Home battery backup solutions are becoming increasingly important in today’s world. With power outages becoming more frequent and unpredictable, having a reliable backup system can provide peace of mind and protect your home and belongings. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of home battery backup solutions, their benefits, installation, costs, and future trends. We’ll explore everything from lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries to UPS systems and solar-powered storage, helping you make informed decisions about safeguarding your home.
From the initial introduction to the different types of battery systems, to the crucial factors influencing your selection, this guide offers a complete overview. We’ll delve into the advantages of having a backup system, including enhanced safety, security, and cost savings. We’ll also explore the complexities of installation and maintenance, ensuring you understand the process and necessary steps for long-term reliability.
Introduction to Home Battery Backup Solutions
Home battery backup solutions are becoming increasingly popular as a way to ensure uninterrupted power supply during outages. These systems provide a crucial safeguard against power disruptions, protecting valuable appliances and sensitive electronic devices. They are a reliable and practical solution for homeowners seeking to mitigate the inconvenience and potential damage caused by power failures.These systems store electricity and release it when needed, enabling essential devices to operate during a power outage.
This crucial function ranges from powering critical medical equipment to running essential home appliances like refrigerators and freezers. Understanding the various types of battery backup systems and the factors influencing their selection is key to choosing the right solution for your specific needs.
Types of Home Battery Backup Systems
Home battery backup systems come in various types, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The primary distinction lies in the type of battery technology used.
- Lithium-ion batteries are gaining popularity due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and relatively low maintenance requirements. These batteries offer a higher power output compared to other options, making them ideal for running numerous devices simultaneously during an outage.
- Lead-acid batteries, a more established technology, are still a viable option due to their affordability and readily available maintenance. While their energy density is lower than lithium-ion, they provide a suitable backup for basic home appliances.
Factors Influencing System Selection
Several factors influence the choice of a home battery backup system. The capacity of the battery, the type of power supply required, and the cost are all crucial considerations.
- Power Requirements: The total wattage required to run essential appliances and devices during a power outage directly affects the size and capacity of the battery backup system. Homeowners should meticulously calculate the combined wattage of all the devices needing power during an outage. For example, a household with a refrigerator, freezer, and a few lights will have different power requirements compared to a household with a home office computer, medical equipment, and other electronic devices.
- Battery Capacity: The battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines how long the system can power the connected devices. A larger capacity will provide more runtime during an outage, but also increases the cost. For instance, a system with a 10 kWh battery might run essential appliances for several hours, while a system with 5 kWh might only provide backup for a few hours.
- Budget: The cost of the system is a significant factor. Lithium-ion systems generally have a higher upfront cost compared to lead-acid systems, but their longer lifespan and reduced maintenance can lead to lower overall costs over time. Homeowners should carefully consider the initial investment and long-term maintenance costs when making their decision.
Comparison of Battery Types
The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of different battery types for home backup solutions.
