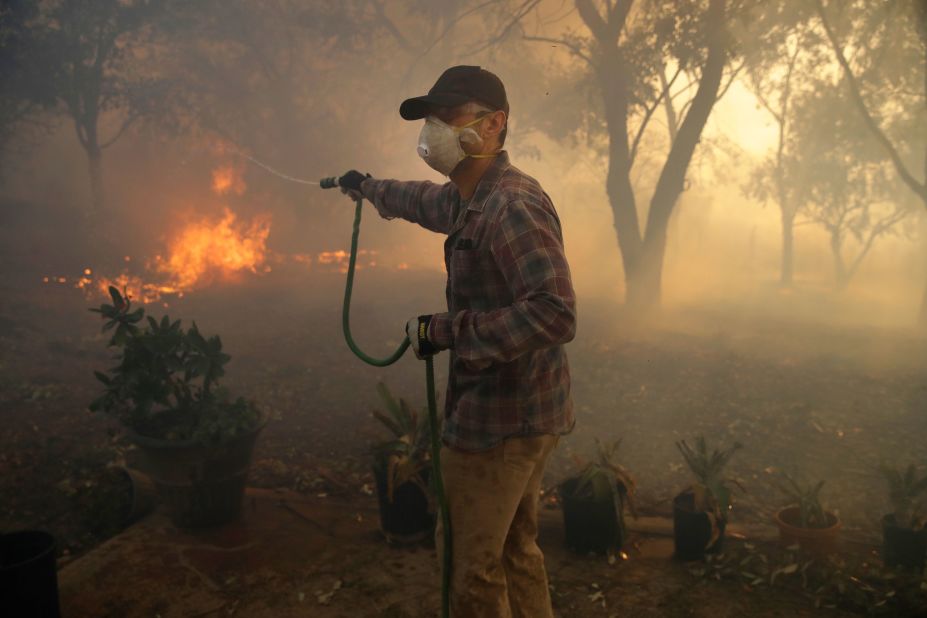
Misinformation about california fires is spreading like well wildfire – Misinformation about California fires is spreading like wildfire, creating a dangerous situation for everyone. This isn’t just about rumors; it’s about false information influencing public perception and potentially jeopardizing crucial emergency responses. From social media to news outlets, the channels for misinformation are many, and the potential impacts are significant.
This article explores the phenomenon of wildfire misinformation, examining its causes, impacts, and how to combat it. We’ll analyze how false narratives can influence emergency response, public behavior, and even emotional reactions. It’s crucial to understand how misinformation spreads and how we can effectively share accurate information during these critical times.
Understanding the Phenomenon
Misinformation surrounding California wildfires is a significant concern, often spreading faster than the flames themselves. This rapid dissemination of inaccurate or misleading information can impact public safety, hinder effective response efforts, and create confusion and distrust. Understanding the nature of this misinformation, the channels it travels through, and the motivations behind its spread is crucial to combating its harmful effects.The prevalence of misinformation in the context of natural disasters like wildfires is a complex issue.
Seriously, the misinformation about the California fires is spreading like wildfire. It’s getting so bad, it’s almost like people are trying to distract from the fact that John Mulaney just dunked on Meghan Markle and Prince Harry at a star-studded Netflix event ( here’s the scoop ). It’s all just adding fuel to the already crazy fire of fake news out there about the fires, though.
Yikes.
It’s not just about the spread of false information, but also about how quickly and easily it can be amplified and shared, often without proper verification or fact-checking. This poses a considerable challenge to the public and authorities in accurately assessing the situation and responding effectively.
The misinformation about California fires is spreading like wildfire, unfortunately. It’s easy to see how this happens, especially when so many other things are happening, like the ongoing debate about high living costs in California and their clash with progressive policies. For example, Walter’s California high living costs conflict progressive policies article explores this complex issue, which unfortunately fuels the fire of misinformation about the fires themselves.
It’s crucial to stay informed from reliable sources, not just social media buzz, to get a clear picture of what’s really going on.
Misinformation in the Context of Wildfires
Misinformation about California wildfires can take many forms. It can range from fabricated accounts of the fire’s origin and spread to false claims about preventative measures or the effectiveness of firefighting efforts. Sometimes, these claims are intentionally designed to sow discord or manipulate public opinion, while in other cases, they may be unintentional errors or misunderstandings. For example, a rumor that a particular area is safe from the fire, when in fact it is not, can lead to dangerous situations.