| Battery Type | Pros | Cons | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | High energy density, long lifespan, relatively low maintenance, high power output, suitable for running numerous devices simultaneously. | Higher upfront cost, potential for thermal runaway if not properly managed. | Homes with significant power needs, such as those with multiple electronic devices or sensitive equipment needing continuous power. |
| Lead-acid | Lower upfront cost, readily available maintenance, suitable for simpler applications. | Lower energy density, shorter lifespan, higher maintenance compared to lithium-ion, less efficient for higher power demands. | Homes with basic power needs, such as powering a few essential appliances during short outages. |
Benefits of Using Home Battery Backup Solutions
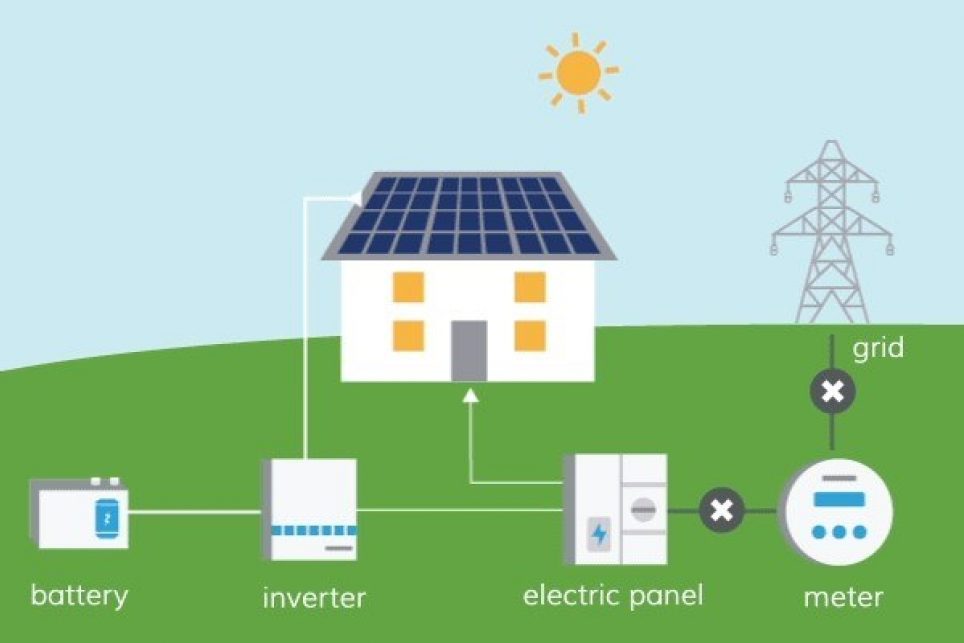
Home battery backup systems are becoming increasingly popular as a way to mitigate the disruption and potential hazards of power outages. These systems offer a range of advantages, from enhancing safety and security to reducing reliance on the grid and potentially saving money. Understanding these benefits can help homeowners make informed decisions about investing in these crucial technologies.Power outages can be inconvenient and even dangerous.
A reliable home battery backup system provides a crucial safeguard against these disruptions. They offer a stable power source during outages, enabling essential appliances and electronics to function, and preventing potential damage or safety hazards.
Enhanced Safety and Security
Power outages can lead to a variety of safety and security concerns, including the loss of essential medical equipment, malfunctioning security systems, and the potential for property damage from frozen pipes or spoiled food. Home battery backup systems offer a significant safeguard against these issues by providing a continuous power supply. This continuity ensures the operation of essential appliances, such as refrigerators and medical devices, maintaining safety and preserving valuable goods during outages.
Furthermore, backup power can keep security systems active, deterring intruders and maintaining a secure environment.
Reduced Reliance on Grid Power
Home battery backup systems reduce dependence on the electrical grid, offering greater resilience to power fluctuations and outages. With a backup system, homes are less susceptible to the disruptions and potential dangers that come with grid instability. This independence allows for greater peace of mind, particularly in regions with a history of frequent or prolonged power outages. The reduced reliance on grid power also contributes to a more sustainable approach to energy management.
Potential Cost Savings
Implementing a home battery backup system can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. Reduced reliance on the grid can lead to lower electricity bills, particularly in areas with high energy costs. Beyond financial savings, these systems offer a return on investment by minimizing potential damages to equipment and sensitive appliances during power failures. Furthermore, the peace of mind and safety afforded by a reliable backup system can be considered a valuable asset.
Specific Benefits of Home Battery Backup Solutions
- Increased Safety and Security: A consistent power supply during outages ensures the operation of essential medical equipment and security systems, reducing risks and maintaining safety during power disruptions.
- Reduced Grid Reliance: Home battery backup systems provide an independent power source, diminishing reliance on the unpredictable electrical grid and enhancing resilience to outages.
- Lower Electricity Bills: By reducing reliance on the grid, especially in regions with high energy costs, home battery backup systems can lead to significant long-term savings on electricity bills.
- Preservation of Perishable Goods: Maintaining power to refrigerators and freezers prevents spoilage of perishable foods during outages, minimizing waste and saving money.
- Protection of Sensitive Electronics: Power outages can cause damage to sensitive electronic devices. Backup systems mitigate this risk by providing a stable power source during grid instability.
- Enhanced Peace of Mind: Knowing essential appliances and systems will function during a power outage provides significant peace of mind and reduces stress associated with grid instability.
Installation and Maintenance of Home Battery Backup Solutions
Installing and maintaining a home battery backup system is crucial for its optimal performance and longevity. Proper installation ensures the system integrates seamlessly with your home’s electrical infrastructure and safety standards. Regular maintenance helps prevent potential issues and extends the lifespan of the batteries and associated components. This section provides detailed guidance on these critical aspects.Implementing a home battery backup system requires careful planning and execution.
This includes selecting the right system, considering electrical load demands, and adhering to local building codes. The steps involved in installation are detailed below, emphasizing safety precautions throughout the process.
Installation Steps
Careful planning is essential for a successful installation. Ensure you have the necessary tools, understand the electrical wiring in your home, and adhere to safety regulations. This includes consulting local electrical codes and seeking professional help if needed. Hiring a qualified electrician is recommended to ensure proper installation and adherence to safety standards.
- System Selection and Assessment: Carefully evaluate your home’s energy consumption patterns and identify your backup power needs. Choose a system that matches your requirements, considering factors like battery capacity, charging rate, and output power.
- Electrical System Assessment: Determine the appropriate location for the battery system, considering access for maintenance and potential safety hazards. Assess the existing electrical panel and wiring to ensure compatibility with the chosen system.
- Wiring and Connection: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions meticulously for wiring and connecting the battery system to your home’s electrical panel. This step requires specific expertise and should be performed by a qualified electrician.
- System Testing and Commissioning: After all connections are made, rigorously test the system’s functionality. Verify that the backup system engages correctly during power outages and that the output voltage and amperage are within the acceptable range.
- Safety Checks: Ensure proper grounding, circuit breakers, and disconnects are in place and functional. Conduct a thorough inspection to confirm the system meets safety standards.
Maintenance Procedures
Consistent maintenance is critical to preserving the battery’s performance and extending its lifespan. A well-maintained system minimizes the risk of premature failure and ensures reliable backup power during outages.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor the battery’s charge level and system performance using the provided monitoring tools. Observe the voltage and temperature readings for potential anomalies.
- Battery Charging and Discharging: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal charging and discharging cycles to maintain the battery’s health and prevent premature degradation. Avoid deep discharging if possible.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Regularly inspect the system for any signs of damage or wear and tear. Clean the battery terminals and other exposed components to prevent corrosion. Ensure all ventilation components are clear of debris.
- Environmental Considerations: Maintain the battery system in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating. Ensure proper temperature control, avoiding extreme heat or cold conditions.
- System Updates: Regularly check for firmware updates or software upgrades for the backup system. These updates often enhance performance and address potential issues.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and addressing issues promptly is essential to minimize downtime and maintain system reliability.
- Low Battery Charge: Verify that the charging system is functioning correctly. Check for any loose connections or obstructions that might be hindering the charging process.
- System Malfunction: Consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide to identify the cause of the issue. Check for any error codes or alarms that might indicate a problem.
- Electrical Issues: Ensure that the electrical connections are secure and correctly routed. Seek professional help if you are unsure about the electrical work.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide
- Initial Assessment: Inspect the system for any visible damage or signs of wear.
- Battery Monitoring: Check the battery charge level and temperature.
- Cleaning: Clean the battery terminals and other exposed components.
- Safety Checks: Verify all connections and ensure proper grounding.
- System Testing: Conduct a complete system test to ensure proper operation.
Types of Home Battery Backup Systems

Home battery backup systems offer a range of solutions for maintaining power during outages. Understanding the various types available is crucial for making an informed decision. Each system type has its own strengths and weaknesses, impacting cost, performance, and long-term viability.Different technologies underpin these systems, leading to varying levels of efficiency and environmental impact. This section delves into the different types, highlighting their characteristics and potential applications.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
UPS systems are designed to provide a seamless transition between the primary power source and the backup battery during outages. They are commonly used for protecting sensitive electronics like computers and servers, where brief power interruptions can lead to data loss.UPS systems typically use lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries. They offer fast response times, minimizing the disruption to connected devices.
A key feature is their ability to provide immediate backup power.Examples include APC Smart-UPS and Eaton Powerware. These systems often come with different power ratings (e.g., 500VA, 1000VA) and features like surge protection and automatic switching.
Solar-Powered Battery Storage Systems
Solar-powered battery storage systems combine solar panels with battery banks to store energy generated by the sun. These systems are becoming increasingly popular for homeowners seeking to reduce their reliance on the grid and lower their energy bills.The key benefit is the ability to utilize renewable energy sources. Solar panels generate electricity during daylight hours, charging the batteries.