Likewise, false reports about evacuation routes or shelter locations can cause confusion and hinder effective response.
Common Misinformation Examples
Several types of misinformation are frequently encountered during California wildfires. These include:
- False claims about the cause of the fire, often attributing it to specific individuals or groups.
- Exaggerated reports about the intensity and extent of the fire, leading to panic and unnecessary evacuations.
- Misinformation about safety procedures and evacuation routes, causing confusion and potentially dangerous situations for those trying to leave the affected area.
- Fabricated accounts of heroism or victimization, designed to garner attention or manipulate public sentiment.
Dissemination Channels
Misinformation about California wildfires spreads through various channels, often overlapping and amplifying each other. These include:
- Social Media Platforms: Social media, with its speed and reach, is a primary vector for the rapid dissemination of wildfire misinformation. Fake news, manipulated images, and fabricated stories can spread quickly through social media networks, often reaching a wide audience before being debunked.
- News Outlets: While reputable news outlets play a vital role in reporting on wildfires, less reliable or biased news sources can spread misinformation through inaccurate or misleading reports.
- Unverified Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities can be breeding grounds for wildfire misinformation. Users may share unverified information, rumors, and speculation without proper fact-checking.
- Word of Mouth: Even in the digital age, word-of-mouth communication remains a significant factor in spreading wildfire misinformation. Unverified information can be easily shared through personal networks and social gatherings.
Impacts on Public Perception and Behavior
The spread of wildfire misinformation can significantly impact public perception and behavior. This misinformation can:
- Create Panic and Fear: Exaggerated reports and rumors can lead to widespread panic and fear, potentially hindering effective response efforts.
- Disrupt Evacuation Procedures: False information about evacuation routes or shelter locations can cause confusion and potentially endanger people trying to leave the affected area.
- Undermine Trust in Authorities: The prevalence of misinformation can erode public trust in official sources of information and response agencies.
- Distort Public Understanding: Misinformation can lead to a distorted understanding of the situation, hindering efforts to take appropriate actions.
Characteristics of Wildfire Misinformation
Wildfire misinformation often exhibits specific characteristics, which can help identify it. These include:
- Lack of Credibility: Misinformation often lacks verifiable sources and supporting evidence.
- Emotional Appeals: Misinformation may employ emotional appeals, such as fear or anger, to manipulate public sentiment.
- Unverified Claims: Unverified or unsubstantiated claims are common in wildfire misinformation.
- Rapid Dissemination: Misinformation spreads quickly through various channels, often before it can be verified or debunked.
Motivations Behind the Spread
Various motivations can drive the spread of wildfire misinformation. These include:
- Intentional Deception: Misinformation can be intentionally created and spread to manipulate public opinion or cause harm.
- Unintentional Errors: Inaccurate or misleading information may sometimes be shared unintentionally, due to misunderstanding or misinterpretation.
- Malicious Intent: Misinformation can be spread with malicious intent, such as disrupting emergency response efforts or creating chaos.