This stored energy powers household appliances during power outages.Systems from companies like Tesla Powerwall and Enphase Energy offer various configurations, ranging from small residential setups to larger systems for commercial applications. They typically incorporate features like advanced battery management systems for optimized performance and longevity.
Home battery backup solutions are crucial for peace of mind, especially during power outages. Thinking about the various options, you might also need to access your Wi-Fi password to configure certain devices. Fortunately, you can easily find your Windows Wi-Fi password using a quick online guide like find windows wifi password. Once you’ve got that sorted, you can get back to ensuring your home has reliable power, no matter what.
Stand-alone Generator-Based Systems
Stand-alone generator-based systems use a generator to power a house during a power outage. These systems are often more robust than UPS systems and provide backup power to the entire home, including appliances and lighting.They offer continuous power backup, but they are generally more expensive than UPS systems. Generators can be fueled by gasoline, propane, or natural gas.
They provide complete power to the house, but they can be noisy and require regular maintenance.Models vary greatly in size, power output, and fuel type. Examples include Generac and Honda generators, with different wattage ratings and features like automatic start-up capabilities.
Comparison Table of Home Battery Backup Systems
| System Type | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| UPS | Fast response time, protects sensitive electronics, typically smaller size | Minimizes disruption, relatively low cost for some systems, immediate backup | Limited backup time, may not power entire house, often less reliable for extended outages |
| Solar-powered battery storage | Renewable energy source, long-term cost savings, quieter operation | Reduced reliance on grid, potential for energy independence, environmental benefits | Higher upfront cost, limited power output, dependent on sunlight |
| Stand-alone Generator-Based Systems | Complete power backup for the entire house, typically reliable for extended outages | Continuous power supply, suitable for critical loads | Higher upfront cost, potential noise pollution, fuel costs and maintenance required |
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Home battery backup systems offer significant benefits, but understanding the associated costs and potential return on investment (ROI) is crucial for making an informed decision. Evaluating the upfront expenses, ongoing maintenance, and potential savings is essential to assess the long-term financial viability of such a system. This analysis considers various factors and provides a framework for calculating ROI based on potential savings.The cost of a home battery backup system isn’t a fixed number; it’s influenced by several key elements.
Factors such as the size of the system, the technology used, the required capacity, and the installation complexity directly impact the overall price tag. Furthermore, ongoing maintenance costs, while generally low, are also a component of the total investment.
Typical Costs
Understanding the typical costs involved in installing and maintaining a home battery backup system is essential for a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis. Initial costs include the purchase price of the battery system, installation labor, and any necessary permits or inspections. These costs vary considerably based on the selected system type and local regulations.
- Purchase Price: This includes the cost of the battery system itself, inverters, and any associated electronics. Prices for lithium-ion batteries, a common choice, range widely depending on the manufacturer, capacity, and features.
- Installation Costs: Labor costs for installation can be significant, especially for complex systems. Electricians or specialized installers will charge for their services. These costs vary based on the complexity of the installation, the location of the home, and the installer’s expertise.
- Permitting and Inspection Costs: Local building codes and regulations may require permits and inspections for the installation of any home improvement, including battery backup systems. The associated fees will vary depending on the location and the complexity of the project.
Factors Influencing Cost
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of a home battery backup system. The specific technology used, the system’s capacity, and the complexity of installation all play a role in determining the final price tag.
- Battery Technology: Lithium-ion batteries are generally more expensive upfront than lead-acid batteries, but they often offer longer lifespans and higher energy storage capacity. The choice of battery technology directly influences the initial cost.
- System Capacity: Larger systems with higher energy storage capacity will naturally cost more than smaller ones. The capacity chosen needs to match the home’s energy consumption and the expected duration of power outages.
- Installation Complexity: The complexity of the electrical work and the specific requirements of the home can significantly affect installation costs. Homes with existing complex electrical systems may require more specialized labor.
Calculating ROI
Calculating the ROI involves comparing the potential savings from the system against its total cost. A crucial element is estimating the frequency and duration of power outages in the region.