- Seeking Attention: Some individuals or groups may share misinformation to gain attention or promote a specific agenda.
Impact Assessment: Misinformation About California Fires Is Spreading Like Well Wildfire
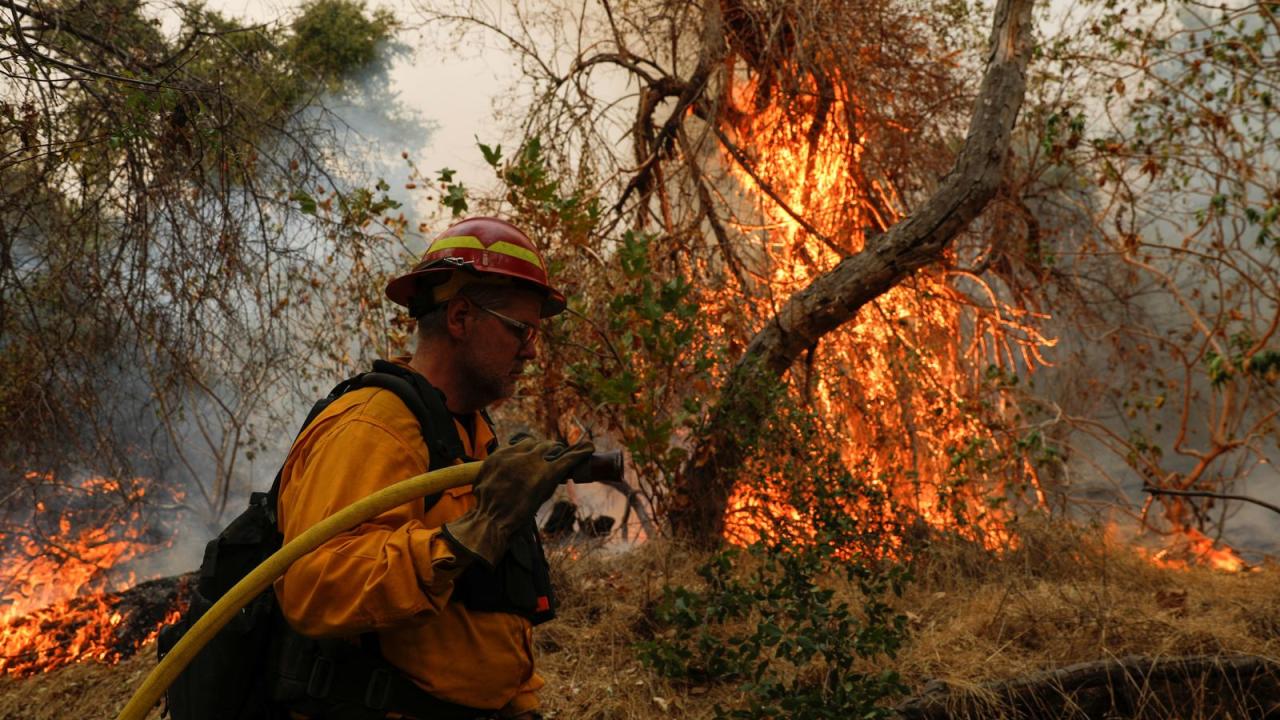

Misinformation surrounding California wildfires poses a significant threat, jeopardizing emergency response efforts and potentially endangering lives. The rapid spread of false narratives can overwhelm communication channels, confuse evacuees, and hinder crucial decision-making processes. Understanding the potential consequences is paramount to developing effective strategies for combating this dangerous trend.Misinformation about wildfire events can severely impact emergency response efforts. For instance, false claims about the extent of a fire or the location of evacuation zones can lead to confusion and delays in evacuations.
This can result in increased risks for those remaining in affected areas and hamper the efficiency of rescue teams and resources. The confusion and stress induced by misinformation can also lead to hesitation in seeking aid, potentially increasing the number of casualties.
Potential Consequences on Emergency Response
False information about fire causes, severity, or evacuation routes can severely hamper emergency response efforts. Disinformation regarding the nature of the fires, such as claiming they are intentionally set or caused by unusual phenomena, can divert resources and personnel from crucial tasks. If the public is misled about the true danger, they may be less inclined to heed evacuation warnings, resulting in delayed or incomplete evacuations.
This could lead to a surge in the number of individuals stranded in hazardous areas.
Effectiveness of Misinformation Countermeasures
Various approaches to combatting wildfire misinformation exist. Fact-checking initiatives, social media campaigns, and partnerships with credible news sources are all valuable strategies. Fact-checking websites and social media accounts dedicated to wildfire updates can help debunk false narratives quickly and effectively. Furthermore, collaborations between local news organizations and trusted community leaders can play a crucial role in spreading accurate information.
However, the effectiveness of these measures depends on their accessibility, reach, and perceived credibility within the affected communities.
Comparison of Factual and False Information
| Category | Factual Information | Misinformation |
|---|---|---|
| Cause of Fire | Human error, lightning strikes, climate change | Aliens, government conspiracies |
| Severity of Impact | Specific details of affected areas, evacuations | Exaggerated claims, fabricated narratives |
| Evacuation Procedures | Clear instructions on evacuation routes and shelters | Conflicting or misleading instructions, rumors of nonexistent shelters |
Emotional Responses and Behaviors
Exposure to misinformation can evoke a range of emotional responses. Fear, anxiety, and distrust are common reactions. This can lead to irrational behaviors, such as panic, hoarding, or reluctance to follow official instructions. People may become less likely to trust established authorities, which can undermine crucial emergency response strategies.
Consequences of Acting on Misinformation
Acting on misinformation related to wildfires can have serious consequences. Individuals may make poor decisions based on inaccurate information, increasing their risk of harm. Misinformation about evacuation routes can lead to individuals taking unsafe paths, exposing themselves to dangers, or failing to reach safety. False information about the severity of the fire could lead to inadequate preparations or a delay in seeking help, increasing the risk of injuries or fatalities.
Dissemination Strategies
Misinformation about California wildfires spreads rapidly, often amplifying anxieties and hindering effective responses. Accurate information sharing is crucial to combatting this, enabling informed decision-making and promoting public safety. This section Artikels strategies to identify and counter misinformation, offering resources and tools for verification, and highlighting the importance of critical thinking in evaluating wildfire-related information.Addressing the wildfire crisis requires a multifaceted approach.
Simply reacting to misinformation isn’t enough; a proactive strategy, focusing on proactive dissemination of verified information, is vital. This involves understanding the dynamics of misinformation, and designing robust methods to counter it.
Identifying and Countering Misinformation
To effectively counter wildfire misinformation, a framework for identification is necessary. This involves recognizing patterns in false or misleading narratives, often relying on emotional appeals, sensationalized language, and unsubstantiated claims. Identifying the sources of misinformation, whether individuals or groups, is also crucial to understanding their motivations and tailoring responses. Understanding the target audience and the specific misinformation they’re encountering is vital for effective countermeasures.
The misinformation surrounding California wildfires is spreading faster than a brushfire. It’s crucial to be cautious about the sources of information, especially online. Thankfully, robust local initiatives like the Oakland property build office real estate develop economy in the East Bay job market here are providing valuable resources for rebuilding and recovery. Unfortunately, this doesn’t stop the wildfire of false information from spreading, and we all need to be more vigilant in fact-checking what we see and hear.
Resources and Tools for Verification
Reliable sources and tools are essential for verifying wildfire information. These include government agencies, reputable news organizations, and scientific institutions. Access to real-time data on fire behavior, weather conditions, and evacuation orders is also important. This allows for the creation of factual, up-to-date narratives to counteract misinformation.
Credible Sources for California Wildfire Information
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
| Government Agencies | Cal Fire, California Governor’s Office, National Weather Service |
| News Organizations | Associated Press, Reuters, The New York Times |
| Scientific Institutions | Scripps Institution of Oceanography, National Interagency Fire Center |
| Fire Agencies | Local fire departments |
Strategies for Sharing Accurate Information, Misinformation about california fires is spreading like well wildfire
Sharing accurate information requires a proactive approach, focusing on clear, concise communication that avoids sensationalism. Leveraging social media platforms strategically, while ensuring that posts are well-sourced, can help reach a wider audience. Using visuals, like maps and graphics, can improve understanding and engagement. Collaborating with influencers and community leaders who have credibility and trust can significantly enhance the reach of accurate information.
Importance of Critical Thinking Skills
Evaluating wildfire-related information critically is essential. Developing critical thinking skills involves questioning the source of the information, looking for evidence, and considering alternative explanations. This includes recognizing biases, and understanding that not all information shared online is factual. Furthermore, comparing information across multiple credible sources helps to identify inconsistencies or inaccuracies, a crucial aspect of verifying the information’s validity.
Visual Representation
Misinformation about California wildfires spreads rapidly, often amplified by social media. Visual representations can effectively track this spread and its impact, helping to combat the false narratives and promote accurate information. Understanding the visual landscape of misinformation is crucial to developing effective countermeasures.
Infographic Design for Misinformation Spread
This infographic will present a timeline of misinformation surrounding California wildfires. The timeline will visually depict the rise and fall of specific false narratives. A key element is illustrating the relationship between the spread of misinformation and the corresponding impact on public perception.
- Timeline Structure: The infographic will utilize a horizontal timeline, with key dates and events marked along it. The timeline will span a period of several years, highlighting the most impactful wildfire events. For example, the timeline could showcase the spread of misinformation related to the 2020 and 2023 wildfire seasons.
- Color Palette: A clear color coding system will distinguish different types of misinformation. Green could represent accurate information, while shades of red or orange would indicate varying degrees of misinformation. This color coding will make it easy to visually identify the different types of claims.
- Icons: Icons representing social media platforms (e.g., a Facebook logo, a Twitter bird, a YouTube icon) will visually represent the channels through which misinformation is spreading. Icons like a flame or a wildfire image will represent the wildfire events themselves.
- Data Points: Data points, such as the number of shares, retweets, or comments associated with specific pieces of misinformation, will be incorporated. These data points will illustrate the scale of the spread.