Calculating ROI: (Total Savings – Total Costs) / Total Costs
This formula provides a straightforward way to calculate the return on investment. Savings can be calculated based on the cost of electricity during outages, potential appliance damage, and lost productivity. The more frequent and prolonged outages, the more significant the potential savings and ROI.
Comparing System Types
Different battery backup systems have varying costs associated with them. Lead-acid systems are generally less expensive upfront, but they have shorter lifespans and lower energy storage compared to lithium-ion systems.
| System Type | Typical Cost | Lifespan | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-acid | Lower | Shorter | Lower |
| Lithium-ion | Higher | Longer | Higher |
Example Cost-Benefit Analysis
A homeowner in an area experiencing frequent power outages considers installing a 10kWh lithium-ion battery backup system. The system costs $10,000, installation costs $2,000, and permitting costs are $500. Annual electricity costs during outages are estimated at $500. The system is expected to last 10 years. The total initial cost is $12,500.
Home battery backup solutions are crucial for ensuring uninterrupted power, especially during outages. Just like backing up your important files on your computer, you need to consider the importance of robust data protection. This is mirrored in the need for reliable server database backup tools, ensuring business continuity. Fortunately, comprehensive home battery backup solutions provide a similar peace of mind, safeguarding your appliances and sensitive data.
Server database backup tools are essential for preventing data loss on servers, and these concepts apply directly to ensuring your home systems stay powered and protected.
The total savings over 10 years are $5,000. Applying the ROI formula, the ROI is (5,000 – 12,500) / 12,500 = -0.6. In this case, the system doesn’t provide a positive return on investment. The example highlights the importance of accurate cost estimations and the need to assess the frequency of outages.
Future Trends in Home Battery Backup Solutions
The home battery backup market is poised for significant evolution, driven by increasing concerns about grid reliability and the desire for greater energy independence. Emerging technologies and smart features are transforming how homeowners manage their energy needs, promising a more efficient and sustainable future. This evolution is characterized by a shift from simple backup power to sophisticated energy management systems.The future of home energy solutions will increasingly incorporate intelligent systems that learn and adapt to individual household needs.
Home battery backup solutions are crucial, especially now that energy prices are fluctuating. With New York Governor Hochul’s recent announcement about potential refund checks for New Yorkers impacted by inflation, this initiative might just make these backup systems even more appealing. Thinking ahead about energy security, these systems can provide peace of mind during potential outages, and with rising energy costs, a home battery backup could be a worthwhile investment.
These systems will be more than just backup power; they will be integral components of a smart home ecosystem, optimizing energy consumption and reducing environmental impact. Key trends include advancements in battery technology, the integration of smart automation, and a growing emphasis on energy efficiency.
Advancements in Battery Technology
Battery technology is constantly evolving, leading to improvements in energy density, lifespan, and safety. Lithium-ion batteries, already prevalent in many applications, are expected to see further enhancements in their performance and cost-effectiveness. Solid-state batteries, with their potential for higher energy density and improved safety features, represent a promising frontier. Their adoption in home backup systems is likely to increase as their production costs decrease.
This evolution in battery technology is crucial for expanding the capacity and reliability of home backup systems.
Integration of Smart Automation
Smart technology is playing an increasingly important role in home battery backup systems. Homeowners can now monitor battery levels, control charging schedules, and integrate backup systems with smart home hubs and other appliances. This integration allows for optimized energy usage and enhances the system’s responsiveness to real-time grid conditions. For example, a smart home system could automatically switch to battery power when a power outage is detected, ensuring essential appliances remain operational.
Predicted Future Market Growth
The market for home battery backup solutions is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years. Factors such as rising electricity costs, growing concerns about grid reliability, and the increasing popularity of renewable energy sources are driving this expansion. The adoption of smart technologies and the continuing advancements in battery technology will likely accelerate this growth. For instance, the rising popularity of solar panel installations has significantly boosted the demand for home energy storage solutions, creating a virtuous cycle for the entire market.
Impact on Future Home Energy Solutions
The integration of home battery backup systems will significantly influence future home energy solutions. The ability to store and manage energy independently will empower homeowners to reduce reliance on the grid, potentially lowering energy bills and improving energy resilience. Further, the capacity to integrate renewable energy sources like solar panels with battery backup systems will create a more sustainable and environmentally conscious approach to home energy.