Impact of Misinformation on Public Opinion
The infographic will also show the impact of misinformation on public opinion regarding wildfires. This will be demonstrated through a timeline that highlights the correlation between misinformation campaigns and shifts in public perception. For example, a surge in misinformation about the cause of a wildfire might coincide with a drop in public trust in official sources.
Elements of a Compelling Visual Representation for Accurate Wildfire Information
Accurate wildfire information needs a clear and concise visual representation. Key elements include:
- Visual Hierarchy: The design should prioritize accurate information, making it easily distinguishable from misinformation. A clear visual hierarchy will help guide the viewer’s eye to the critical details.
- Clarity and Simplicity: Complex information should be presented in a simple and accessible format. Avoid jargon and technical terms. Visuals should be clear and unambiguous.
- Credibility and Trustworthiness: The infographic should clearly source information from credible organizations (e.g., National Park Service, California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection). This element will help build trust and acceptance of the information.
- Accessibility: The infographic should be accessible to a wide audience, using clear language and avoiding overly technical terminology.
Flowchart for Verifying Wildfire Information
A flowchart will demonstrate the steps for verifying wildfire information.
- Identify the Source: Determine the origin of the information. Is it a trusted news organization, a social media post, or an unknown source?
- Check Multiple Sources: Consult multiple credible sources, such as official wildfire agencies or reputable news outlets. Comparing information from various sources helps determine if the claim is consistent and accurate.
- Look for Evidence: Verify the information by checking if there’s supporting evidence (e.g., photos, videos, official statements). Does the information align with established facts and scientific knowledge?
- Assess the Context: Understand the context surrounding the claim. Are there any underlying motives or agendas behind the information? For instance, consider whether the source is trying to manipulate public opinion or create fear.
- Consider the Timeline: Evaluate the timing of the information. Is the claim timely or part of a deliberate misinformation campaign?
Case Studies
Misinformation about California wildfires, often amplified by social media, can significantly impact public safety and preparedness. Understanding real-world examples, identifying patterns, and analyzing the effectiveness of fact-checking initiatives are crucial for developing strategies to mitigate future harm. These case studies highlight the evolving nature of wildfire misinformation and the challenges in countering it.Analyzing past wildfire seasons reveals how misinformation tactics have adapted and intensified, posing a complex challenge for authorities and community members alike.
Examining the impact of these tactics on public response is critical for understanding the evolving nature of the threat.
Real-World Examples of Misinformation Impact
California wildfires have seen numerous instances where misinformation has distorted public understanding and response. One example involves the spread of false narratives about evacuation orders, leading to confusion and delays in crucial response times. Another common theme involves the exaggeration of the extent of damage or the spread of the fire. These instances demonstrate the real-world consequences of unchecked misinformation, highlighting the urgent need for proactive mitigation strategies.
Common Patterns in Misinformation
Misinformation surrounding California wildfires often exhibits several recurring patterns. A prevalent pattern involves the use of emotionally charged language and sensationalized imagery to create a sense of urgency or fear. Another common characteristic is the propagation of false claims through social media platforms, where misinformation can spread rapidly. These patterns underscore the need for critical media literacy and fact-checking skills.
Comparison of Misinformation Spread Across Fire Seasons
The spread of misinformation varies across different wildfire seasons. In some seasons, misinformation may center on the cause of the fires, while in others, it might focus on the severity of the damage or the efficacy of response efforts. For example, in a season with particularly intense media coverage, misinformation may spread more rapidly due to the increased public attention and heightened emotional response.
Effectiveness of Fact-Checking Initiatives
Fact-checking initiatives play a vital role in countering wildfire misinformation. These initiatives aim to identify and debunk false claims, providing accurate information to the public. However, the effectiveness of these initiatives can vary depending on the platform and the nature of the misinformation. For example, some fact-checking efforts may prove more effective on social media platforms than on other outlets.
Evolution of Misinformation Tactics
Misinformation tactics related to California wildfires have evolved significantly over time. Early tactics often focused on simple fabrications, while modern tactics involve more sophisticated strategies, including the use of deepfakes and manipulated images to create a sense of credibility. The sophistication of these techniques highlights the need for evolving fact-checking methods.
Summary

In conclusion, the rapid spread of misinformation about California wildfires is a serious concern. It highlights the need for critical thinking, accurate verification, and a coordinated effort to combat false information. By understanding the channels, motivations, and impacts of this misinformation, we can better prepare for future wildfire seasons and safeguard public safety. Let’s work together to ensure accurate information prevails during these critical moments.