Role of Smart Technology and Automation in Home Battery Systems
Smart technology enables real-time monitoring and control of battery systems. Smart home hubs can communicate with backup systems, optimizing charging schedules and triggering automatic switching to backup power during outages. These systems can also learn homeowner energy patterns, enabling more efficient usage and extending battery lifespan. Advanced algorithms can predict potential outages and preemptively prepare the system, minimizing disruption.
This integration of smart technology allows for a more personalized and responsive approach to energy management.
Illustrative Examples of Home Battery Backup Systems
Home battery backup systems offer a crucial lifeline during power outages, safeguarding essential appliances and maintaining a comfortable living environment. Understanding the diverse options available allows homeowners to select the best fit for their specific needs and budget. Different technologies and features cater to varying demands, ensuring a reliable power source during critical moments.Various home battery backup systems cater to diverse needs and budgets.
Each system has unique characteristics impacting its functionality, installation, and cost-effectiveness. Choosing the right system requires considering factors like power requirements, space constraints, and desired level of protection.
Lithium-ion Battery Systems
Lithium-ion batteries are gaining popularity for their high energy density and long lifespan. They offer a significant advantage over traditional lead-acid batteries in terms of storage capacity and efficiency. These systems typically use inverters to convert the DC power from the battery to AC power for household appliances.
- Features: High energy density, long lifespan, and relatively quick charging times.
- Advantages: Superior performance compared to lead-acid batteries, allowing for running more devices during outages, and higher efficiency.
- Disadvantages: Higher initial cost compared to lead-acid systems, potential for higher maintenance costs over time due to more complex technology.
- Functionality: The system automatically switches to battery power when the grid fails, providing backup power for critical loads like lights, refrigerators, and medical equipment.
- Installation: Installation involves mounting the battery system, connecting it to the home’s electrical panel, and configuring the inverter. Professional installation is often recommended for safety and proper integration.
Lead-Acid Battery Systems
Lead-acid batteries are a more established technology, offering a balance between cost and performance. These systems are simpler in design and often more affordable than lithium-ion alternatives. They are suitable for homes with lower power demands.
- Features: Lower initial cost, simpler design, and readily available.
- Advantages: Cost-effective solution for basic backup needs, extensive availability of parts and expertise for maintenance.
- Disadvantages: Lower energy density compared to lithium-ion, shorter lifespan, and slower charging times.
- Functionality: Similar to lithium-ion systems, they switch to battery power during outages, powering essential appliances. The output power depends on the battery size and the capacity of the inverter.
- Installation: Installation is generally straightforward, involving connecting the battery bank to the home’s electrical panel and ensuring proper grounding. However, lead-acid batteries may require more space due to their physical size.
Hybrid Systems, Home battery backup solutions
Hybrid systems combine features of both lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, often incorporating solar panels to maximize energy independence. These systems are particularly useful for homes with high energy demands or those seeking to reduce their reliance on the grid.
- Features: Combining the strengths of lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, potentially integrating solar panels.
- Advantages: Can provide a significant amount of backup power, maximizing energy independence, particularly when combined with solar.
- Disadvantages: Generally more expensive than simpler systems, complexity of the installation process can increase maintenance costs.
- Functionality: The system prioritizes solar power, then lithium-ion, and finally lead-acid batteries to provide backup power during grid outages. The system can adjust power output depending on the availability of solar and grid power.
- Installation: The installation process involves connecting solar panels (if included), the battery system to the home’s electrical panel, and configuring the inverter. This usually necessitates professional installation due to the complex system integration.
Scenario: A Crucial Backup System
Imagine a remote cabin with limited access to electricity. A lithium-ion battery backup system is crucial to power essential medical equipment, lighting, and communication devices during prolonged power outages. This system ensures critical functions are maintained, preventing potential health risks and enabling essential communication.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, home battery backup solutions offer a crucial layer of protection against power outages. This guide has explored the diverse options available, highlighting the benefits, costs, and future trends. From understanding the different battery types to navigating the installation and maintenance process, we’ve aimed to equip you with the knowledge to make informed choices. Ultimately, the right solution depends on your specific needs and budget, but having a reliable backup system is an investment in peace of mind and safety.

